Setting Up the XP3000 for Your Application 4-2
carryover
Contamination of a volume of fluid by residual fluid from a previous aspiration or
dispense. Carryover causes variability in final volume and concentration.
cavitation
Formation of air bubbles due to rapid pressure changes.
dilution effect
Reduction in sample or reagent concentration, caused by contact with system fluid or
residual fluid from a previous aspiration or dispense.
I.D. (“inner diameter”)
Diameter of the constraining wall of a fluid path.
priming
Completely filling the pump tubing and syringe with bubble-free fluid to allow
sustained, reproducible pumping action. The air in an unprimed line acts as a spring,
adversely affecting accuracy and precision.
reagent tubing
Connects the valve input port (1/4-28 thread or M6 fitting) to a reagent source.
Reagent tubing is used to fill the pump syringe; it tends to have a larger I.D. than
aspirate/dispense tubing, and a blunt-cut end which extends into the reagent.
system fluid
A fluid used to prime the pump system that does not act as sample or reagent.
Typically the system fluid is deionized water or a wash buffer and is isolated from
sample or reagent fluid by an air gap to avoid intermixing.
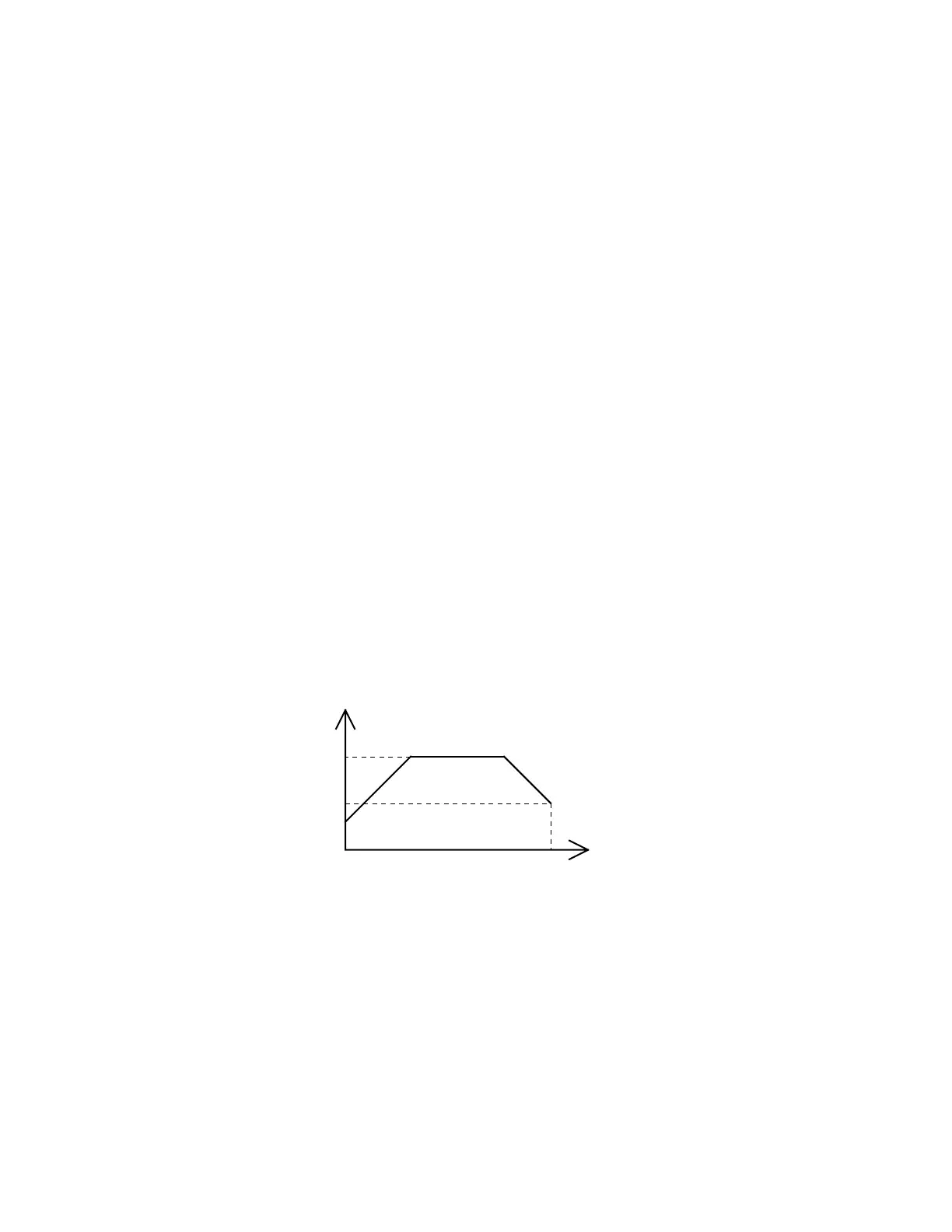
Typically, the syringe plunger begins moving slowly, then ramps up to top velocity.
This allows the plunger to start moving gradually, without overloading the motor,
and still provide maximum flowrate. The syringe plunger stops by ramping down in
speed. This results in the most reproducible fluid breakoff for accurate dispensing.
v
V
Speed [Hz]
c
time in st
Figure 4-1. Syringe Speed
start velocity (v)
The speed at which the syringe plunger starts moving.
top velocity (V)
The maximum speed at which the syringe plunger moves.
cutoff velocity (c)
The speed of the syringe plunger just before stopping.
 Loading...
Loading...