Web-based Configuration Guide
20
4.9.2 DNS Proxy
Caution
This feature is supported by only the router mode and the WISP mode.
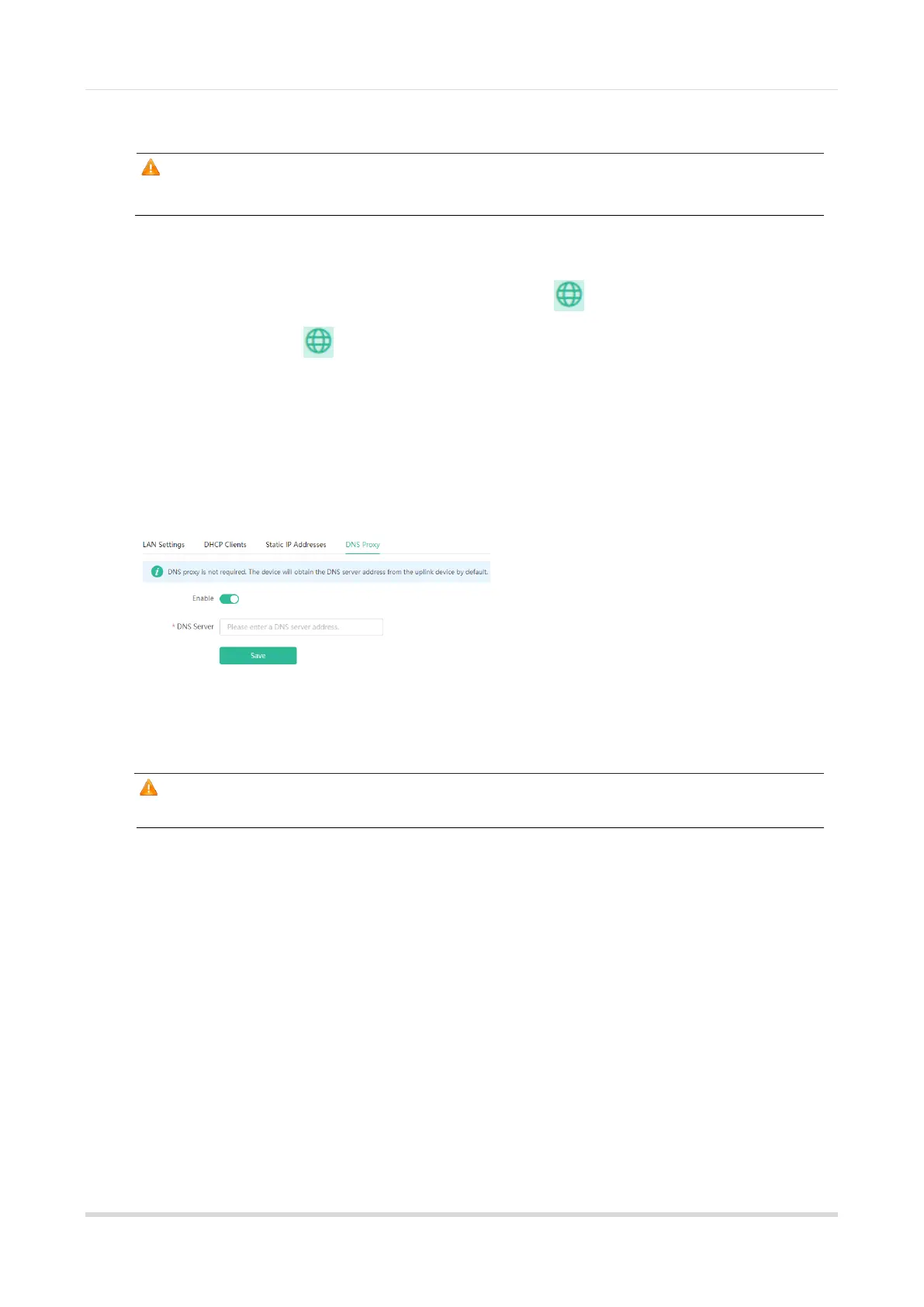
The DNS server proxy is optional. By default, the device obtains the DNS server address from the uplink device.
Mobile Phone View: Choose More > Switch to PC view > More > Basics > LAN > DNS Proxy.
PC View: Choose More > Basics > LAN > DNS Proxy.
DNS proxy: By default, the DNS proxy is disabled, and the DNS address delivered by the ISP is used. If the
DNS configuration is incorrect, the network may be successfully connected and mobile phones can access the
Internet by using APPs, but web pages cannot be opened. You are advised to keep the DNS proxy disabled.
DNS Server: By default, clients use the DNS service provided by the primary router when accessing the Internet.
The default settings are recommended. After the DNS proxy is enabled, you can enter the IP address of the
DNS server. The DNS address varies according to regions, and you can consult the local ISP.
4.10 Configuring Port Mapping
Caution
This function is supported only in router mode.
4.10.1 Overview
Port mapping needs to be set in the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: When you need to access network cameras or PCs at home while you are away from home, port
mapping needs to be configured.
Scenario 2: When a server is set up on the home network so that you can access it while you are away from
home, port mapping or demilitarized zone (DMZ) needs to be configured.
Port mapping maps the IP address of a device on the LAN to an external network in the form of WAN IP
address and port number, so as to provide the access service for the external network.
Port mapping maps the WAN port IP address of a router to an LAN host and port so that Internet users can
proactively access hosts on the LAN.
DMZ forwards all packets from the Internet to DMZ hosts to provide the Internet access service.

 Loading...
Loading...