Technical data
73
Cyclic loads
If the load cycle is shorter than 10 seconds, the thermal time constant of the heatsink can be ignored,
and the following simple procedure can be applied to find out whether the drive can handle the cycle.
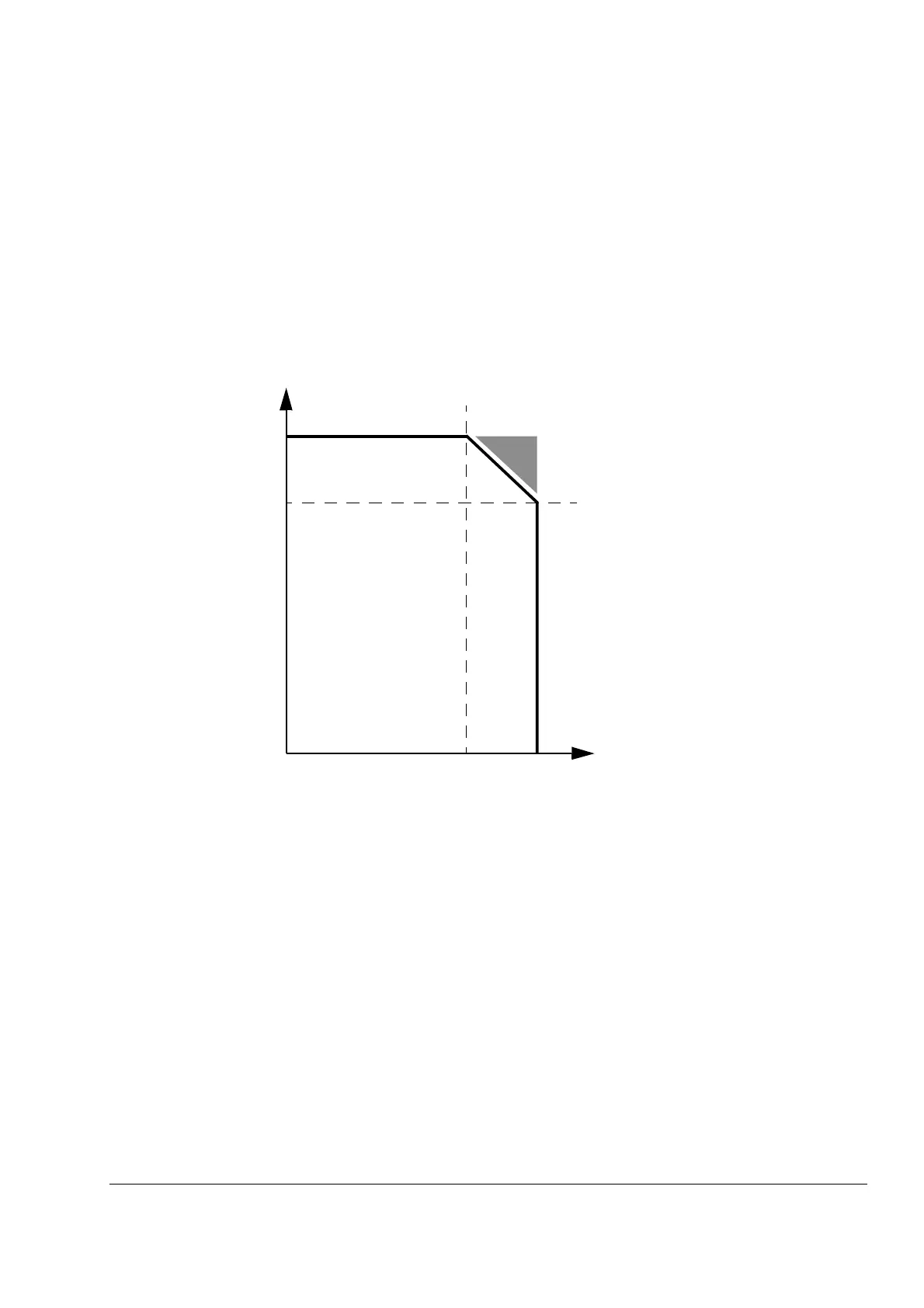
1. Determine the rms value (I
2rms
) of the output current over the whole load cycle.
2. Determine the maximum instantaneous rms value (I
2peak
) of the output current during the load cycle.
3. Determine the point (I
2rms
, I
2peak
) on the graph below.
If the point falls within the region bordered by a solid line, the load cycle is safe. For I
2contxk
and I
2max
,
use the ratings stated for the drive type and switching frequency used.
If the point falls within the shaded area, a more detailed study is required.
The above procedure can also be applied to longer load cycles by dividing the cycle into subcycles no
longer than 10 seconds. If any of the subcycles fail the test, a more detailed study is required.
The DriveSize dimensioning tool available from ABB is recommended for more detailed dimensioning.
I
2rms
I
2peak
I
2contxk
0.75×I
2contxk
I
2max
I
2contxk

 Loading...
Loading...