345
7679H–CAN–08/08
AT90CAN32/64/128
25.6.5 Programming the EEPROM
The EEPROM is organized in pages, see Table 25-12 on page 341. When programming the
EEPROM, the program data is latched into a page buffer. This allows one page of data to be
programmed simultaneously. The programming algorithm for the EEPROM data memory is as
follows (refer to “Programming the Flash” on page 342 for details on Command, Address and
Data loading):
1. A: Load Command “0001 0001”.
2. G: Load Address High Byte (0x00 - 0xFF).
3. B: Load Address Low Byte (0x00 - 0xFF).
4. C: Load Data (0x00 - 0xFF).
5. E: Latch data (give PAGEL a positive pulse).
K: Repeat 3 through 5 until the entire buffer is filled.
L: Program EEPROM page
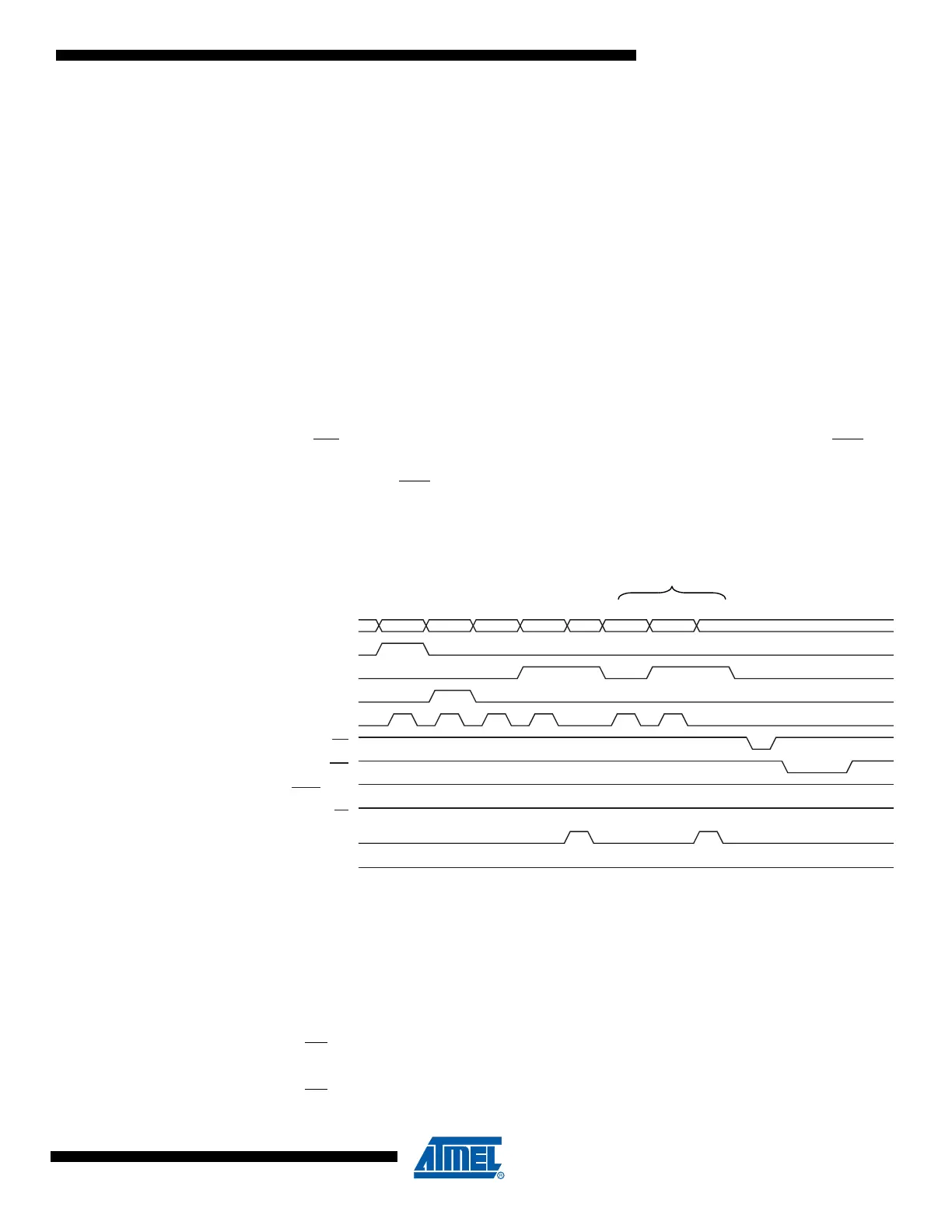
1. Set BS1 to “0”.
2. Give WR
a negative pulse. This starts programming of the EEPROM page. RDY/BSY
goes low.
3. Wait until to RDY/BSY
goes high before programming the next page (See Figure 25-4
for signal waveforms).
Figure 25-4. Programming the EEPROM Waveforms
25.6.6 Reading the Flash
The algorithm for reading the Flash memory is as follows (refer to “Programming the Flash” on
page 342 for details on Command and Address loading):
1. A: Load Command “0000 0010”.
2. G: Load Address High Byte (0x00 - 0xFF).
3. B: Load Address Low Byte (0x00 - 0xFF).
4. Set OE
to “0”, and BS1 to “0”. The Flash word low byte can now be read at DATA.
5. Set BS1 to “1”. The Flash word high byte can now be read at DATA.
6. Set OE
to “1”.
0x11 ADDR. HIGH ADDR. LOW DATA ADDR. LOW DATA XX
XX
AGBCEBC EL
K
RDY/BSY
WR
OE
RESET +12V
PAGEL
BS2
DATA
XA1
XA0
BS1
XTAL1

 Loading...
Loading...