Maintenance
Startup 250:Users:Danny:Desktop:Operation manuals:line pumps:maverick
(P305):pHseriesMAINTENANCE.fm
43
Operation Manual - SP 305
• If you lower the pressure at which the system runs,
you can defeat the power of the system. For
example, you ask the machine to develop 2400 PSI
hydraulic pressure to push the concrete where you
want it to go. You want to replace a hydraulic hose
with a less expensive, lower pressure hose, so you
lower the hydraulic pump pressure setting from
2500 PSI to 1500 PSI. What is the result? The
concrete still requires 2400 PSI to get where you
want it, but your pump can only put out oil up to
1500 PSI. Now the oil that should be pushing the
concrete is instead telling the hydraulic pump to
stop putting out oil. Nothing moves, and your
concrete pump has been rendered useless by a
cheap hydraulic hose.
• If you raise the pressure at which the system runs,
you can harm the system. Using a new example,
the concrete requires that the machine develop
2900 PSI hydraulic pressure to push it where you
need it. Your machine is factory set to run at a
maximum of 2500 PSI, so you raise the setting of
the pump compensator to do the job. The hydraulic
pump can’t withstand 2900 PSI for more than a
few minutes, and it breaks. You now have to
replace a pump before you can make another pour.
• If you leave the machine at the factory
specification, you DO NOT harm the system. It
gives you years of dependable service. This means
you should only use fittings and hoses that have a
sufficient WORKING PRESSURE to handle the
system requirements. If you take a job that needs
more pressure than your machine has, you should
buy or rent a higher pressure machine.
Specific Information
• Schwing uses high pressure fittings and hoses on
all circuits, even if the relief valve for that circuit is
set to low or medium pressure. The fittings and
hoses are rated at a minimum of 5000 PSI working
pressure, and in the case of some fittings, up to
15,000 PSI. We advise against changing any circuit
to lower rated hoses or fittings.
• We use metric fittings and hoses, with metric
threads on the couplings. There are four diameter
sizes of tubes and fittings used on this unit and four
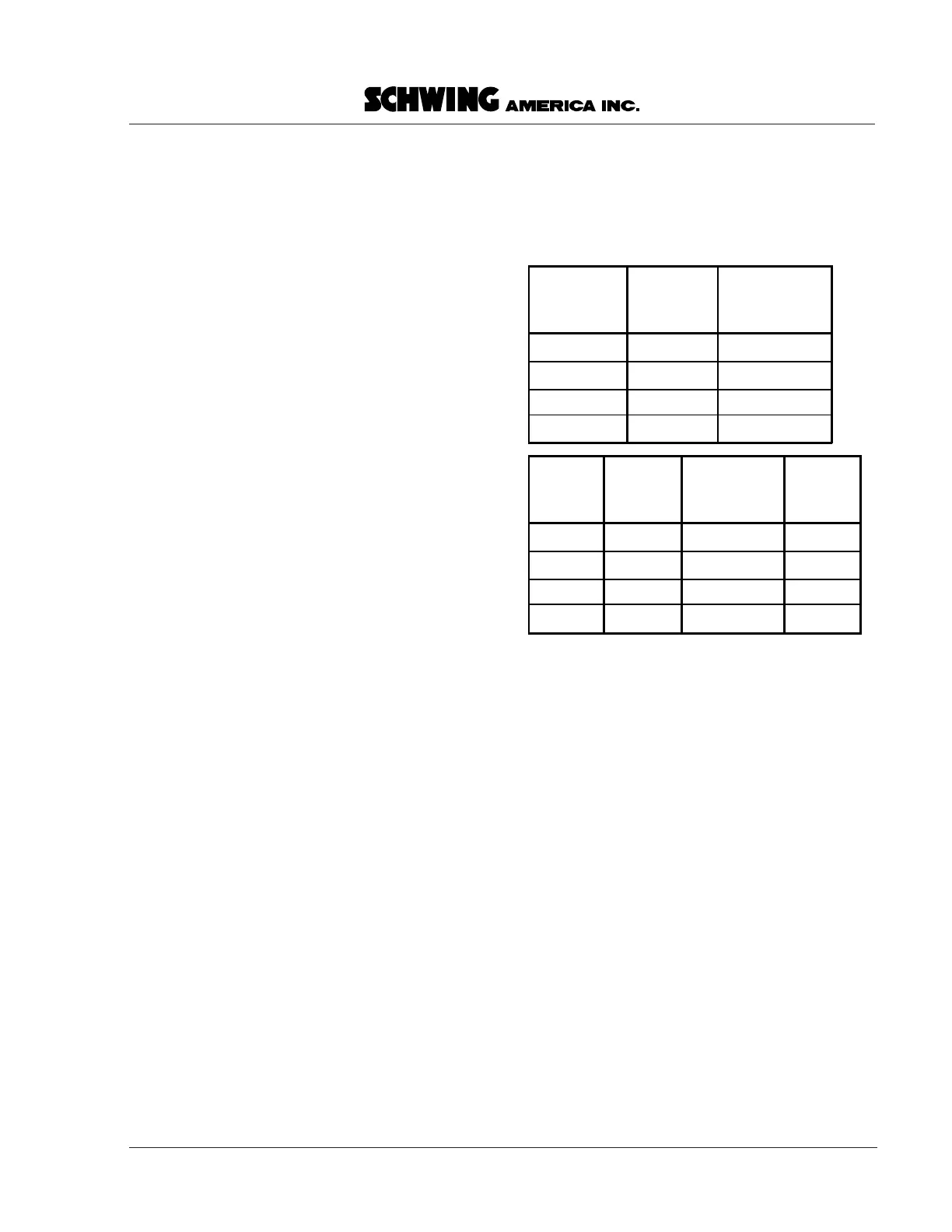
diameter sizes of hoses. The chart in Figure 29 tells
you what the sizes are and what they will attach to.
• All block threads are metric or BSPP.
• Instructions for setting the relief functions are
shown in the preventative maintenance section of
this manual.
Hose Size Hose I.D.
8 8 mm
13 13 mm
16 16 mm
20 20 mm
Connects
with Fitting
& Tube Size
12
16
20
25
12
16
20
25
Tube &
Fitting
Size
8
13
16
20
Connects
with
Hose Size
Tube &
Fitting
O.D.
12 mm
16 mm
20 mm
25 mm
Tube &
Fitting
I.D.
8 mm
13 mm
16 mm
20 mm
1COLPhoseFITTING.eps
Figure 29
Hose, fitting and tube sizes versus
connection sizes
 Loading...
Loading...