ADR141A /
Ref ID : ADR241A/IM/PLF
Rev No. : 02
Trip Circuit Supervision (TCS)
The trip circuit supervision is use to monitor healthiness of circuit breaker. The trip circuit
extends beyond the relay enclosure and passes through more components, such as fuse,
wires, relay contacts, auxiliary switch contact and so on. The failure of any one of component
result bypassing the protection. The relay is provide with special trip circuit supervision
function which continuously monitor continuity of trip circuit and generate ALARM to take
appropriate action.
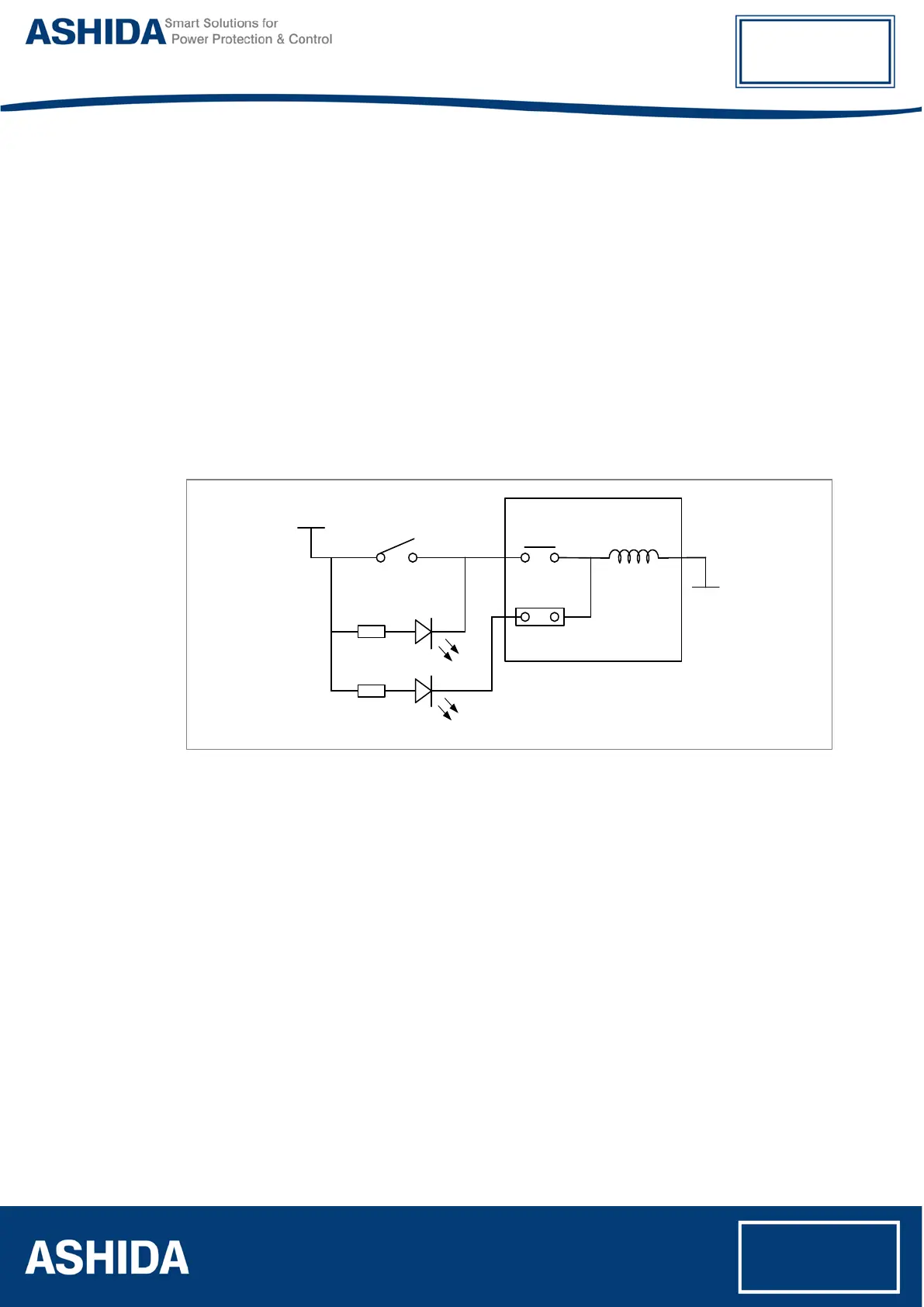
The figure 1 represents the logic implementation of Trip Circuit Supervision , It monitors the
continuity of trip circuit through either normally open (CB NO) or normally close (CB NC)
contact of CB connected to dedicated Opto isolator digital inputs CBNO (S4) and CBNC
(S3). If any discontinuity is observed, then the L1 red LED (ERROR) will glow.
Trip Output Relay
+Ve
-Ve
Circuit Breaker
CBNO
CBNC
R1
R2
S4
S3
Figure 1: Logic Diagram for Trip Circuit Supervision
When the CB is closed, supervision current passes through the Opto-input, into the trip coil
via CBNO. When the CB is open, supervision current flows through the Opto-input and into
the trip coil via the CBNC auxiliary contact. This means that TCS (Trip Coil healthy) signal is
high when the CBNO or CBNC signal is available. Otherwise IED Generates TCS Fail signal
which is used to block the protection function.
Breaker Failure Setting (50BF)
If the Circuit Breaker fails to operate within the settable time following the protection trip then
relay generates a circuit breaker failure trip signal. Following the inception of a fault one or
more main protection functions will operate. Operation of the circuit breaker is essential to
isolate the fault, and prevent damage or further damage to the power system.
For transmission and sub-transmission systems, slow fault clearance can also threaten
system stability. It is therefore common practice to install circuit breaker failure protection
[50BF], which monitors that the circuit breaker has opened within a reasonable time. If the
 Loading...
Loading...