22
Chord Basics
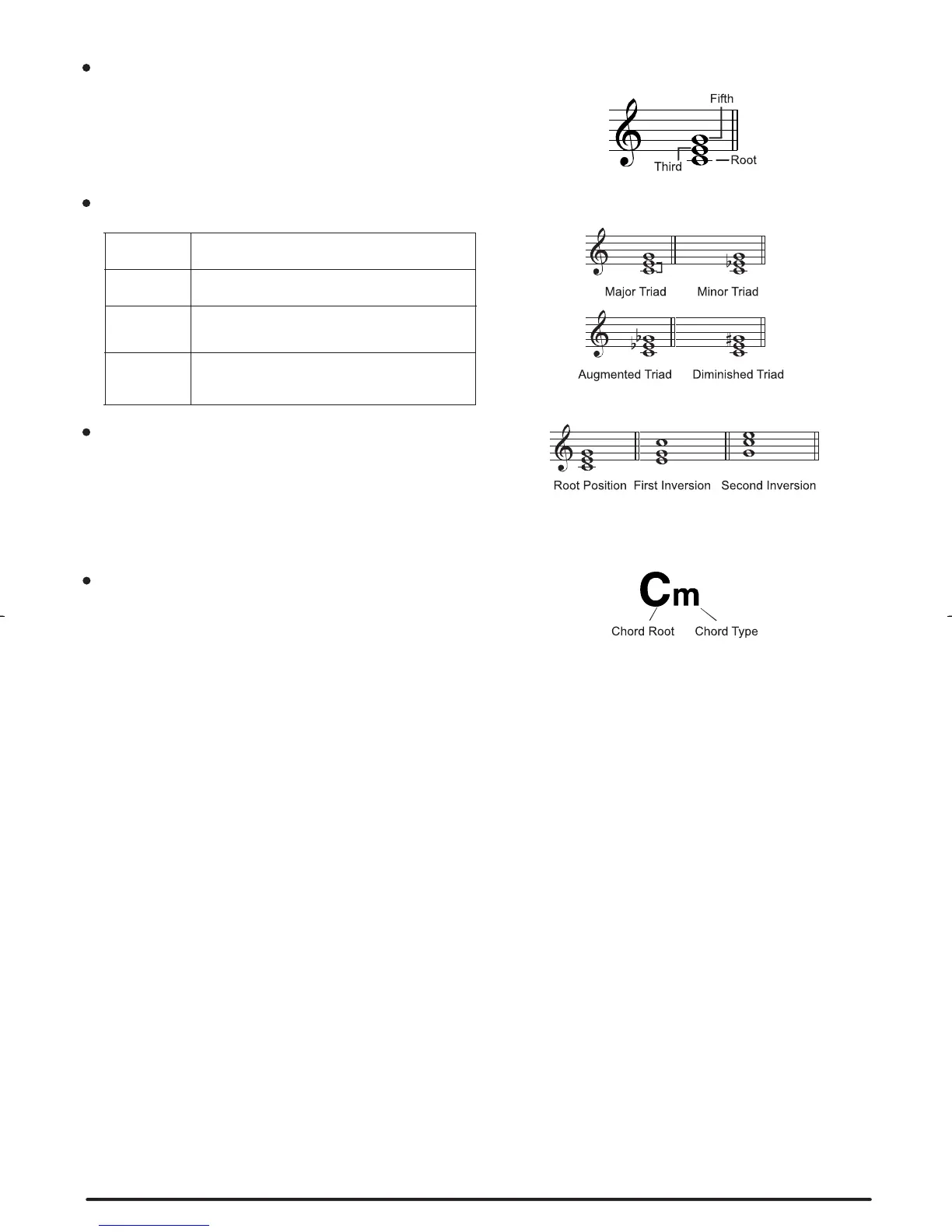
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more
notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. The most
frequently encountered chords are triads. A triad is a set of
three notes that can be stacked in thirds. When stacked in
thirds, the triad's members, from lowest pitched tone to
highest, are called: the Root, the Third, and the Fifth.
Triad Type
Chord Inversion
Chord Name
There are following basic triad types:
We define this chord its root is not in the bass (i.e., is not the
lowest note) as an inversion chord. When the root is in the
bass, we call the chord: root-position chord. If we put the
Third and Fifth in the root position, then it forms Inversion,
we call this chord Inversion Chord. See the following major
triad and its inverted chord.
The chord name contains two parts content: Chord root and
Chord type.
Major Triad
Minor Triad
Augmented
Triad
Diminished
Triad
A root with a major third added above and a
perfect Fifth will consist as a Major Triad.
A root with a minor third added above and a
perfect fifth will consist as a Minor Triad.
A root with a major third added above and an
augmented fifth will consist as an Augmented
Triad.
A root with a minor third added above and a
diminished fifth will consist as a Diminished
Triad.
 Loading...
Loading...