170
by default. If set it can cause temporary loss of connectivity after
changes in a spanning trees active topology as a result of persistent
incorrectly learned station location information. It is set by a network
administrator to prevent bridges external to a core region of the network,
causing address flushing in that region, possibly because those bridges
are not under the full control of the administrator. or the status of MAC
operation for the attached LANs transitions frequently.
Mcheck:
The same definition as in the RSTP specification for the CIST
ports.
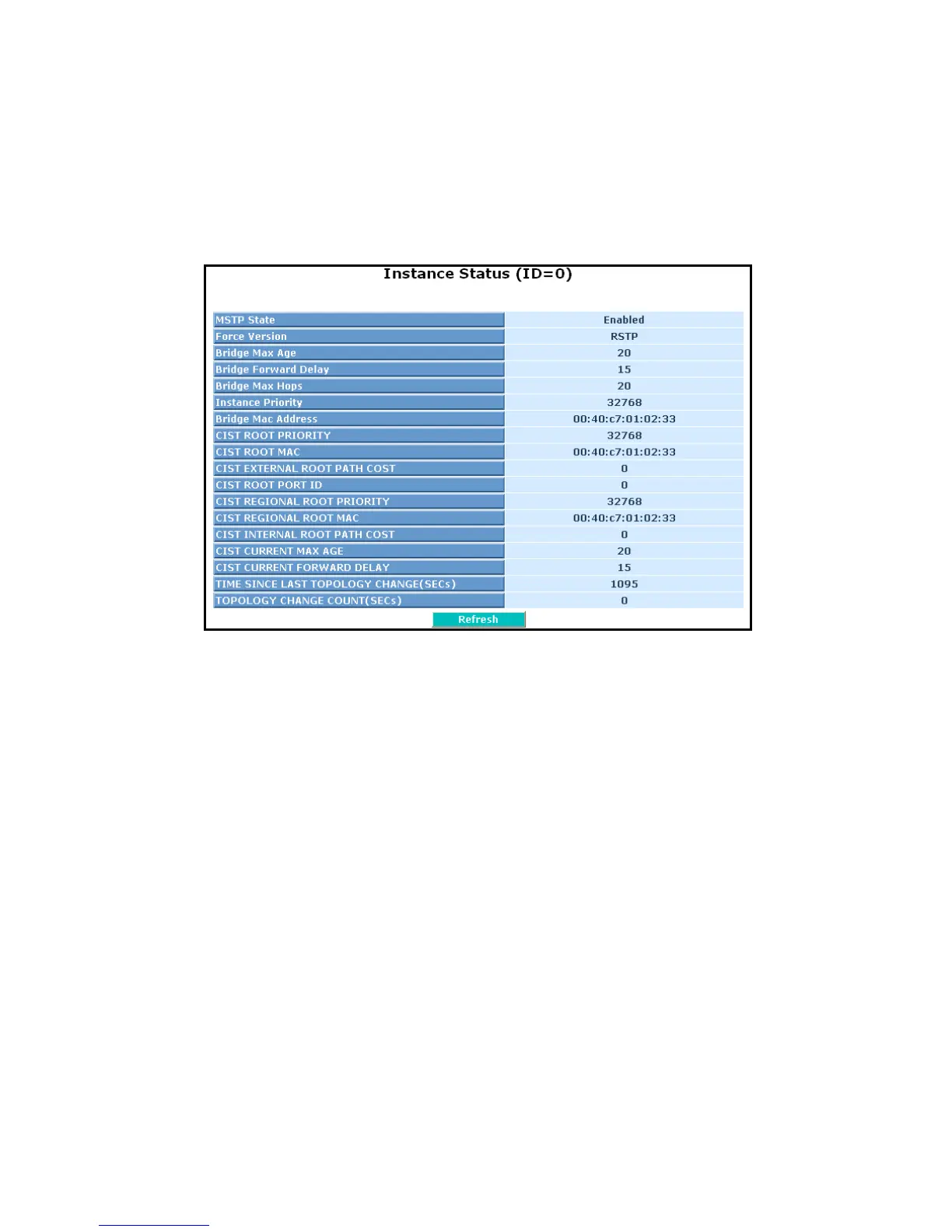
Fig. 3-160 Instance Status
Parameter description:
MSTP State:
MSTP protocol is Enable or Disable.
Force Version:
It shows the current spanning tree protocol version configured.
Bridge Max Age:
It shows the Max Age setting of the bridge itself.
Bridge Forward Delay:
It shows the Forward Delay setting of the bridge itself.
Bridge Max Hops:
It shows the Max Hops setting of the bridge itself.
 Loading...
Loading...