move
to
the right hand
as
lower part
(A)
is
supporting point and pullback the
cont~ol
rack
to
the idling position.
Centrifugal force
of
flyweight, weak force of control spring and spring force of
start spring act each other and keep the smooth idling by this force balance.
As
efjgine speed rise, centrifugal force
of
flyweight becomes
large
and push the
contrpl spring and floating lever moves to the right hand, and transfer the
contrpl rack
to
the fuel feed "decrease".
As
engine
SP~
becomes
to
fall,
it
acts the opposite action of above and keep
the constant idling by this action and reaction.
Fig.
3-30 shows the situation
of
max. !!ngine speed control.
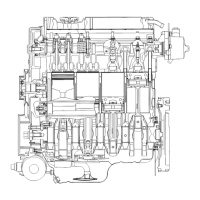
Camshaft bushing
Stopper
bolt
Fig.3-30
RUV
governor, movement
of
max.
engine speed
control
When
the
engine speed
rise
from regulation speed
by
the rapid down
of
load
while the engine running, centrifugal force of flyweight overcome the spring
force of control spring, and flyweights expand
to
the outside and move the
gover.,or sleeve
to
the right hand.
(as
illustrated arrow mark) At this time
supporting point (8) of floating lever, which contact
to
the governor sleeve,
move
lO
the
right hand as
(A)
is
supporting point.
Therefore it moves control rack to the fuel feed
"decrease" and acts not to
over the regulation max. speed.
4)
In
any:
case whatever,
don't
tamper with the seals on (Fig. 3-31),
-
33-

 Loading...
Loading...