MC96F6432
248 June 22, 2018 Ver. 2.9
11.13.16 USI1 I2C Start / Repeated Start / Stop
One master can issue a START (S) condition to notice other devices connected to the SCL1, SDA1 lines that it
will use the bus. A STOP (P) condition is generated by the master to release the bus lines so that other devices
can use it.
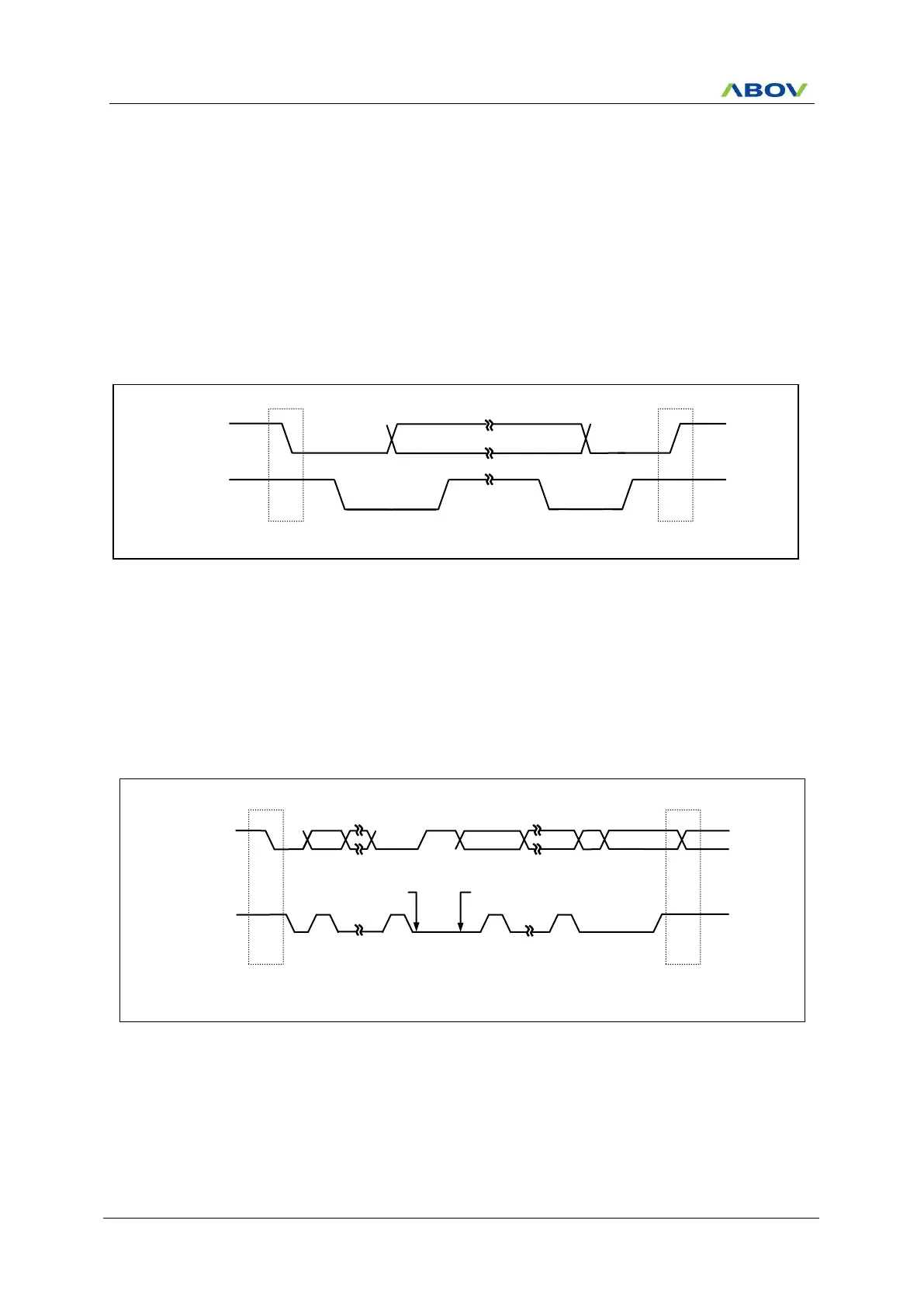
A high to low transition on the SDA1 line while SCL1 is high defines a START (S) condition.
A low to high transition on the SDA1 line while SCL1 is high defines a STOP (P) condition.
START and STOP conditions are always generated by the master. The bus is considered to be busy after
START condition. The bus is considered to be free again after STOP condition, ie, the bus is busy between
START and STOP condition. If a repeated START condition (Sr) is generated instead of STOP condition, the bus
stays busy. So, the START and repeated START conditions are functionally identical.
Figure 11.89 START and STOP Condition (USI1)
11.13.17 USI1 I2C Data Transfer
Every byte put on the SDA1 line must be 8-bits long. The number of bytes that can be transmitted per transfer
is unlimited. Each byte has to be followed by an acknowledge bit. Data is transferred with the most significant bit
(MSB) first. If a slave can’t receive or transmit another complete byte of data until it has performed some other
function, it can hold the clock line SCL1 LOW to force the master into a wait state. Data transfer then continues
when the slave is ready for another byte of data and releases clock line SCL1.
Figure 11.90 Data Transfer on the I2C-Bus (USI1)
START or Repeated
START Condition
STOP or Repeated
START Condition
Acknowledgement
Signal form Slave
Acknowledgement
Signal form Slave
Byte Complete,
Interrupt within Device
Clock line held low while
interrupts are served.
 Loading...
Loading...