www.qutools.com quTAG MC Manual 5
• High energy/accelerator physics
• High precision time measurements
1.3 Jitter Measurement
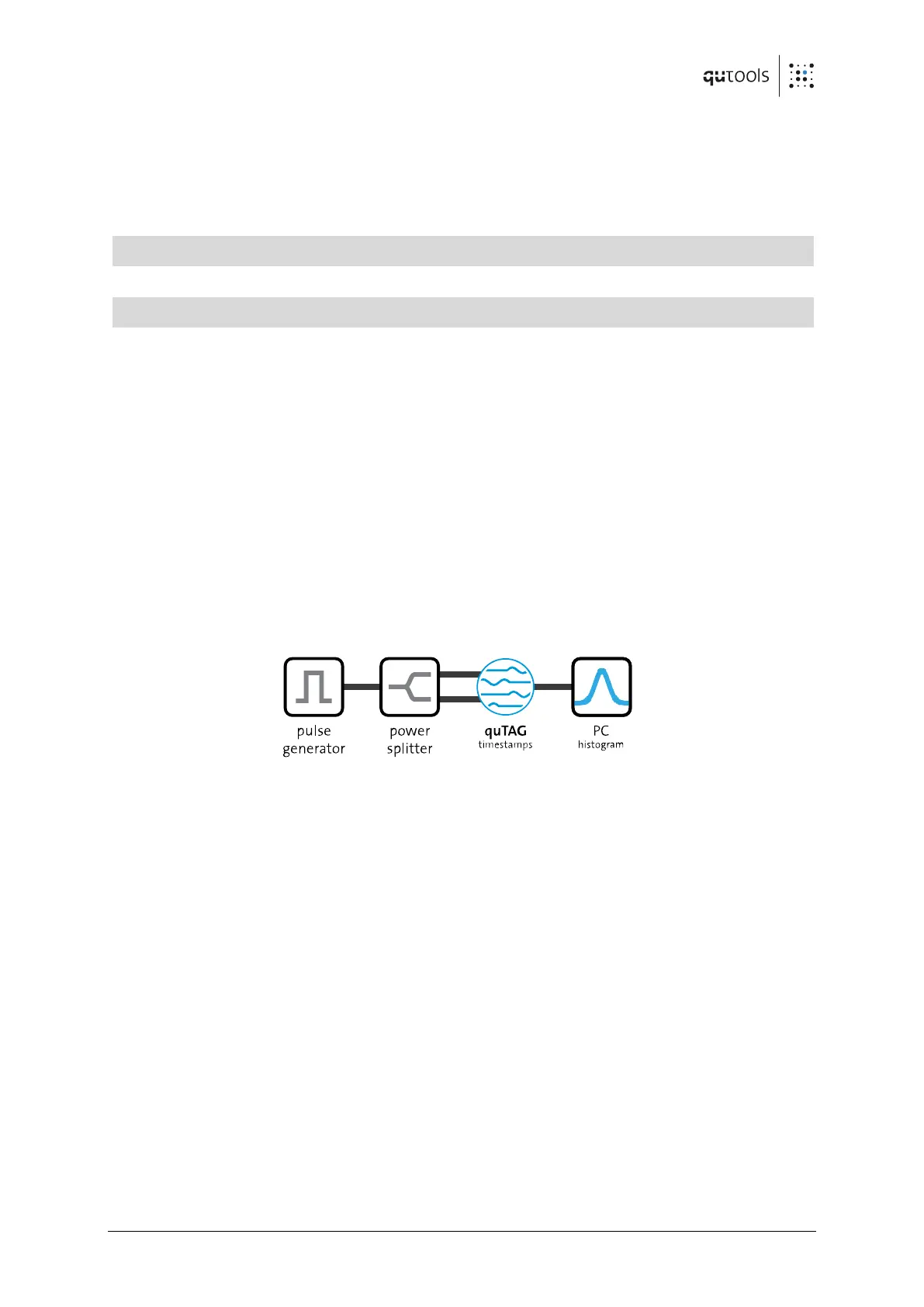
In order to measure the jitter, we generate an electrical pulse with steep edges. This pulse gets
split into two by a power splitter and sent into two different inputs of the quTAG (i.e. start and
stop-X or stop-X and stop-Y). Then we use the quTAG software to generate a start-stop-
histogram.
We fit a Gaussian function to this histogram and determine RMS and FWHM. The single
channel jitter corresponds to σ / √2 from this two-channel measurement, assuming equal
Gaussian contributions from both signals. The FWHM can be obtained by the standard
deviation with the relation FWHM = 2 √2 ln 2 σ ≈ 2.35 σ.
 Loading...
Loading...