OM-291417 Page 63
12-13. Troubleshooting
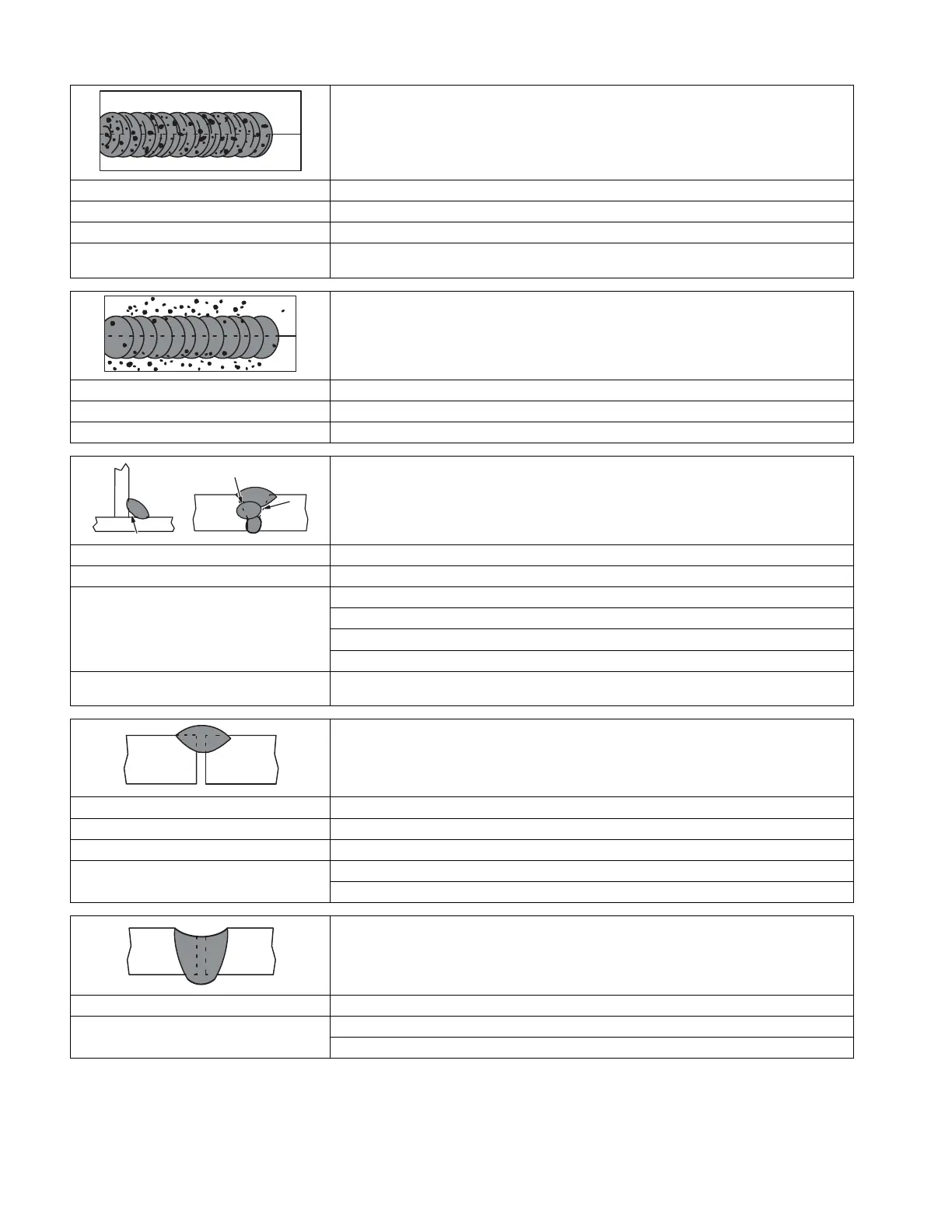
Porosity - small cavities or holes resulting from gas pockets in weld metal.
Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Arc length too long. Reduce arc length.
Damp electrode. Use dry electrode.
Workpiece dirty. Remove all grease, oil, moisture, rust, paint, coatings, slag, and dirt from work surface before
welding.
Excessive Spatter - scattering of molten metal particles that cool to solid form near weld bead.
Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Amperage too high for electrode. Decrease amperage or select larger electrode.
Arc length too long or voltage too high. Reduce arc length or voltage.
Incomplete Fusion - failure of weld metal to fuse completely with base metal or a preceding
weld bead.
Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Insufficient heat input. Increase amperage. Select larger electrode and increase amperage.
Improper welding technique. Place stringer bead in proper location(s) at joint during welding.
Adjust work angle or widen groove to access bottom during welding.
Momentarily hold arc on groove side walls when using weaving technique.
Keep arc on leading edge of weld puddle.
Workpiece dirty. Remove all grease, oil, moisture, rust, paint, coatings, slag, and dirt from work surface before
welding.
Lack Of Penetration - shallow fusion between weld metal and base metal.
Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Improper joint preparation. Material too thick. Joint preparation and design must provide access to bottom of groove.
Improper weld technique. Keep arc on leading edge of weld puddle.
Insufficient heat input. Increase amperage. Select larger electrode and increase amperage.
Reduce travel speed.
Excessive Penetration - weld metal melting through base metal and hanging underneath
weld.
Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Excessive heat input. Select lower amperage. Use smaller electrode.
Increase and/or maintain steady travel speed.
 Loading...
Loading...