103
Chapter 3 Features and Functions
Arbitrary Waveforms
3
Arbitrary Waveforms
There are five built-in arbitrary waveforms stored in non-volatile memory
.
You can also store up to four user-defined waveforms in non-volatile
memory in addition to one in volatile memory. Each waveform can
contain between 1 (a dc voltage) and 65,536 (64K) data points.
Refer to chapter 7, “Tutorial”, for more information on the internal
operation of downloading and outputting an arbitrary waveform.
To Create and Store an Arbitrary Waveform
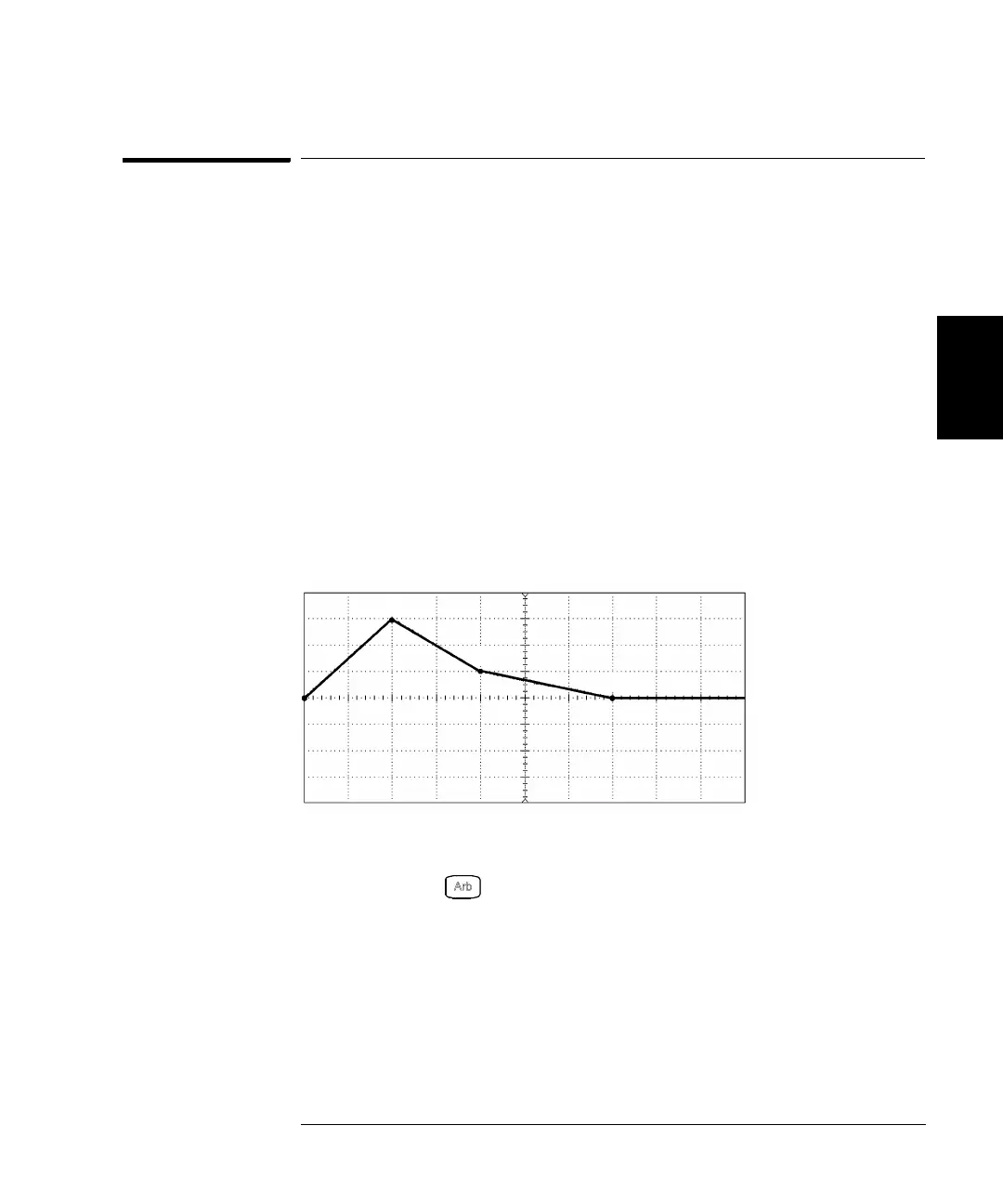
This section gives an example which shows you how to create and store
an arbitrary waveform from the front panel. To download an arbitrary
waveform from the remote interface, see “Arbitrary Waveform Commands”
starting on page 198. For this example, you will create and store the
ramp waveform shown below using four waveform points.
1 Select the arbitrary waveform function.
When you press to select the arbitrary function, a temporary
message is displayed indicating which waveform is currently selected.
2 Start the arbitrary waveform editor.
Press the Create New softkey to start the waveform editor. While in the
waveform editor, you define the waveform by specifying time and voltage
values for each point in the waveform. When creating a new waveform,
the previous waveform in volatile memory is overwritten.
Volt/Div = 1 Volt
Time/Div = 1 ms
2
3
4
1
1
 Loading...
Loading...