Command Syntax
2-14
TDS200, TDS1000/2000, TDS1000B/2000B, TPS2000 Programmer
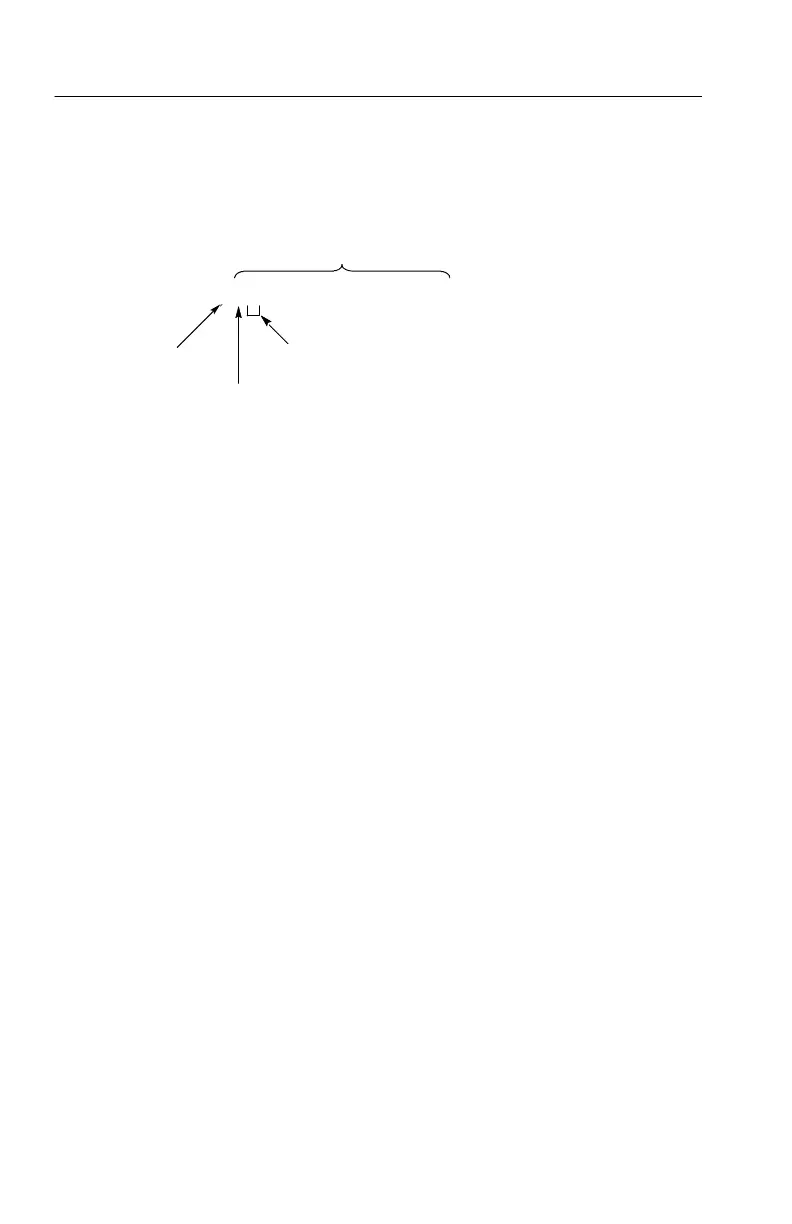
Figure 2--2 shows an example of a block argument.
*DDT #217AC Quire:STATE RUN
Block header
Specifies number of
length digits that follow
Specifies data length
Block argument
Figure 2- 2: Block Argument example
<NZDig> specifies the number of <Dig> elements that follow. Taken
together, the <Dig> elements form a decimal integer that specifies
how many <DChar> elements follow.
#0 means that the <Block> is an indefinite length block. The
<terminator> ends the block. You should not use indefinite length
blocks with RS-232, because there is no way to include a <termina-
tor> character as a <DChar> character.
Thefirstoccurrenceofa<terminator> character signals the end of
the block and any subsequent <DChar> characters will be interpreted
as a syntax error. With the GPIB, the EOI line signals the last byte.
With the USB, the EOM bit signals the last byte.

 Loading...
Loading...