The rheobase, which is the minimum intensity that must be achieved in order to produce stimulation even
if the pulse duration is very long, actually corresponds to the coecient 𝑖 of the Weiss formula which has
dimensions of electrical intensity.
Lapicque gave the name chronaxy to the minimum length of time in which a current with double the
intensity of the rheobase must be applied in order achieve stimulation. In fact, he realised that the
chronaxy is a time constant which characterises the excitability of tissue and that its value is the ratio /𝑖.
Lapicque’s development also shows that, even when the length of time that the current is applied is
infinite, (𝑡 = ∞), the current must have a minimum intensity known as the rheobase (𝑅h) in order to
produce stimulation.
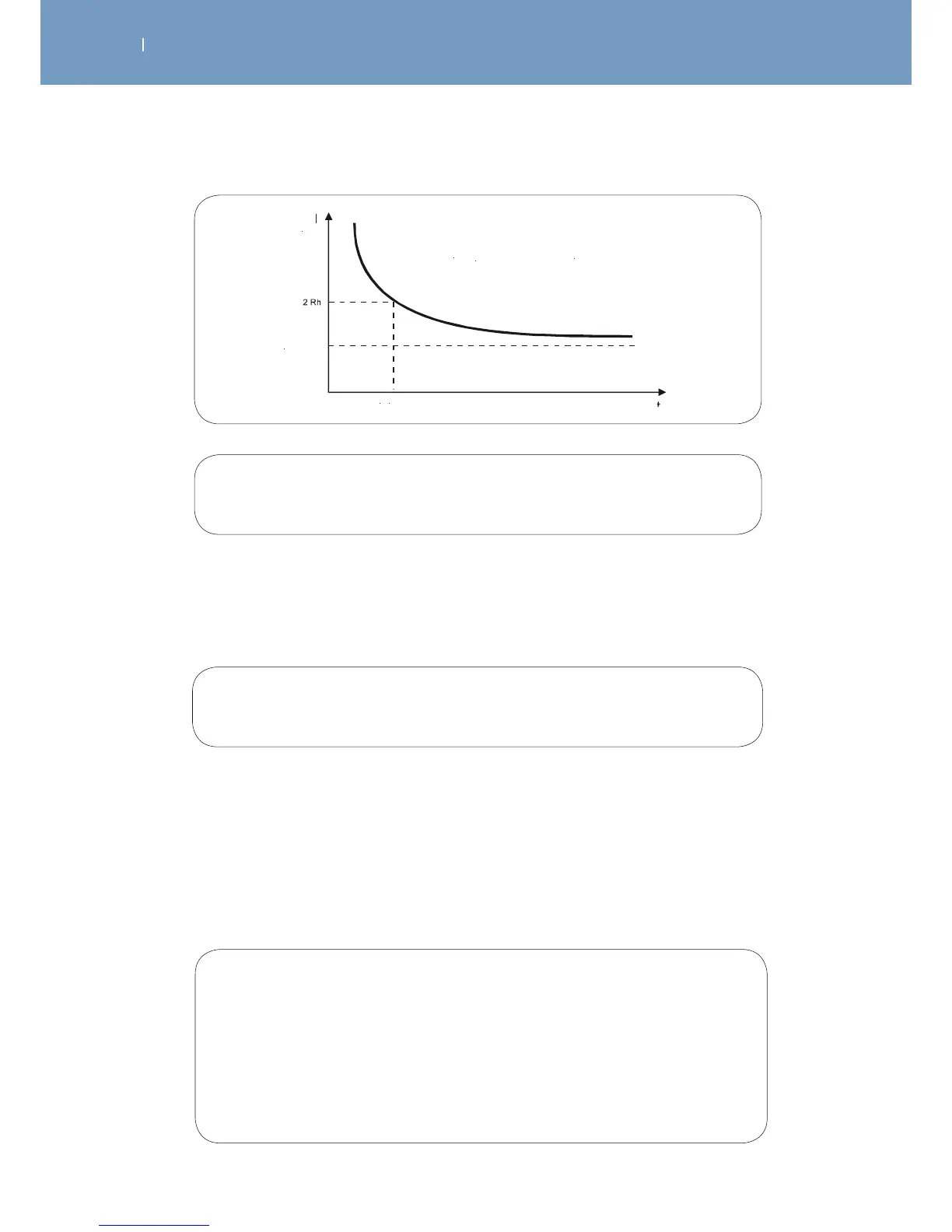
Hyperbolic relationship between the current intensity and pulse duration
demonstrated by Lapicque and given by the formula 𝐼 /𝑡 + 𝑖 , derived from Weiss’
fundamental formula.
if 𝑡 = ∞ therefore /𝑡 = 0
in this case 𝐼 is the rheobase (𝑅ℎ)
and 𝑅ℎ = 𝑖
Intensity-duration curve
Chronaxy
Rheobase
Fig. 3
This means that:
since 𝑅ℎ = 𝑖 when 𝐼 =
2
𝑅ℎ
therefore 𝐼 =
2
𝑖
and 𝑡 is the chronaxy (𝑡 𝑐ℎ)
when 𝐼 =
2
𝑅ℎ
therefore from the equation 𝐼/𝑡+𝑖
the result is 2𝑖 /𝑡𝑐ℎ + 𝑖
therefore 𝑖 /𝑡𝑐ℎ → 𝑡𝑐ℎ = /𝑖
 Loading...
Loading...