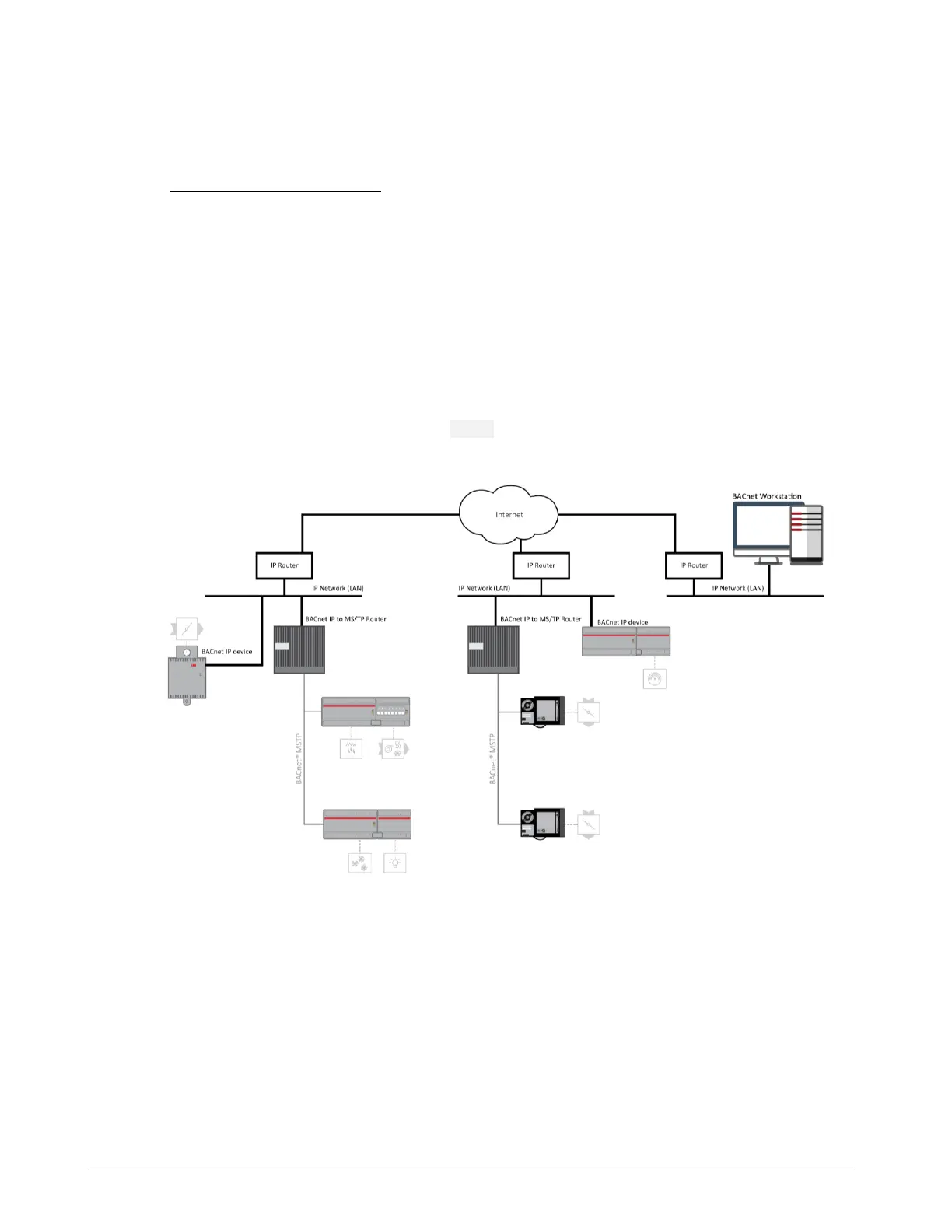
BACNET IP
BACnet/IP uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to send data packets. ASHRAE adopted BACnet/IP
in annex j of the 135- 1995 standard.
BACnet/IP communicates using four methods.
• BACnet/IP to BACnet/IP (same subnet): Assuming that two devices know each other's IP addresses
and the UDP ports they are using, i.e., their respective B/IP addresses, there is nothing that restricts
them from communicating directly.
• BACnet/IP to BACnet/IP (different subnet): The location of the two devices is already known by the
host and the message is routed to the device using switches and routers.
• Broadcast (same subnet): This is a standard Who is/ I am message sent across a local subnet for the
BBMD to discover what the address are for the BACnet devices on the subnet.
• Broadcast (different subnet): This is a standard Who is/ I am message sent across a local subnet for
the BBMD to discover what the address are for the BACnet devices on other subnets.
BACNET IP BROADCAST MANAGEMENT DEVICE (BBMD)
Some BACnet services use “broadcasts” (e.g. “Who-Is”). On a LAN with standard routers, these broadcasts are
“blocked”. Thus, BACnet broadcasts are limited to the IP Subnet of the BACnet device. With a BACnet/IP
network of 2 or more IP subnets, a device with BBMD can be used.
A BBMD located on an IP subnet monitors the origin of a broadcast message on that subnet and, in turn,
constructs a “peer to peer”
message
in order to pass through an IP router. This “peer to peer” message is
received by other BBMDs on other IP subnets and transmitted as a broadcast on their attached subnets.
Since the BBMD messages are directed messages, individual messages must be sent to each BBMD. Each
BBMD device maintains a
Broadcast Distribution Table (BDT)
, the content of which is usually the same for all
BBMDs within the network. BBMDs must know the IP address of all other BBMDs in the network.
It is possible to communicate to a device on a subnet that does not have a BBMD as in the BACnet
Workstation example above. This type of device is called a foreign device since it resides on a different IP
subnet from devices attempting to communicate with it.
Usually, in BACnet/IP, a foreign device is on a different subnet.
The foreign device (e.g. BOWS) registers with each BBMD, after which it can communicate with all other
devices on the network. The BBMD then maintain a Foreign Device Table (FDT)
which keeps track of foreign
devices.

 Loading...
Loading...