Instruction Manual
99
2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
2.1 OPERATING PRINCIPLE
M10 has been designed with the aim of fulfillment of all the requirements of modern water management
systems, through a flexible and hybrid electronics which, depending on the model, oers various power
supply solutions.
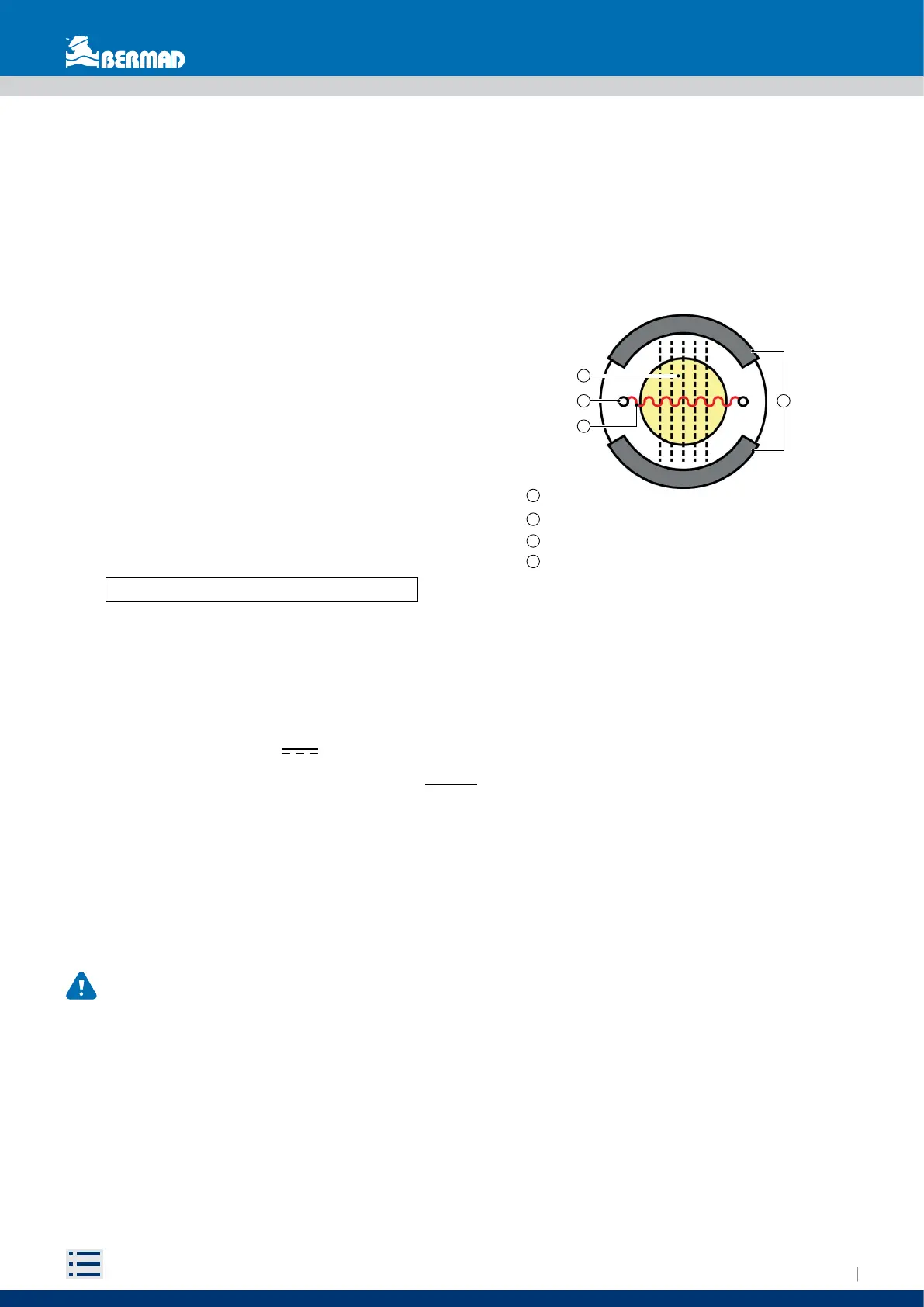
An electromotive force is induced at the ends of a
conducting fluid that moves with velocity v in a magnetic
induction field B and can be expressed as:
e = kBDv
Where it is:
B is constant by construction;
D is constant and represents the distance between
the electrodes E1 and E2 (equivalent to the diameter
of the flowmeter);
v is the fluid velocity;
k is the calibration constant;
emf «e» is proportional to the velocity «v»
2.2 POWER SUPPLY
The M10 meter is available with three dierent power supply setup:
Battery-powered via a lithium battery (LiSOCL2)
Mains powered 12Vdc
Mains powered 12Vdc with backup lithium battery
It the case of lithium battery power supply is used; it is necessary to consider the following cautions:
Lithium batteries are the primary energy source because of their high-energy density, and are made to
meet the highest safety standards. However, they can be potentially hazardous if they are exposed to
electrical or mechanical abuse. In many cases, this is associated with excessive heat production in which
the increased internal pressure could lead to cell rupture.
These basic precautions need to be followed when handling and using lithium batteries:
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS!
Do not short-circuit, recharge, overload or reverse-connect the battery
Do not expose the battery to temperatures higher than those specified, as it will incinerate
Do not crush, puncture or open the cells or disassemble the battery packs
Do not weld or solder the battery body or battery packs
Do not expose the contents to water
The use of lithium batteries is regulated under the United Nations Model Regulations on the Transport of
Dangerous Goods (UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods), document ST/SG/ AC.10/1/
Rev.22.
1
- Electromotive force (proportional to the velocity);
2
- Electrodes;
- Magnetic field;
3
4
- Coils;
1
2 4
3

 Loading...
Loading...