Technical data and characteristic curves
4.1 Operating range and characteristics
1FT7 Synchronous Motors
78 Configuration Manual, (PFT7S) 01/2009, 6SN1197-0AD13-0BP2
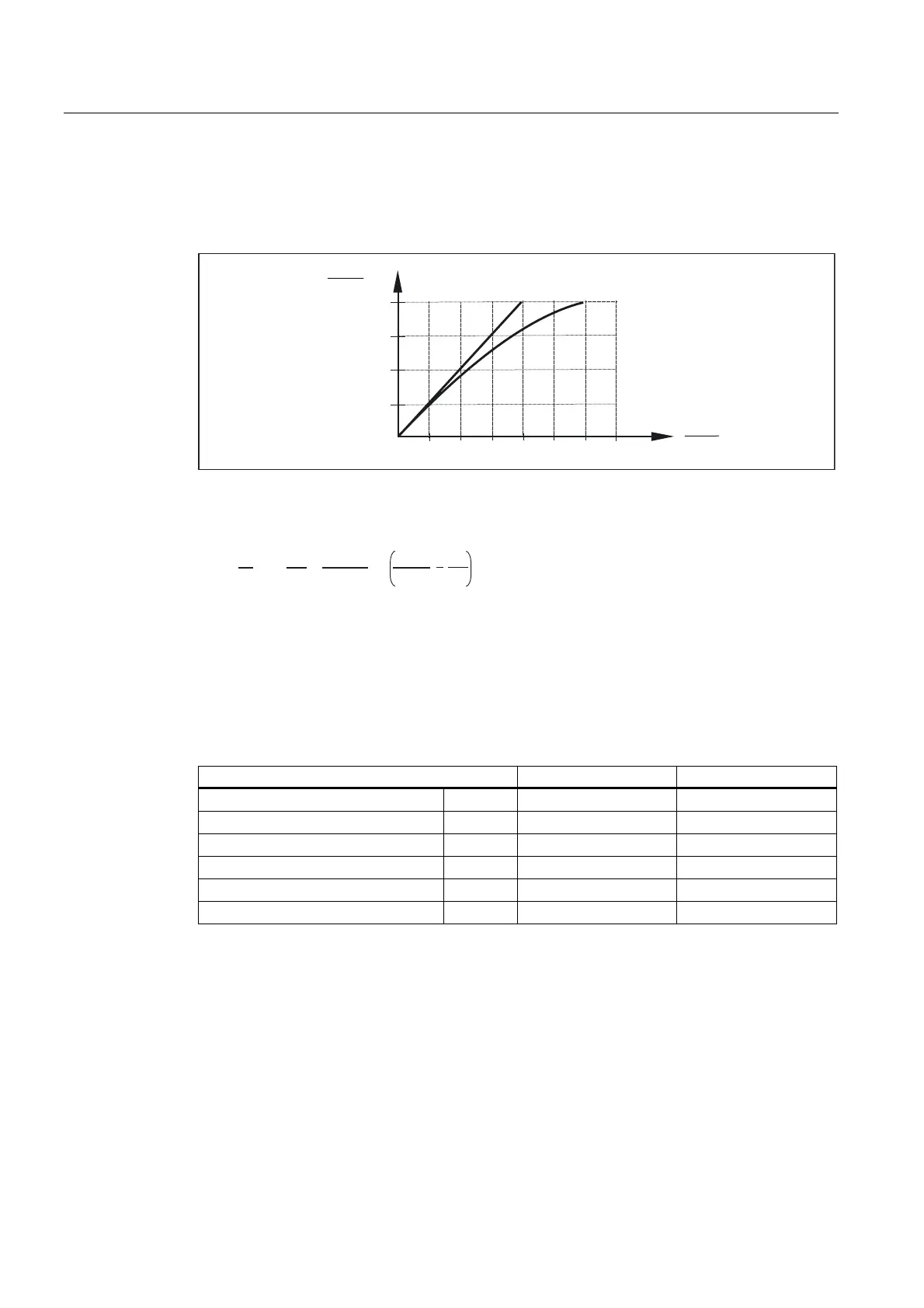
Typical M/I characteristic
Because of saturation effects, the achievable torque cannot be calculated linearly from the
current (particularly at high currents).
.
,
.
,
0
0
ZRUVWFDVH
EHVWFDVH
Figure 4-5 Torque-current characteristic curve for self-cooled motors
From M
0
(or I
0
), the following formula can be used to determine the torque or the torque
constant as a function of the current:
N,
෬
,,
PD[
PD[
7
0
,
,
0
,
,
,
0
PD[
,
0
,
Tolerance data
The data shown in the data sheets are nominal values that are subject to natural scatter. The
following tolerances apply:
Table 4- 2 Tolerance data in the motor list data
Motor list data Typ. value Guaranteed value
Stall current I
0
± 3 % ± 7,5 %
Electrical time constant T
el
± 5 % ± 10 %
Torque constant k
T
± 3 % ± 7,5 %
Voltage constant k
E
± 3 % ± 7,5 %
Winding resistance R
ph
± 5 % ± 10 %
Moment of inertia J
mot
± 2 % ± 10 %

 Loading...
Loading...