6.2 Binary Information
Binary messages are strictly machine readable format and are ideal choice for
application of large amount data transmission. Since the inherent compression format,
binary message has much smaller data amount compared to ASCII, so the
communication ports of the receiver are able to transmit or receive more data. Binary
format is difined as below.
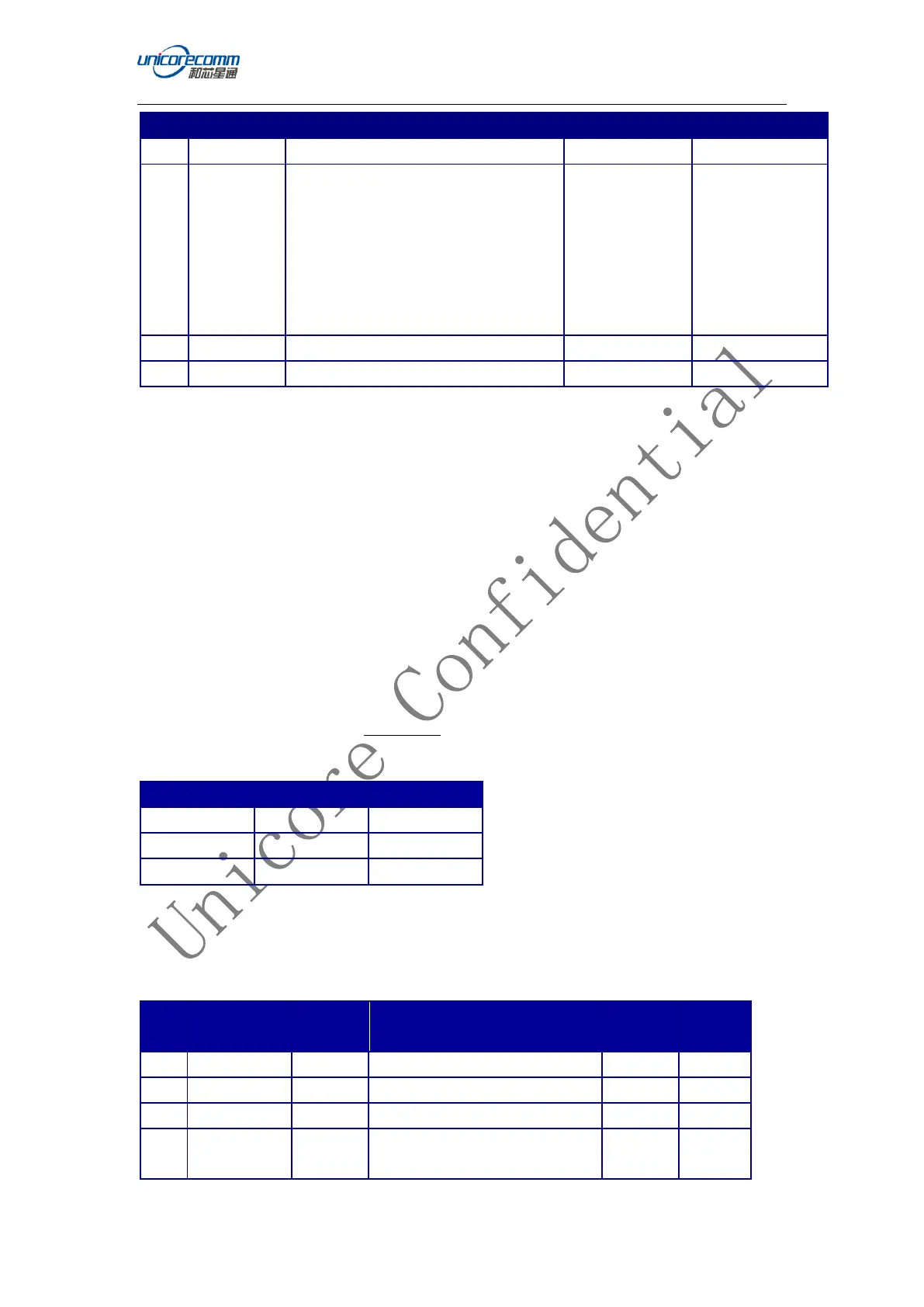
Basic Format:
Header 3 Sync bytes plus 24 bytes of header information. The header length is
variable as fields may be appended in the future. Always check the header length.
Data variable
CRC 4 bytes
The 3 Sync bytes fixed as
Table 6-14:
Table 6-14: The 3 Sync Bytes Values
This CRC applies to all data, including 32-bit CRC of the header.
Binary and ASCII header format for reference as follows:
Table 6-15: Binary Message Header Structure
 Loading...
Loading...