6.8 Traversing blocks
Description
A traversing block describes a positioning instruction for the drive.
The converter saves 16 dierent traversing blocks, which it normally executes one after the
other. However, you can also directly select a specic traversing block or skip traversing blocks.
Table 6-1 Components of a traversing block
Element Meaning
Number With this number in the range 0 to 15, every traversing block can be selected using
binary-coded control signals.
Job Positioning command: You can give the converter various commands. For some
jobs, you must also specify a parameter. See the table below.
Parameter
Mode Positioning mode: Positioning relative to the start position or absolute to the ma‐
chine zero point.
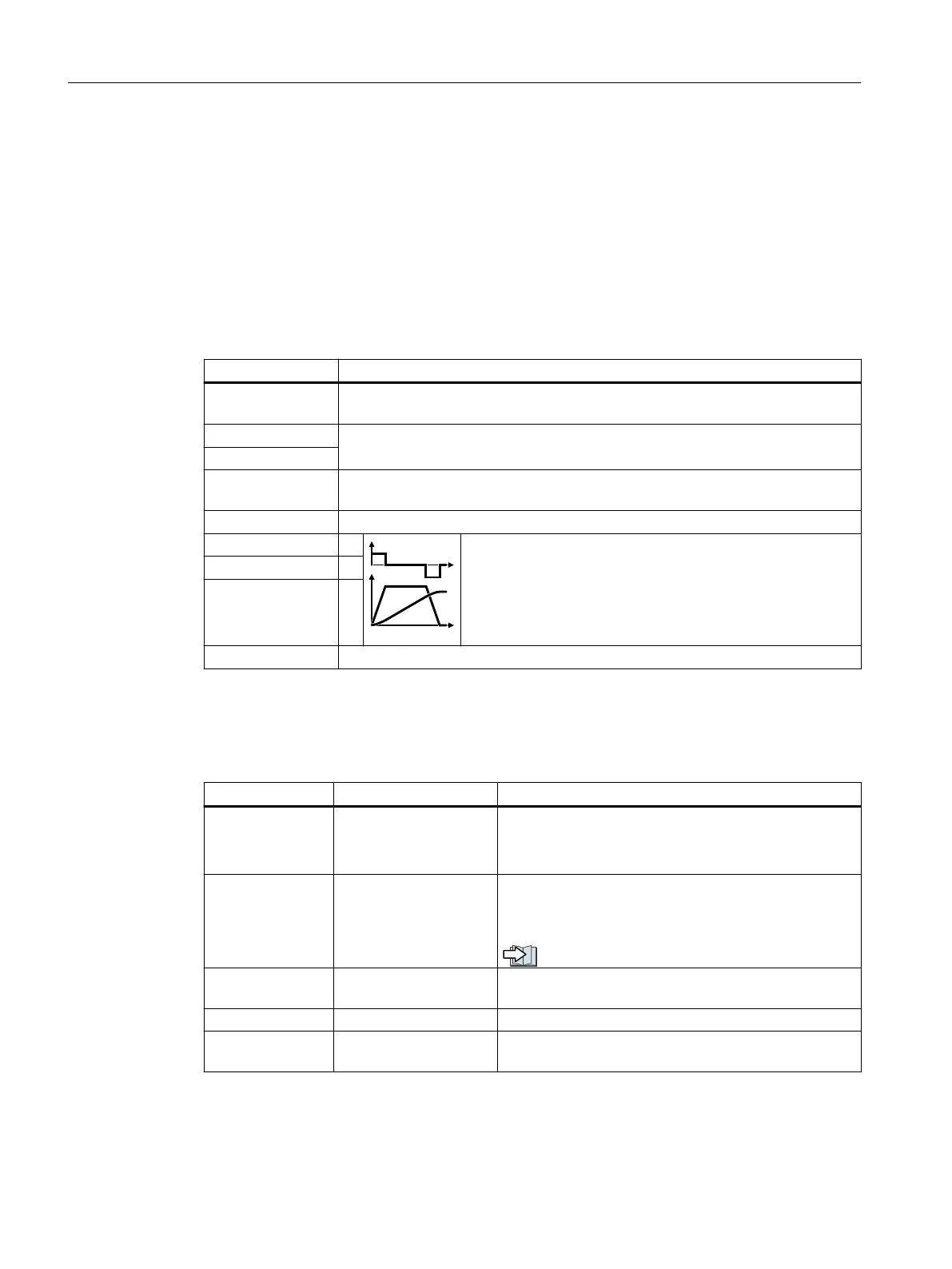
Position Target position
Velocity v
Setpoints for the traversing prole.
Acceleration a
Braking -a
Advance Jump condition to the next traversing block. See the table below.
Job and parameters
Table 6-2 Job and parameters
Job Parameter Meaning
Positioning ---
• Axis absolute or relative positioning.
• Rotary axis with modulo correction in a positive or
negative direction, absolute positioning.
Travel to xed stop Force [N] or torque
[0.01 Nm]
Traverse axis to a xed stop:
• Linear axis with reduced force.
• Rotary axis with reduced torque.
Travel to xed stop (Page 81)
Endless travel --- Traverse the axis at the specied velocity to the positive
or negative end of the traversing range.
Wait Time [ms] Wait the specied time.
Go to Number The converter then executes the next traversing block
with the specied number.
Commissioning
6.8 Traversing blocks
Basic positioner
74 Function Manual, 09/2020, FW V4.7 SP13, A5E34257659B AG

 Loading...
Loading...