9 Socket Service
9-2
NJ-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherNet/IP Port User’s Manual (W506)
9-1 Basic Knowledge on Socket
Communications
A socket is an interface that allows you to directly use TCP or UDP functions from the user program. In
a host computer (e.g., personal computer), sockets are provided in the form of a C language interface
library. If you load the library, you can program communications via TCP and UDP in the user program.
In a UNIX computer, a socket interface is provided in the format of system calls. For the built-in Ether-
Net/IP port, you execute instructions in the user program to use sockets. You can use these communi-
cations services to send and receive any data to and from remote nodes, i.e., between host computers
and Controllers or between Controllers. The built-in EtherNet/IP port provides a UDP socket service
and a TCP socket service.
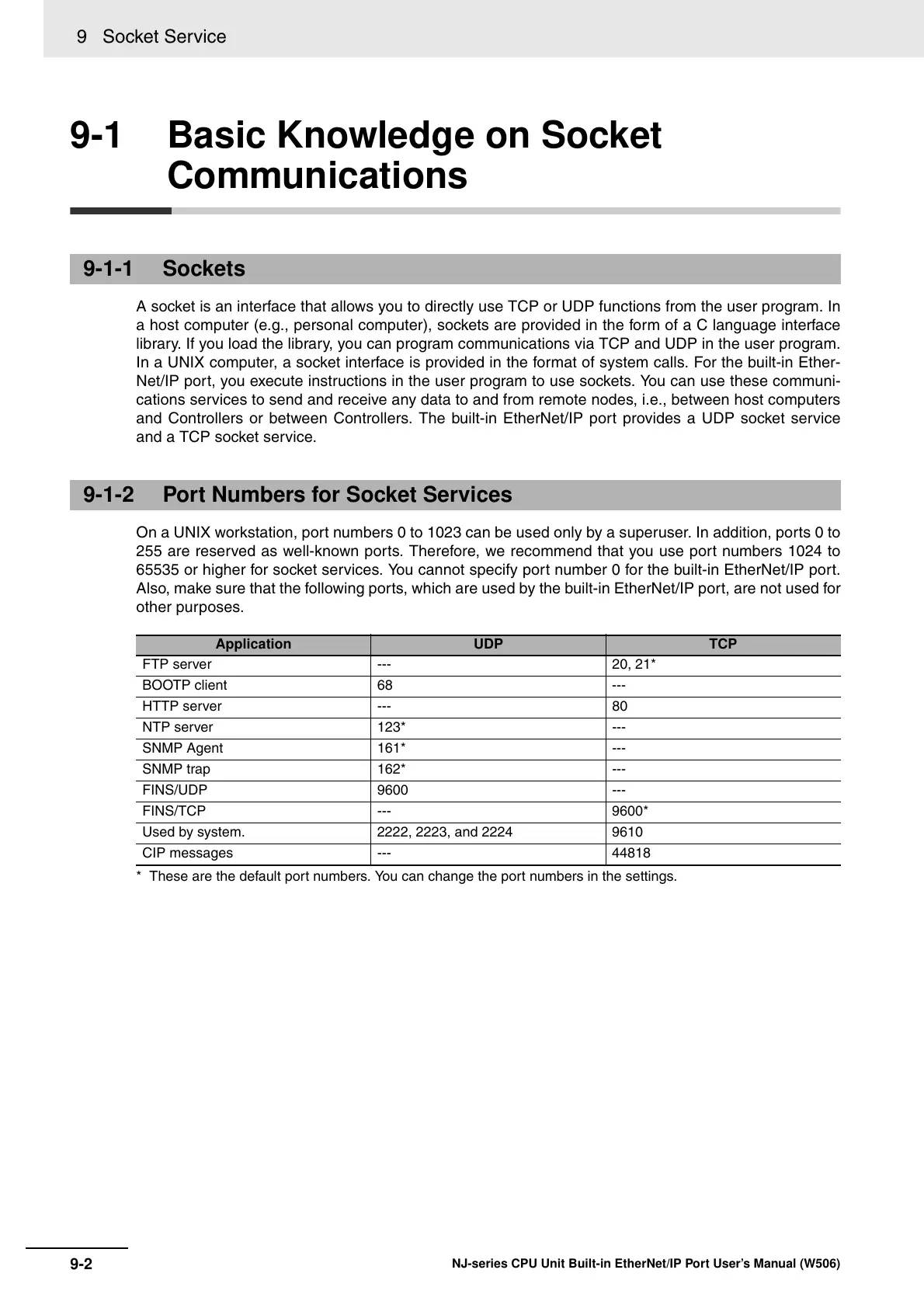
On a UNIX workstation, port numbers 0 to 1023 can be used only by a superuser. In addition, ports 0 to
255 are reserved as well-known ports. Therefore, we recommend that you use port numbers 1024 to
65535 or higher for socket services. You cannot specify port number 0 for the built-in EtherNet/IP port.
Also, make sure that the following ports, which are used by the built-in EtherNet/IP port, are not used for
other purposes.
* These are the default port numbers. You can change the port numbers in the settings.
9-1-1 Sockets
9-1-2 Port Numbers for Socket Services
Application UDP TCP
FTP server --- 20, 21*
BOOTP client 68 ---
HTTP server --- 80
NTP server 123* ---
SNMP Agent 161* ---
SNMP trap 162* ---
FINS/UDP 9600 ---
FINS/TCP --- 9600*
Used by system. 2222, 2223, and 2224 9610
CIP messages --- 44818

 Loading...
Loading...