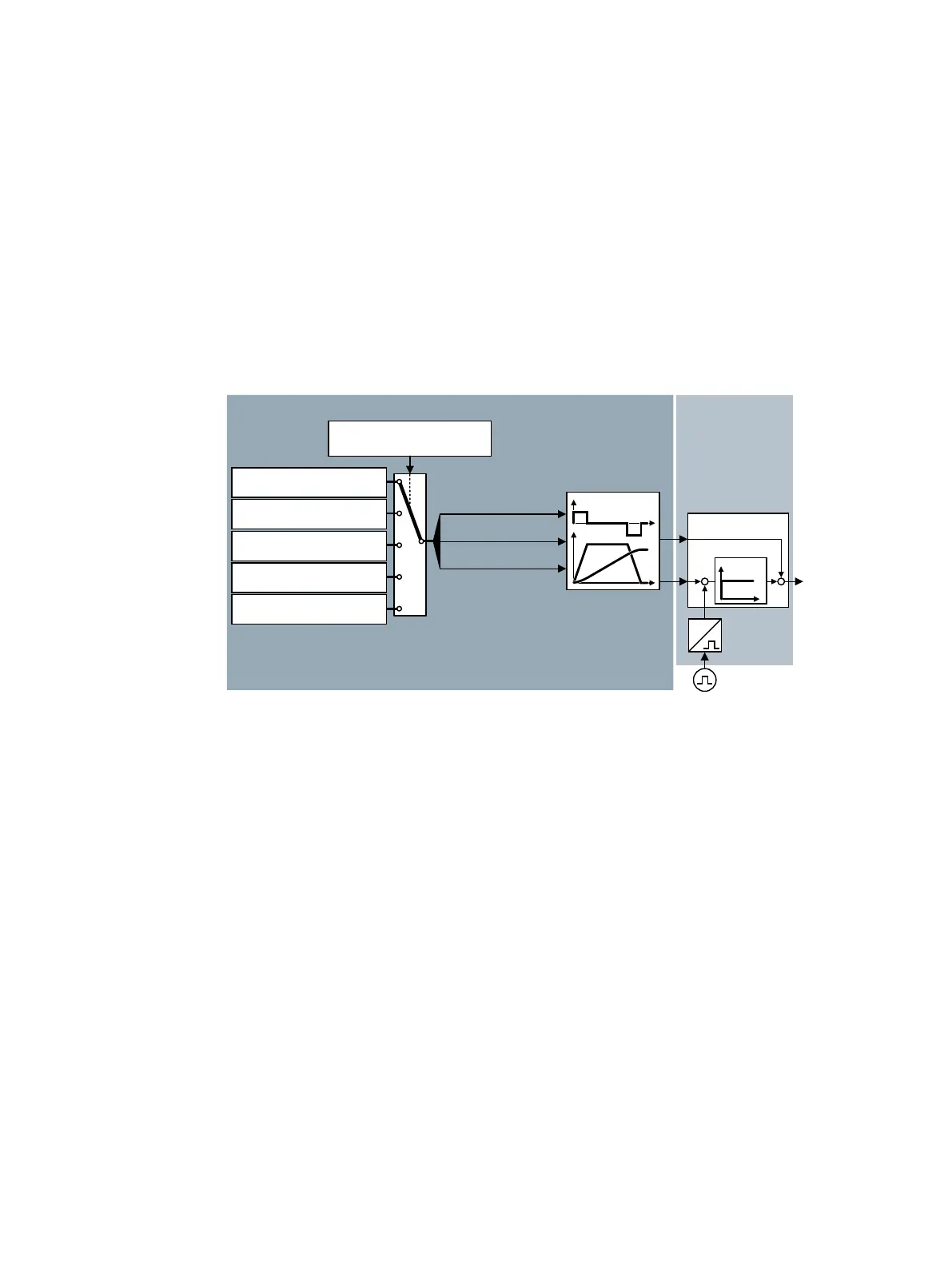
Basic positioner and position control
3
Overview
Position control means controlling the position of an axis. An "axis" is a machine or system
component that comprises the converter with active position control and the driven mechanical
system.
The basic positioner (EPos) calculates the traversing prole for the time-optimized traversing of
the axis to the target position.
0','LUHFWO\LQSXW
VHWSRLQW
6HOHFWWUDYHUVLQJEORFNV
5HIHUHQFLQJ
-RJJLQJ
7UDYHOWRIL[HGVWRS
3RVLWLRQ
&RQWURODQGVHOHFWLRQRI
RSHUDWLQJPRGH
9HORFLW\
$FFHOHUDWLRQ
*HQHUDWH
WUDYHUVLQJSURILOH
(QFRGHU
6SHHG
FRQWUROOHU
%DVLFSRVLWLRQHU3RVLWLRQFRQWUROOHU(3RV
/8
V
D
Y
V
Y
Y
V
D
.
3
Figure 3-1 Basic positioner and position control
The basic positioner has the following operating modes:
• Direct setpoint input (MDI): The external control species the position setpoint for
the axis.
• Traversing block selection: Position setpoints are saved in dierent traversing blocks
in the converter. The external control selects a traversing
block.
• Referencing: Referencing establishes the reference of the position
measurement in the converter to the machine.
• Jogging: This function is used to incrementally traverse the axis
(Set up).
• Travel to xed stop: The converter positions the axis with a dened torque
against a mechanical xed stop.
Basic positioner
Function Manual, 09/2020, FW V4.7 SP13, A5E34257659B AG 13

 Loading...
Loading...