Descriptions of functions
10.3 Communication according to PROFIdrive
SINAMICS DCM DC Converter
406 Operating Instructions, 12/2018, A5E34763375A
Properties of the Controller, Supervisor and drive units
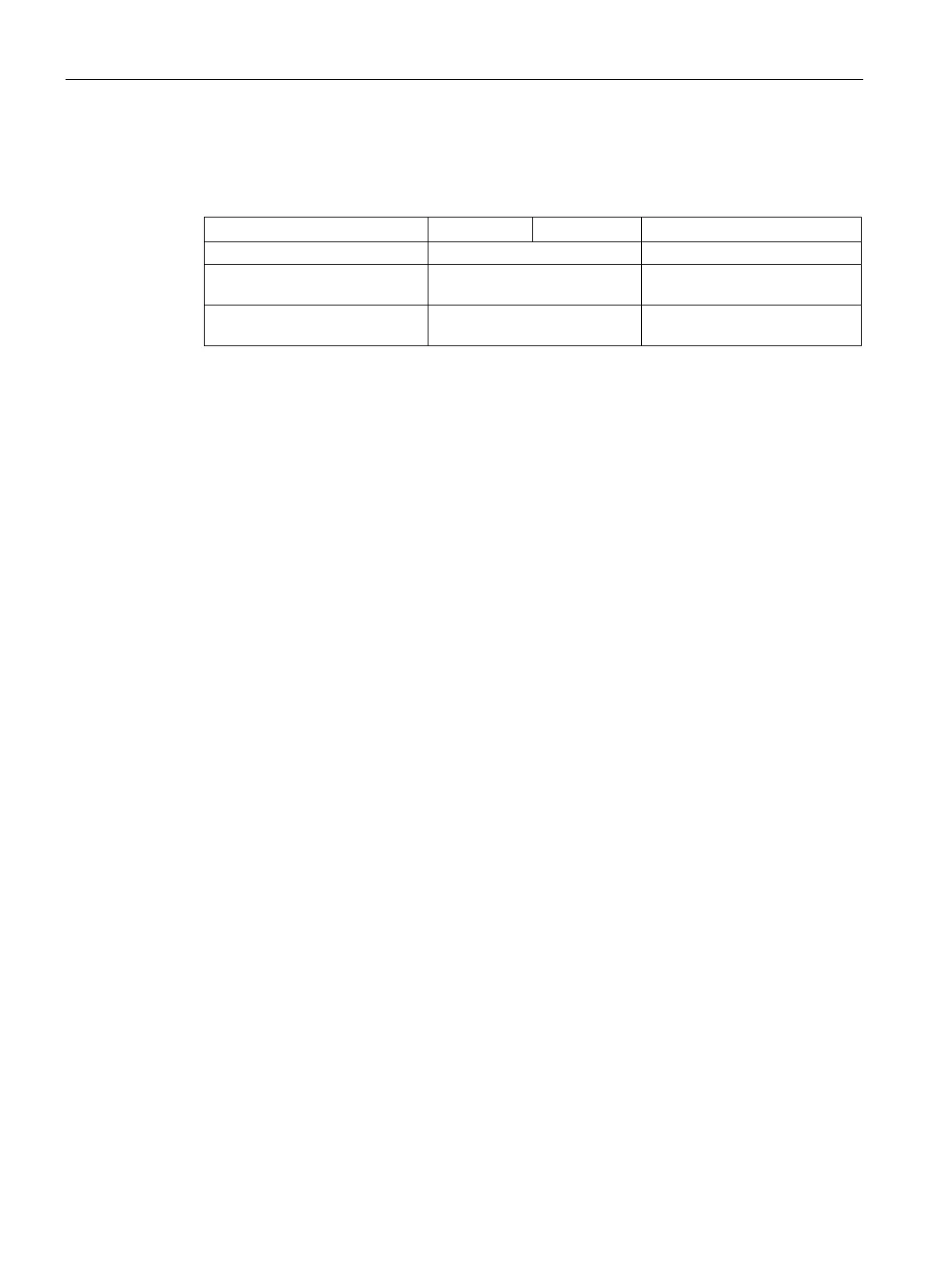
Table 10- 4 Properties of the Controller, Supervisor and drive units
Send messages Permitted without external
Only possible on request by the
Receive messages Possible without any
Only receive and acknowledge
● Drive unit (PROFIBUS: Slave, PROFINET IO: IO Device)
Example: Control Unit CUD
● Controller (PROFIBUS: Master Class 1, PROFINET IO: IO Controller)
A controller is typically a higher-level controller in which the automation program runs.
Example: SIMATIC S7 and SIMOTION
● Supervisor (PROFIBUS: Master Class 2, PROFINET IO: IO Supervisor)
Devices for configuring, commissioning, operator control and monitoring while the bus is
in operation – and
devices, which only exchange non-cyclic data with drive units and controllers.
Examples: Programming devices, human machine interfaces
Two communication services are defined in the PROFIdrive profile; namely, cyclic data
exchange and acyclic data exchange.
● Cyclic data exchange via a cyclic data channel:
Motion control systems require cyclically updated data in operation for open-loop and
closed-loop control tasks. This data must be sent to the drive units in the form of
setpoints or transmitted from the drive units in the form of actual values, via the
communications system. Transmission of this data is usually time-critical.
● Acyclic data exchange via an acyclic data channel:
An acyclic parameter channel for exchanging parameters between the controller/
supervisor and drive units is additionally available. Access to this data is not time-critical.
● Alarm channel
Alarms are output on an event-driven basis, and show the occurrence and expiry of error
states.

 Loading...
Loading...