4.11 Primary, secondary and per unit
scaling
4 Measurement functions Technical description
148
VAMP 24h support phone +358 (0)20 753 3264 VM50.EN004
Example 7: Secondary to per unit for residual current.
Input is I
0Calc
.
CT = 750/5
Currents injected to the relay's I
L1
input is 0.5 A.
I
L2
= I
L3
= 0.
Per unit current is
I
PU
= 0.5/5 = 0.1 pu = 10 %
Example 8: Per unit to secondary for residual current.
Input is I
0Calc
.
CT = 750/5
The relay setting is 0.1 pu = 10 %.
If I
L2
= I
L3
= 0, then secondary current to I
L1
is
I
SEC
= 0.1x5 = 0.5 A
4.11.2. Voltage scaling
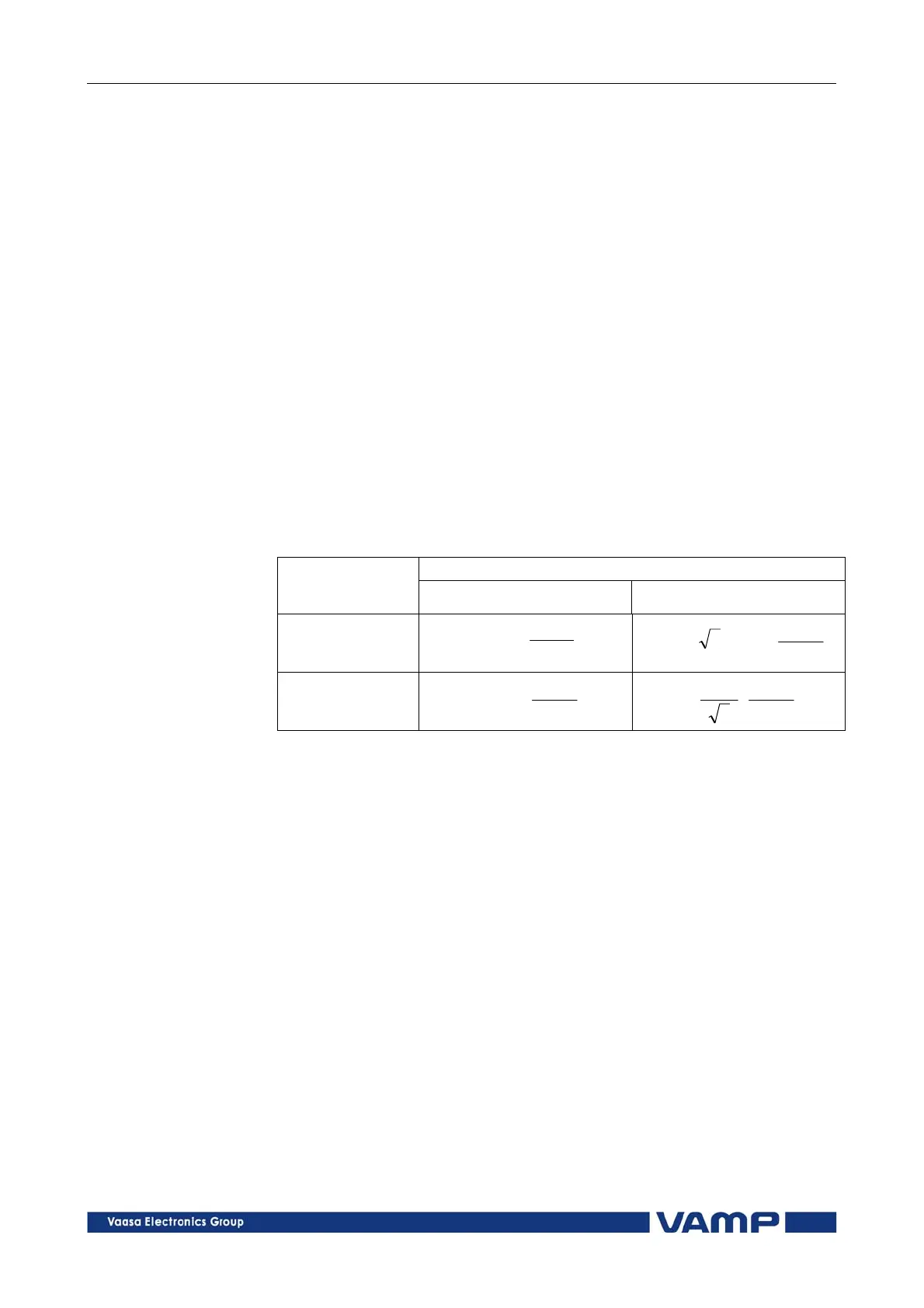
Primary/secondary scaling of line-to-line voltages
Line-to-line voltage scaling
Voltage measurement mode =
"1LL"
Voltage measurement mode =
"1LN"
secondary primary
SEC
PRI
SECPRI
VT
VT
UU
SEC
PRI
SECPRI
VT
VT
UU
3
primary secondary
PRI
SEC
PRISEC
VT
VT
UU
PRI
SEC
PRI
SEC
VT
VT
U
U
3
Example 1: Secondary to primary. Voltage measurement mode
is "1LL".
VT = 12000/110
Voltage connected to the relay's input is 100 V.
Primary voltage is U
PRI
= 100x12000/110 = 10909 V
Example 2: Secondary to primary. Voltage measurement mode
is "1LN".
VT = 12000/110
The voltage connected to the relay's input is 57.7 V.
Primary voltage is U
PRI
= 3x58x12000/110 = 10902 V
Example 3: Primary to secondary. Voltage measurement mode
is "1LL".
VT = 12000/110
The relay displays U
PRI
= 10910 V.
Secondary voltage is U
SEC
= 10910x110/12000 = 100 V
 Loading...
Loading...