12.2.2.4 Duration of rectangular electrical pulse
First of all, it must be specified that this is in a specific pulse duration phase. Weiss’ law is used for
stimulation pulse durations close to the excitation constants 𝑘.
In the case of motor neurons, this means a time period ranging from 100 to 3,000 microseconds.
k Chronaxy / In
2
Chronaxy / 0,693
The third electrical factor, which should be minimised in order to produce the most comfortable possible
stimulation, is electrical energy 𝑊.
We know that electrical energy is given by the formula 𝑊 = 𝐼2 . 𝑡 . 𝑅, where:
𝐼 : is the current intensity
𝑡 : its pulse duration
𝑅 : the skin resistance
The Weiss or Lapicque relationship states
𝐼/𝑡+𝑖
and we can replace I by its value in the energy equation.
We get 𝑊 (/𝑡 + 𝑖 𝑡.𝑅.
by developing: 𝑊(
2
/𝑡
2
+ 2 𝑖 /𝑡 + 𝑖
2
𝑡.𝑅. (
2
/𝑡+ 2 𝑖 + 𝑖
2
𝑡 𝑅.
When 𝑡 → 0, 𝑊 → ∞
When 𝑡 → ∞, 𝑊 → ∞
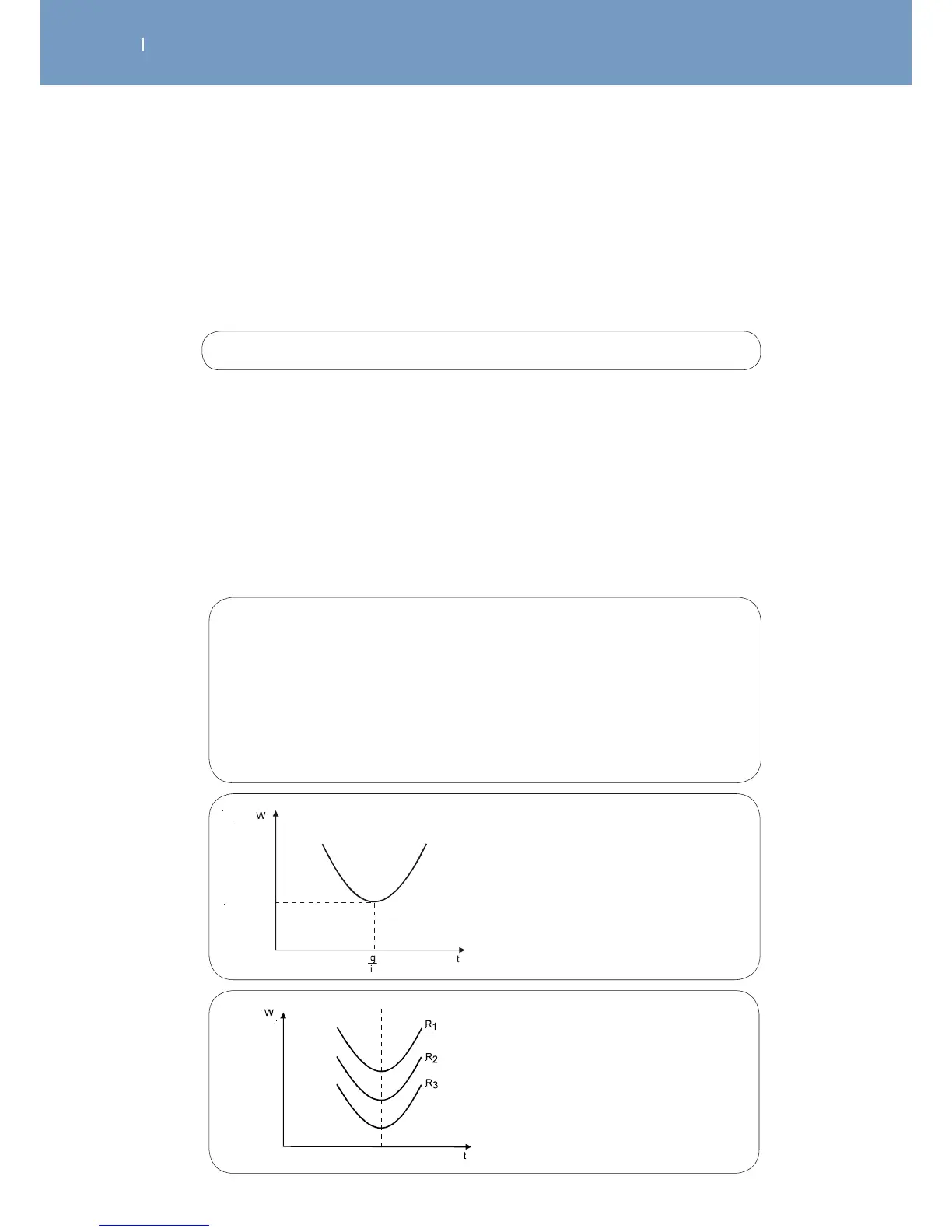
The shape of this curve is given in Figure 4.
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Relationship between energy and
the pulse duration
 Loading...
Loading...