22
JPK Instruments NanoWizard
®
Handbook Version 2.2
Calculation from cantilever geometry
Cantilevers purchased by manufacturers are generally delivered together with a
data sheet, which gives the cantilever specifications. Properties such as the spring
constant have generally been calculated from the cantilever
geometry, and have
not been experimentally measured.
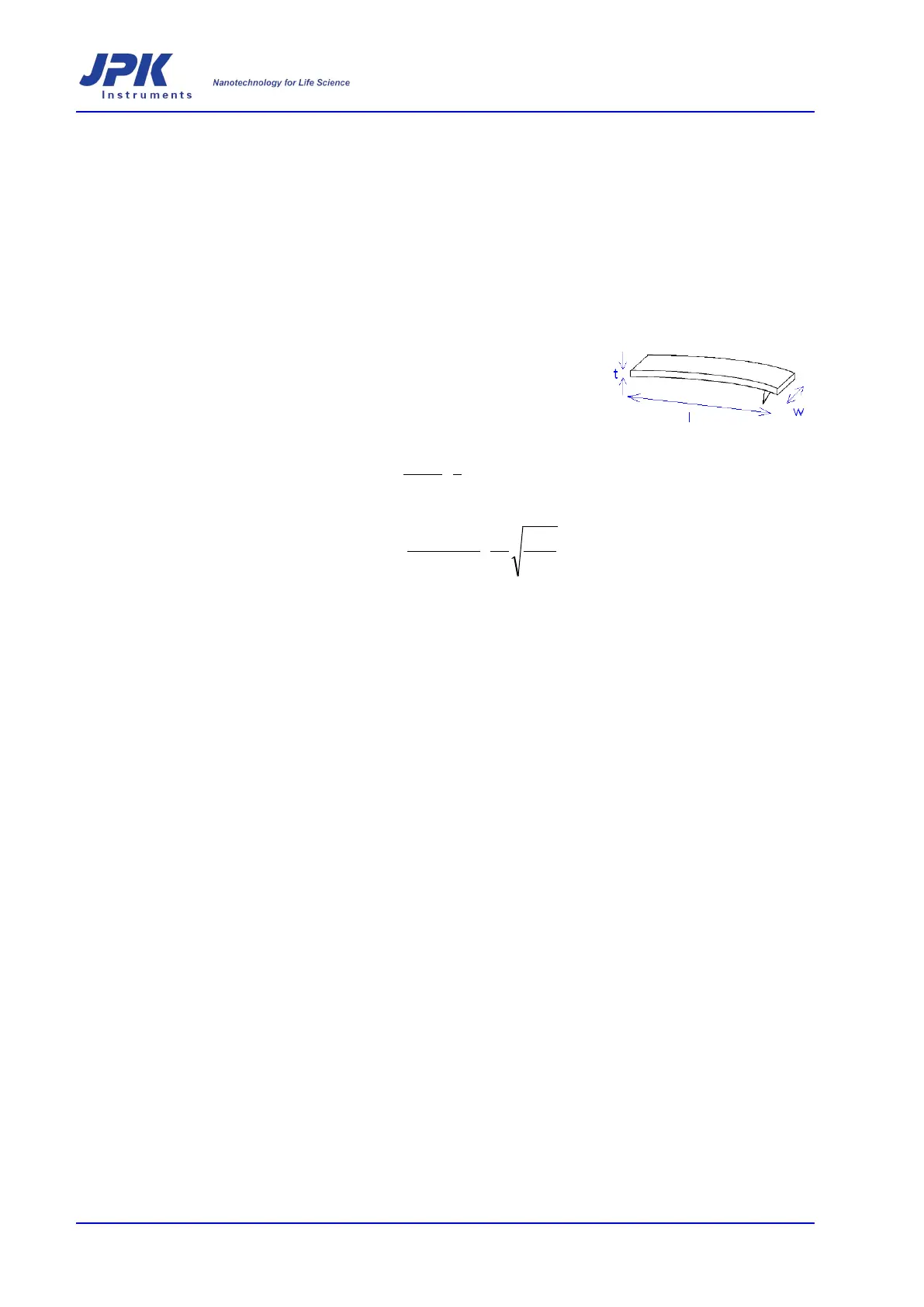
Calculation of spring constant
3
4
⋅
=
l
twE
k
Calculation of resonant frequency
Note that the force constant is independent of the mass of the cantilever, but the
resonance frequency is not. Typical values for silicon; E
<110>
= 168.1 GPa) and ρ
3
-3
E Young’s modulus
w width
t thickness
l length
ρ mass density
The thermal noise analysis is becoming the main standard for AFM experiments,
because it is available in liqu
id, online during the experiment, through a fast,
automated software analysis. There are some difficulties in the theoretical analysis
due to cantilever shape, liquid damping, etc., but the convenience and speed
means it is now very widely used.
 Loading...
Loading...