Advanced functionalities
4 Understanding aerial mapping with the eBee
Goal of this section: Aerialmapping using the eBee is designed to be
simple and fully automatic, requiring very little input from the user.
Understanding the basics of aerial navigation, however, can help you
map more complex terrain and yield higher quality results. This sec-
tion explains the basics of waypoint-basednavigationand the control
strategies used by the drone for flight.
4.1 Waypoints and their properties
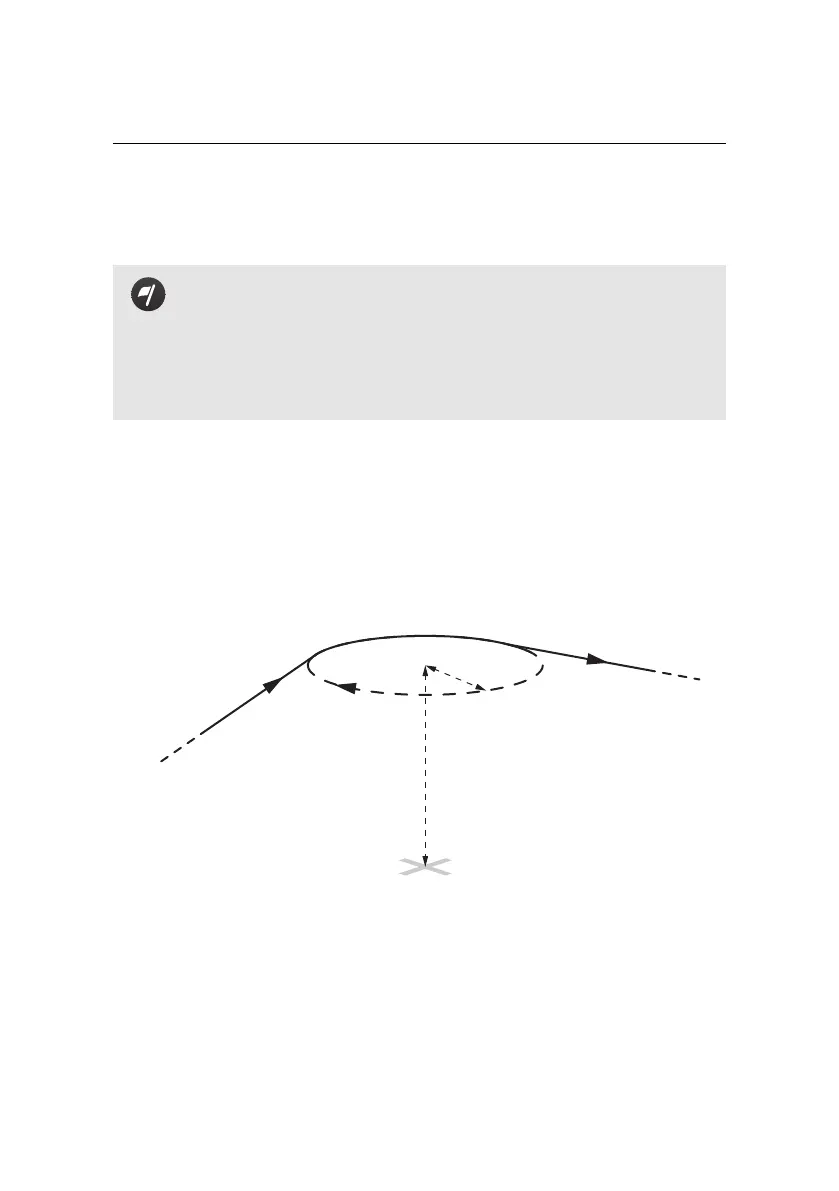
The eBee uses a flight plan consisting of a list of waypointsto navigate. A waypoint
essentially consists of a circle about a given position and information that defines
how the drone should behave when reaching them. The entire list of waypoints
is stored in the drone autopilot and can be remotely edited using eMotion.
from previous
waypoint
to next
waypoint
Position (GPS coordinates)
Altitude:
Above Take-off location (m/ATO)
OR
Above Mean Sea Level (m/AMSL)
Radius
Direction
In eMotion every waypoint is defined by the following parameters:
• ID: Every mission waypoint has a unique ID, beginning at 1. The eBee can
store up to 50 mission waypoints. Setup phase waypoints (Start and Home)
do not have an ID.
56

 Loading...
Loading...