JPK Instruments NanoWizard
®
Handbook Version 2.2a
7
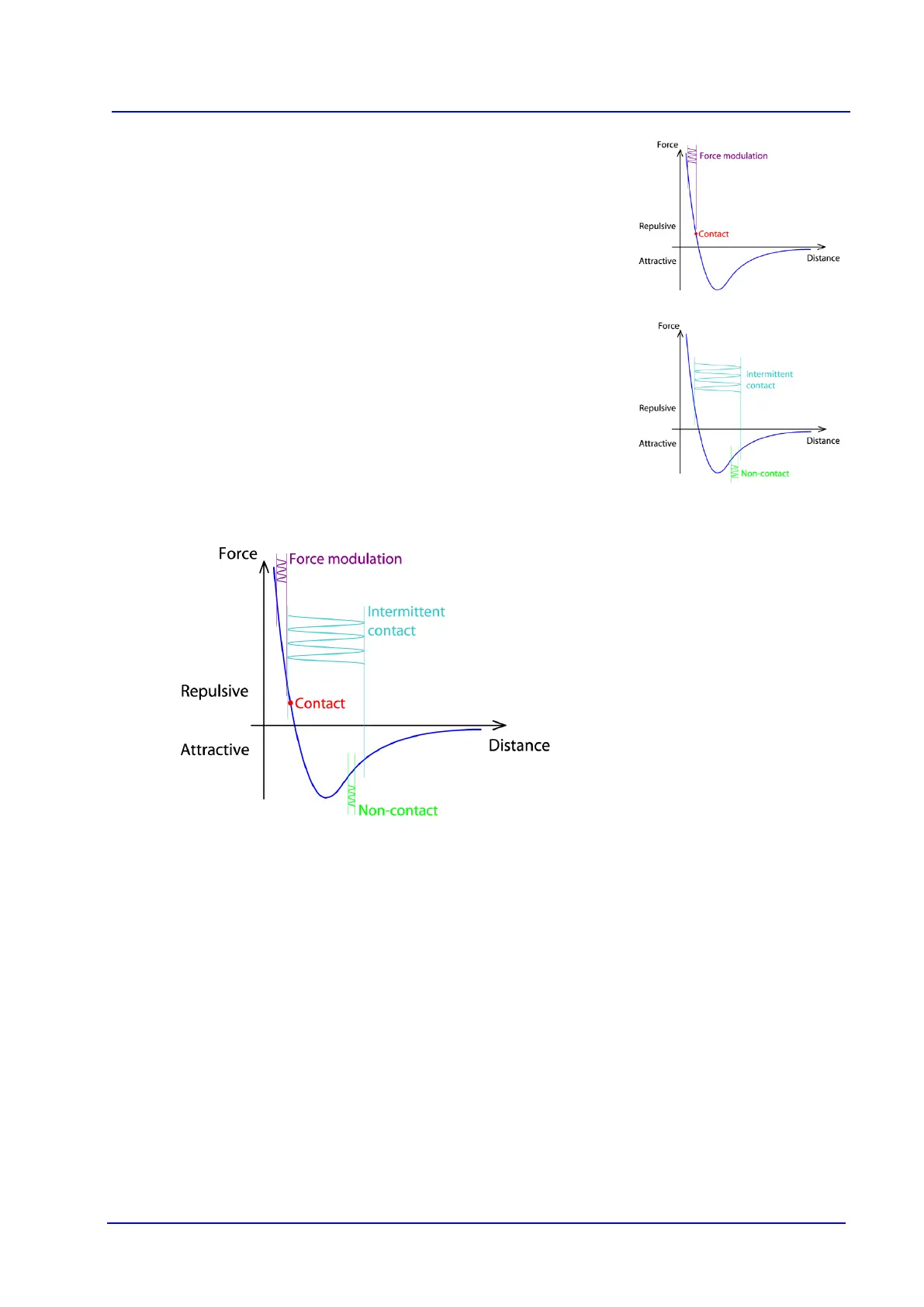
Contact and Force modulation modes both stay entirely in the repulsive part of the
curve. In this kind of model of two objects a
pproaching one another, there is no
one point where the objects go from being “not in contact” to being “in contact”,
since they interact in some way over the whole range of distances that separate
them. So “contact mode” is just a shorthand for choosing
a particular value of
repulsive force for the feedback to use to control the height. In contact mode a
single value of the force is chosen and in force modulation mode the force is
varied.
Intermittent contact mode moves between the attractive and repu
lsive parts of the
curve. The maximum force perpendicular to the sample may be higher or lower
than in contact mode, but this is only applied for a short part of the cantilever cycle.
Therefore the sample damage and lateral drag can both be reduced compar
contact mode for some samples.
Non-
contact mode is the only one that stays in the attractive part of the curve, but
this makes it difficult to control, so it is not often used. In liquid, the attractive part
of the curve may not be so obvious, an
d the oscillation is heavily damped, so it is
not usually possible to use it on biological samples in liquid.
The ranges for the operation of the different modes also vary a lot, so the force
values can overlap for different modes, but this overview
shows the general
operating regimes for the different imaging modes.
 Loading...
Loading...