© Technosoft 2007 7 IBL2403 Technical Reference
2.3. Supported Motor-Sensor Configurations
IBL2403 supports the following configurations:
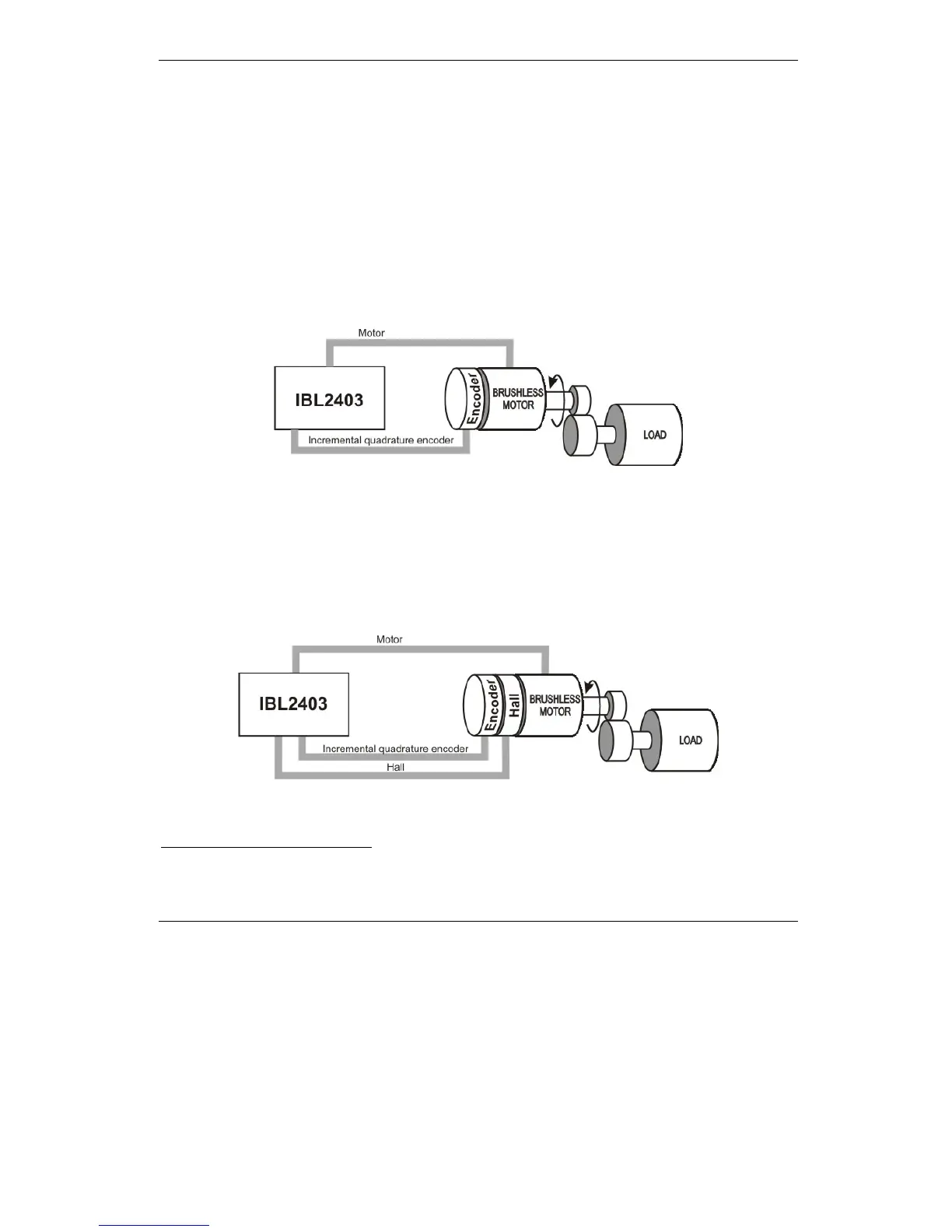
1. Position, speed or torque control of a brushless AC rotary motor with an incremental
quadrature encoder on its shaft. The brushless motor is vector controlled like a
permanent magnet synchronous motor. It works with sinusoidal voltages and currents.
Scaling factors take into account the transmission ratio between motor and load (rotary or
linear). Therefore, the motion commands (for position, speed and acceleration)
expressed in SI units (or derivatives) refer to the load
1
, while the same commands,
expressed in IU units, refer to the motor.
Figure 2.1. Brushless AC rotary motor. Position/speed/torque control. Quadrature encoder on motor.
2. Position, speed or torque control of a brushless DC rotary motor with digital Hall
sensors and an incremental quadrature encoder on its shaft. The brushless motor is
controlled using Hall sensors for commutation. It works with rectangular currents and
trapezoidal BEMF voltages. Scaling factors take into account the transmission ratio
between motor and load (rotary or linear). Therefore, the motion commands (for position,
speed and acceleration) expressed in SI units (or derivatives) refer to the load, while the
same commands, expressed in IU units, refer to the motor.
Figure 2.2. Brushless DC rotary motor. Position/speed/torque control. Hall sensors and quadrature encoder
on motor
1
Motion commands can be referred to the motor by setting in EasySetUp a rotary to rotary transmission with ratio 1:1
 Loading...
Loading...