Quick review
1.1 Basic information about how the CPU works
Getting started with S7-1200
Getting Started, 11/2009, A5E02486791-01
11
1.1.4 Data types supported by the S7-1200
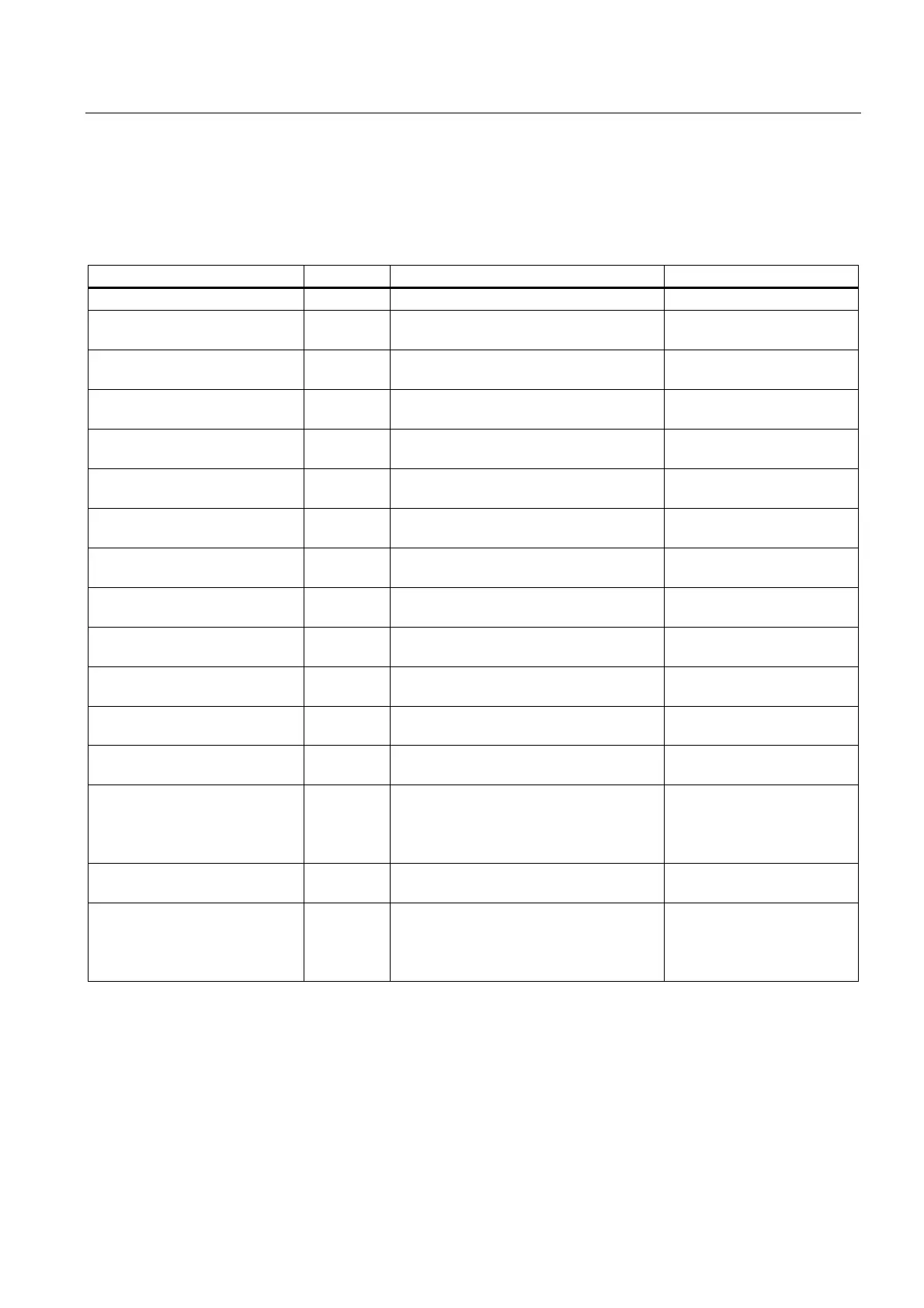
The data type specifies not only the size of a data element, but also the structure of the bits
within the data.
Data type Size Range Constant Entry Examples
Bool (Boolean) 1 bit 0 to 1 TRUE, FALSE, 0, 1
Byte
(byte)
8 bits
(1 byte)
16#00 to 16#FF 16#12, 16#AB
Word
(word)
16 bits
(2 bytes)
16#0000 to 16#FFFF 16#ABCD, 16#0001
DWord
(double word)
32 bits
(4 bytes)
16#00000000 to 16#FFFFFFFF 16#02468ACE
Char
(character)
8 bits
(1 byte)
16#00 to 16#FF 'A', 't', '@'
SInt
(short integer)
8 bits
(1 byte)
-128 to 127 123, -123
USInt
(unsigned short integer)
8 bits
(1 byte)
0 to 255 123
Int
(integer)
16 bits
(2 bytes)
-32,768 to 32,767 123, -123
UInt
(unsigned integer)
16 bits
(2 bytes)
0 to 65,535 123
DInt
(double integer)
32 bits
(4 bytes)
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 123, -123
UDInt
(unsigned double integer)
32 bits
(4 bytes)
0 to 4,294,967,295 123
Real
(real or floating point)
32 bits
(4 bytes)
+/-1.18 x 10
-38
to +/-3.40 x 10
38
123.456, -3.4, -1.2E+12,
3.4E-3
LReal
(long real)
64 bits
(8 bytes)
+/-2.23 x 10
-308
to +/-1.79 x 10
308
12345.123456789
-1.2E+40
Time
(time)
32 bits
(4 bytes)
T#-24d_20h_31m_23s_648ms to
T#24d_20h_31m_23s_647ms
Stored as: -2,147,483,648 ms
to +2,147,483,647 ms
T#5m_30s
5#-2d
T#1d_2h_15m_30x_45ms
String
(character string)
Variable 0 to 254 byte-size characters 'ABC'
DTL
1
(date and time long)
12 bytes Minimum:
DTL#1970-01-01-00:00:00.0
Maximum:
DTL#2554-12-31-23:59:59.999 999 999
DTL#2008-12-16-
20:30:20.250
1
The DTL data type is a structure of 12 bytes that saves information on date and time in a predefined structure. You can
define a DTL in either the Temp memory of the block or in a DB.

 Loading...
Loading...


















