Overview
Fundamentally, the SpO
2
algorithm measured the differences between the PPG waveforms captured by
the Red and IR LEDs to estimate the blood oxygenation levels. The algorithm is based on PPG data so
the following factors can negatively impact the SpO
2
estimation:
Motion artifacts: Motion and movement severely impact PPG quality and the ability of the
algorithm to calculate the SpO2. The SpO
2
algorithm is intended to be used at rest condition only.
Measurement obstacles: Hair, sweat, imperfect contact, skin variations, excessive or non-periodic
motion, etc., all negatively impact SpO2 performance.
PPG settings: Improper LED/PD settings resulting in a low-quality PPG signal with negatively
impacted performance.
Additionally, similar general guidelines can be followed for the measurements:
General Guidelines:
The SpO2 algorithm needs Red and IR input PPG data. The algorithm is built upon the
characteristics of these wavelengths and how they interact with the skin.
LED driver current should be increased as much as the power consumption requirements of the
application allow to get the highest amplitude signals. Typically, a DC or average level of 400k ADC
counts should be the target for the IR and Red PPG signals needed for SpO2 measurements.
Sample rate should be increased as much as power consumption requirements allow so that
better sample averaging can take place, smoothing noise artifacts while increasing algorithm
responsiveness.
Motion and movements should be limited; remain as still as possible during the measurement
period.
Starting and Stopping a Measurement
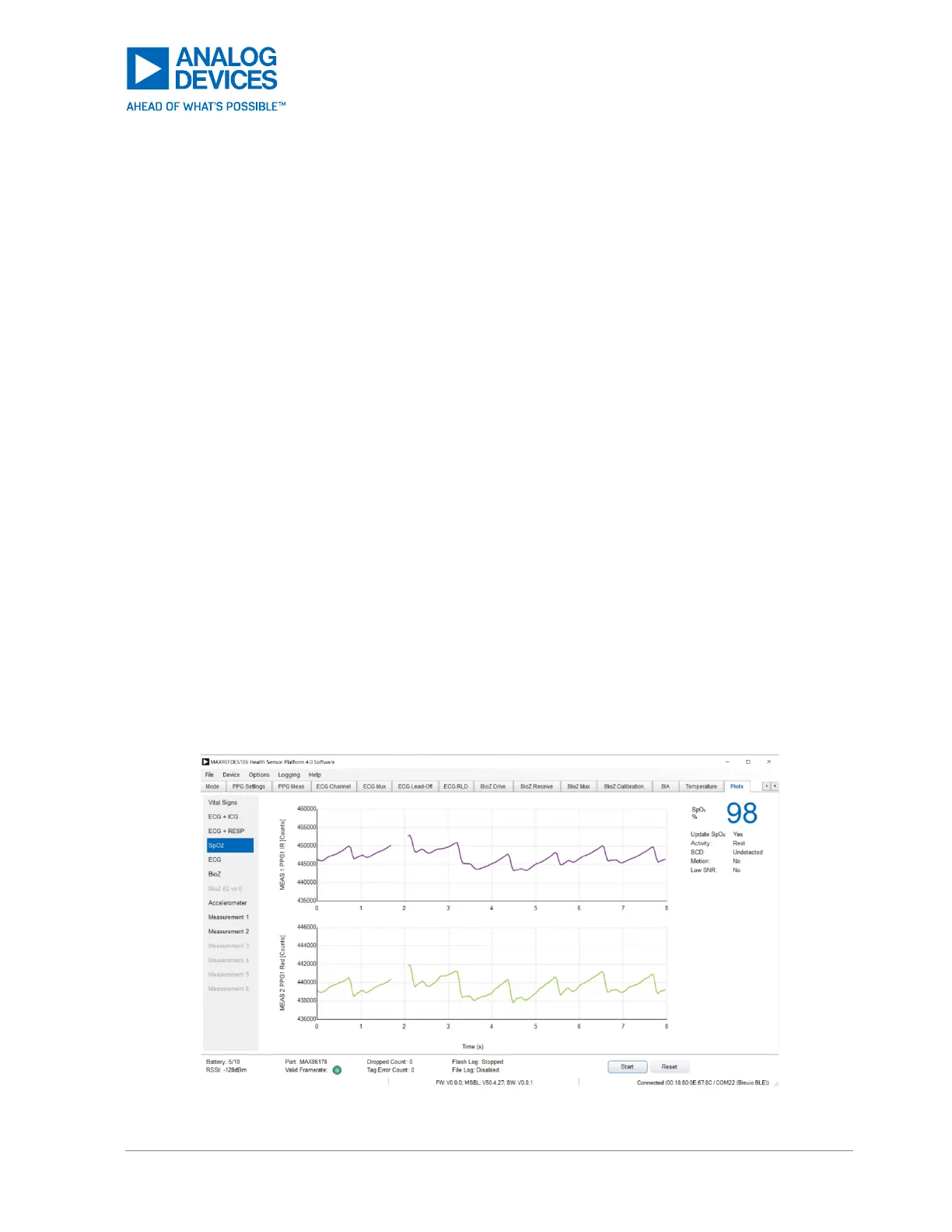
Figure 47. Example SpO
2
Algorithm Output
 Loading...
Loading...