'XHWRRXUSROLF\RIFRQWLQXRXVSURGXFWLQQRYDWLRQVRPHVSHFL¿FDWLRQVPD\FKDQJHZLWKRXWQRWL¿FDWLRQ
©
/*(OHFWURQLFV86$,QF(QJOHZRRG&OLIIV1-$OOULJKWVUHVHUYHG³/*´LVDUHJLVWHUHGWUDGHPDUNRI/*&RUS
144 |5()5,*(5$17'(6,*1
MULTI V IV Outdoor Unit Engineering Manual
General Information / Guidelines
Figure 41: Examples of Inverted Traps.
LAYOUT BEST PRACTICES
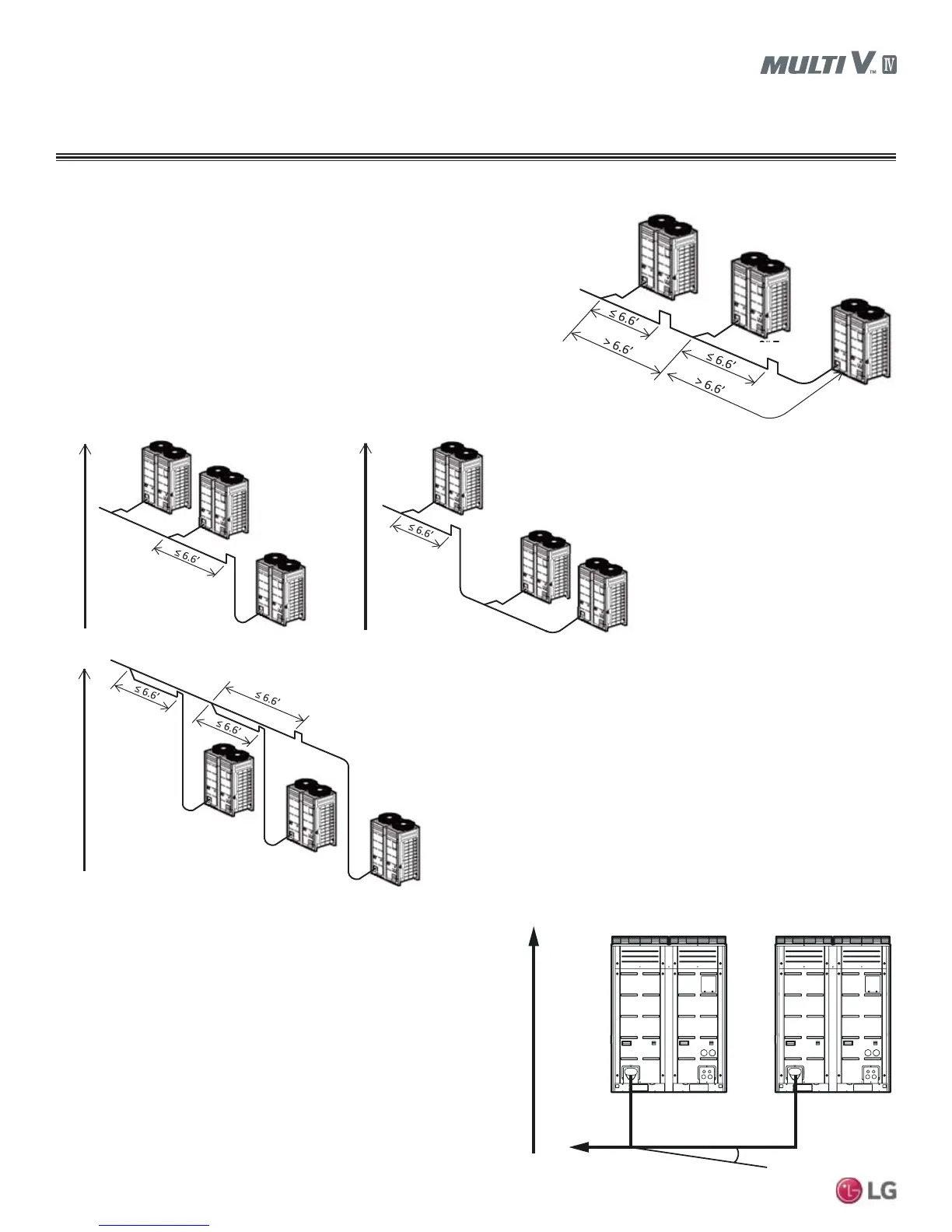
Pipe Slope
Horizontal pipe slope should be level or slightly away from the
outdoor units, otherwise refrigerant and oil will migrate toward the
outdoor units and accumulate in the pipe segment serving the frame
that is not running or at the lowest elevation. Piping should never
slope more than -10° (see figure) without installing an inverted trap
within 6.6' of the outdoor unit Y-branch and before the pipe slopes
downward toward the outdoor unit.
Toward indoor unit
Elevation
-10°
2. Inverted traps are required when:
a. Piping in a horizontal direction from the outdoor Y-branch towards an out-
door unit or another outdoor unit Y-branch is greater than 6.6'.
The inverted trap should be installed close to the outdoor unit Y-branch (no
more than 6.6' away).
Oil Trap
To IDUs / HRUs
Oil Trap
b. Anytime piping turns downward leaving an outdoor unit Y-branch toward an
outdoor unit or another outdoor unit Y-branch.
The inverted trap should be installed close to the outdoor unit Y-branch (no more
than 6.6' away), and before the pipe toward the outdoor unit turns downward.
Oil Trap
Elevation
Elevation
Elevation
Oil Trap
To IDUs /
HRUs
To IDUs / HRUs
Oil Trap
Oil Trap
Oil Trap
Figure 42: Inverted Trap Applications.
Figure 43: Allowable Pipe Slope.

 Loading...
Loading...