Operation Section
23
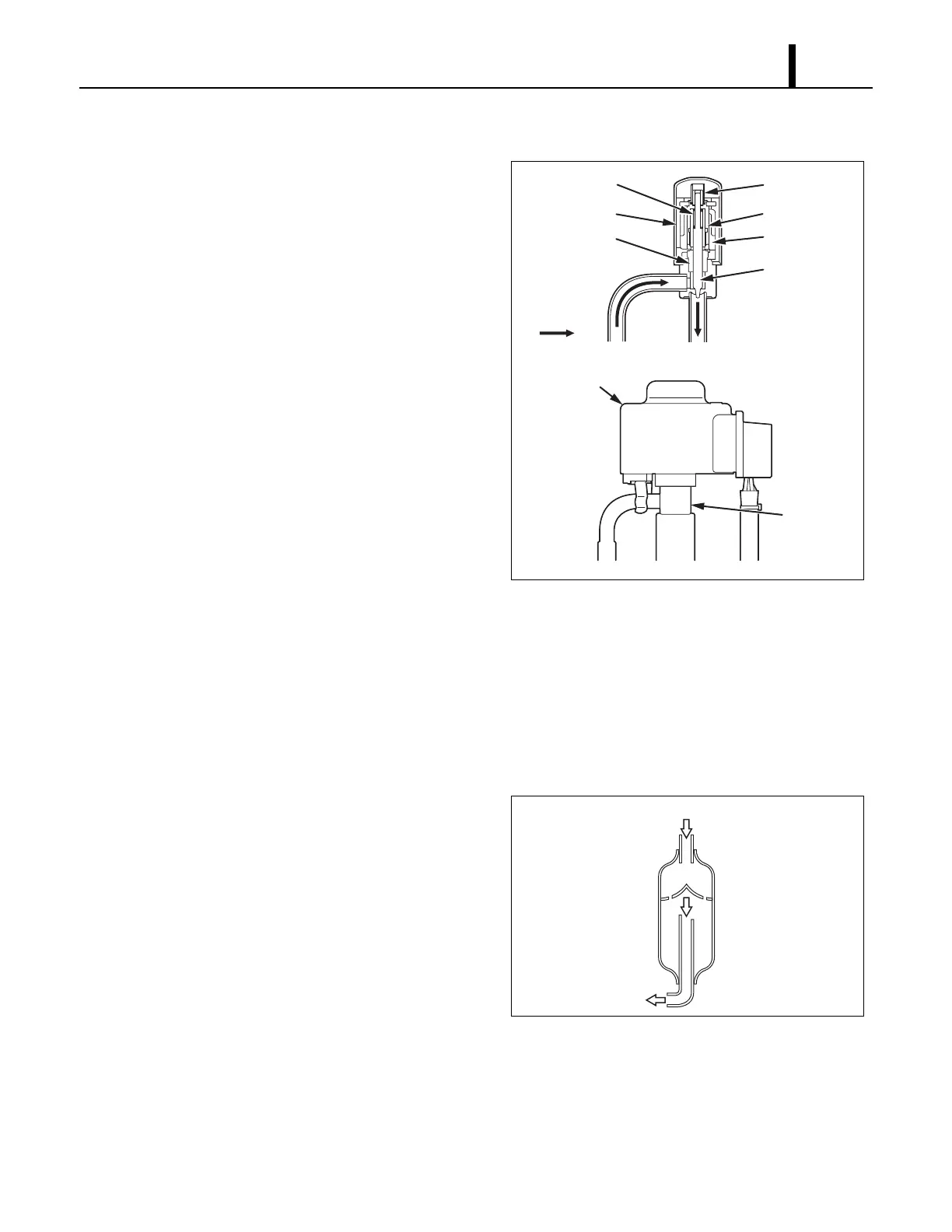
4.4 Electronic Expansion Valve
• The electronic expansion valve causes rapid
refrigerant expansion by injecting "high-
temperature, high-pressure liquid refrigerant"
from the condenser through a small orifice. The
resultant "low-temperature, low-pressure mist
refrigerant" is then sent to the evaporator. A
solenoid valve adjusts the refrigerant quantity
according to the evaporator inlet air and outlet
air thermistors such that the mist refrigerant
can undergo heat exchange in the evaporator
under optimal conditions.
4.5 Evaporator
• The evaporator is a heat exchanger covered with plate fins. Heat is removed from the air being
pulled across the evaporator by the centrifugal fan. The resulting cool air is expelled through the
cool air vent.
4.6 Accumulator
• The accumulator is mounted on the suction
gas piping between the evaporator and the
compressor. The accumulator separates the
liquid refrigerant from the gas refrigerant,
allowing only the gas refrigerant to enter the
compressor. In the accumulator, suction gas is
led into a cylindrical vessel where the speed of
the gas is decreased. This process separates
the refrigerant contained in the gas by the force
of gravity, causing the refrigerant to accumulate at the bottom of the vessel. As a result, the
compressor is protected from possible damage caused by liquid refrigerant intake.
I003162
Refrigerant
Flow
Valve Spring Spring
Valve Holder
Valve
Control Coil
Magnet
Stopper
Delivery Screw
Valve
I000514
from Evaporator
to Compressor
 Loading...
Loading...











