Configuration and operation
5.6 CPU scan cycle
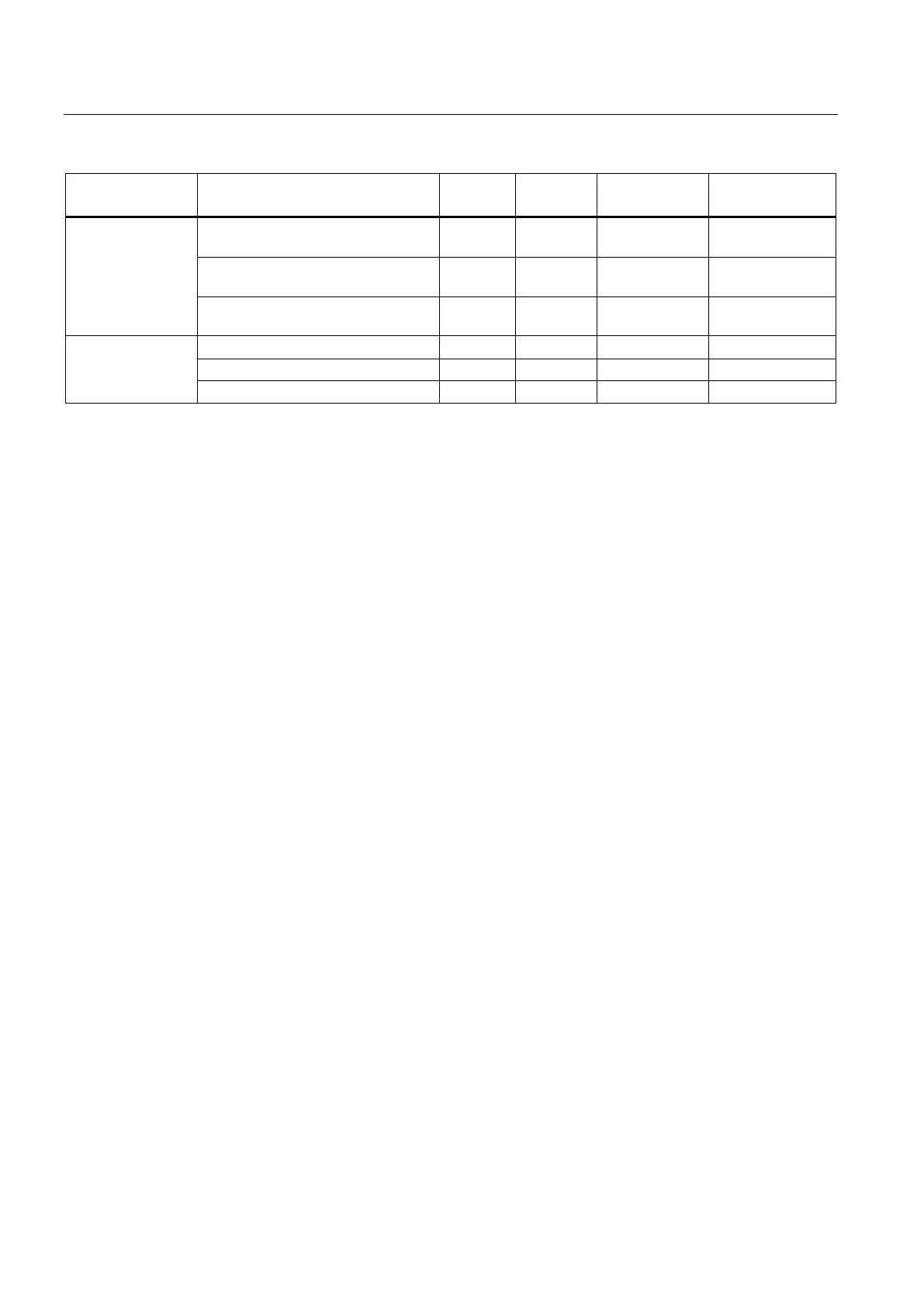
CP 1243-1 DNP3, CP 1243-1 IEC
38 Operating Instructions, 02/2014, C79000-G8976-C312-02
Format (memory
requirements)
Floating-point
number (32 bits)
Measured value, short floating point
<13> in REAL Q, M, DB
Measured value, short floating point
1)
<36> in REAL Q, M, DB
Set point command, short floating
<50> out REAL Q, M, DB
Block of data
(1...32 Bit)
1)
2)
1)
Bitstring of 32 bits with time tag
1)
2)
1)
2)
1)
For information on the format of the time stamp, refer to the next section.
With these data point types, contiguous memory areas up to a size of 32 bits can be transferred. All S7 data types with a
size between 1 and 32 bits are compatible. If the array is modified later, the data point must be recreated.
Time stamp with the IEC CP
IEC CP time stamps are transferred according to the IEC specification in the "CP56Time2a"
format. Note that in the frames only the first 3 bytes for milliseconds and minutes are
transferred.
CPU scan cycle
Structure of the CPU scan cycle
The cycle (including the pause) with which the CP scans the memory area of the CPU is
made up of the following phases:
●
For data points of the type "Input", which are configured with the "High priority" setting in
the data point configuration in "General > Priority in the scan cycle", the PLC tags are all
read in one scan cycle.
●
In every cycle, the values of a certain number of unsolicited write jobs are written to the
CPU. The number of tags written per cycle is specified for the CP in the "Communication
with the CPU" parameter group with the "Max. number of write jobs" parameter. The tags
whose number exceeds this value are then written in the next or one of the following
cycles.

 Loading...
Loading...











