C
HAPTER
7
| Wireless Configuration
WLAN Security
– 70 –
◆ WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK_WPA2-PSK — See “WPA Pre-
Shared Key” on page 71
◆ WPA, WPA2, WPA1_WPA2 — See “WPA Enterprise Mode” on
page 72
◆ 802.1X — See “IEEE 802.1X and RADIUS” on page 74
WIRED EQUIVALENT
PRIVACY (WEP)
WEP provides a basic level of security, preventing unauthorized access to
the network, and encrypting data transmitted between wireless clients and
an access point. WEP uses static shared keys (fixed-length hexadecimal or
alphanumeric strings) that are manually distributed to all clients that want
to use the network.
When you select to use WEP, be sure to define at least one static WEP key
for user authentication or data encryption. Also, be sure that the WEP
shared keys are the same for each client in the wireless network.
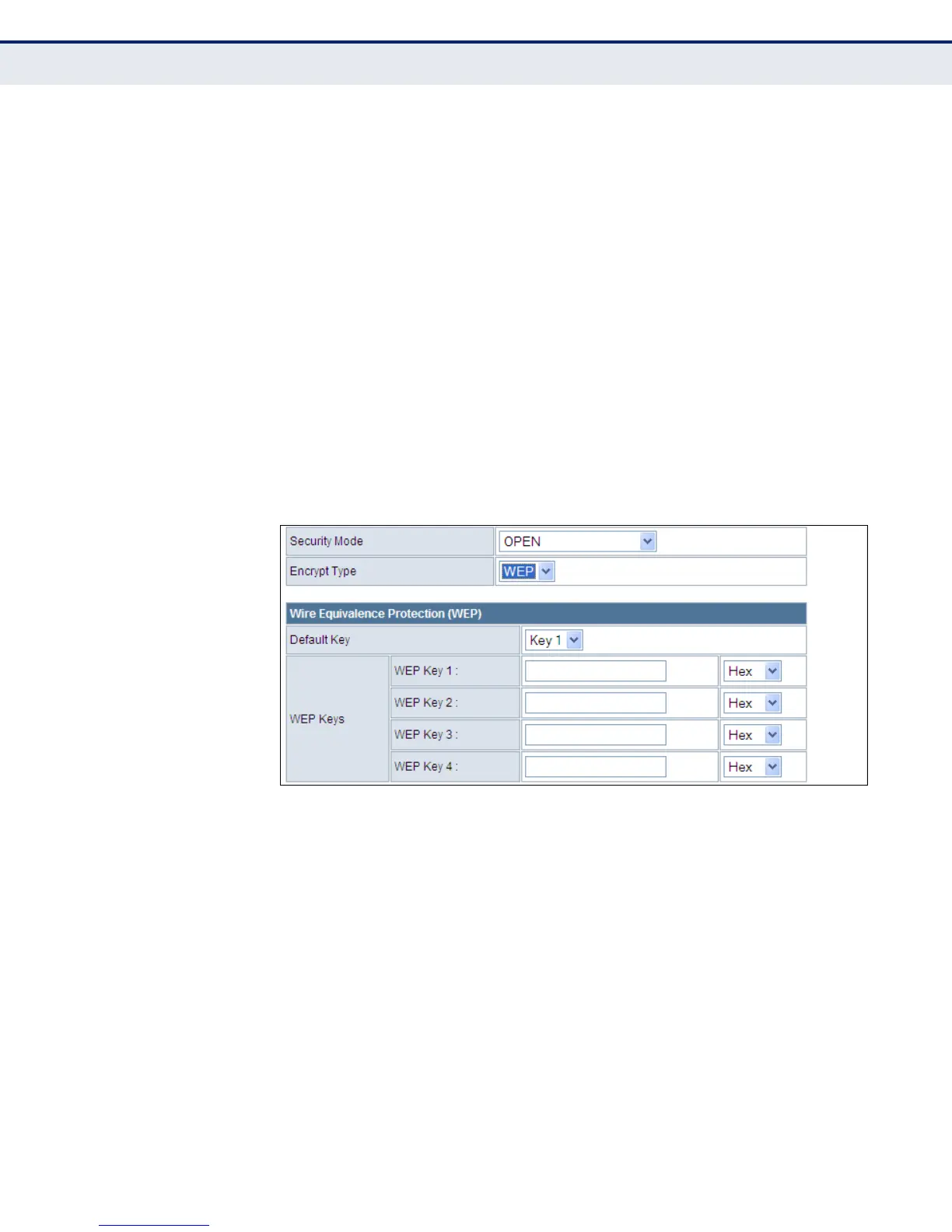
Figure 31: Security Mode - WEP
Security Mode — Configures the WEP security mode used by clients.
When using WEP, be sure to define at least one static WEP key for the
Wireless Broadband Router and all its clients. (Default: Disable)
◆ OPEN — Open-system authentication accepts any client attempting to
connect the Wireless Broadband Router without verifying its identity. In
this mode the default data encryption type is “WEP.”
◆ SHARED — The shared-key security uses a WEP key to authenticate
clients connecting to the network and for data encryption.
◆ WEP-AUTO — Allows wireless clients to connect to the network using
Open-WEP (uses WEP for encryption only) or Shared-WEP (uses WEP
for authentication and encryption).
◆ Encrypt Type — Selects WEP for data encryption (OPEN mode only).

 Loading...
Loading...









