Model 55,75,90, & HMC FLEX-AUGER Installation
15
MA1702D
Supporting the System Inside the Building
Support the Auger Tubing with chain and "S" Hooks every 5 feet [1.5m]. Steel Tube systems require support every
10 feet [3m]. The system should be restrained from swinging by using chain and "S" hooks to brace the auger tube,
every 20 feet [6m], as shown in Figure 7.
Horizontal elbows need to be supported in at least two places. Chain, screw hooks, and "S" hooks are supplied as
a suspension kit for supporting the equipment. Keep the line as level and straight as possible.
If Drop Feeders, Extension Hoppers, Outlet Drops with long angled Drop Tubes, or other loads are imposed on
the system, extra support will be required.
Power Units require extra support to resist the twisting encountered when the motor starts and stops. Use the motor
mount base, all of the "ears" on the gearhead as well as the suspension point provided on the 46800 Control Unit
Box to support the Power Unit.
Adequate chain and "S" hooks are provided with each system to properly support it. Other means of supporting
the system are permissible as long as the system receives the correct support and the auger tube is not dented or
flattened. Alternative support systems must allow for expansion and contraction of the Auger Tubes.
When the auger tube passes through a side wall or partition, especially where it enters the building, the opening
should be made large enough so the auger tube can be supported without resting on the wall. If the auger tube rests
on the wall or partition, the auger tube may flatten out or become kinked--causing excessive wear. (See Figure 8).
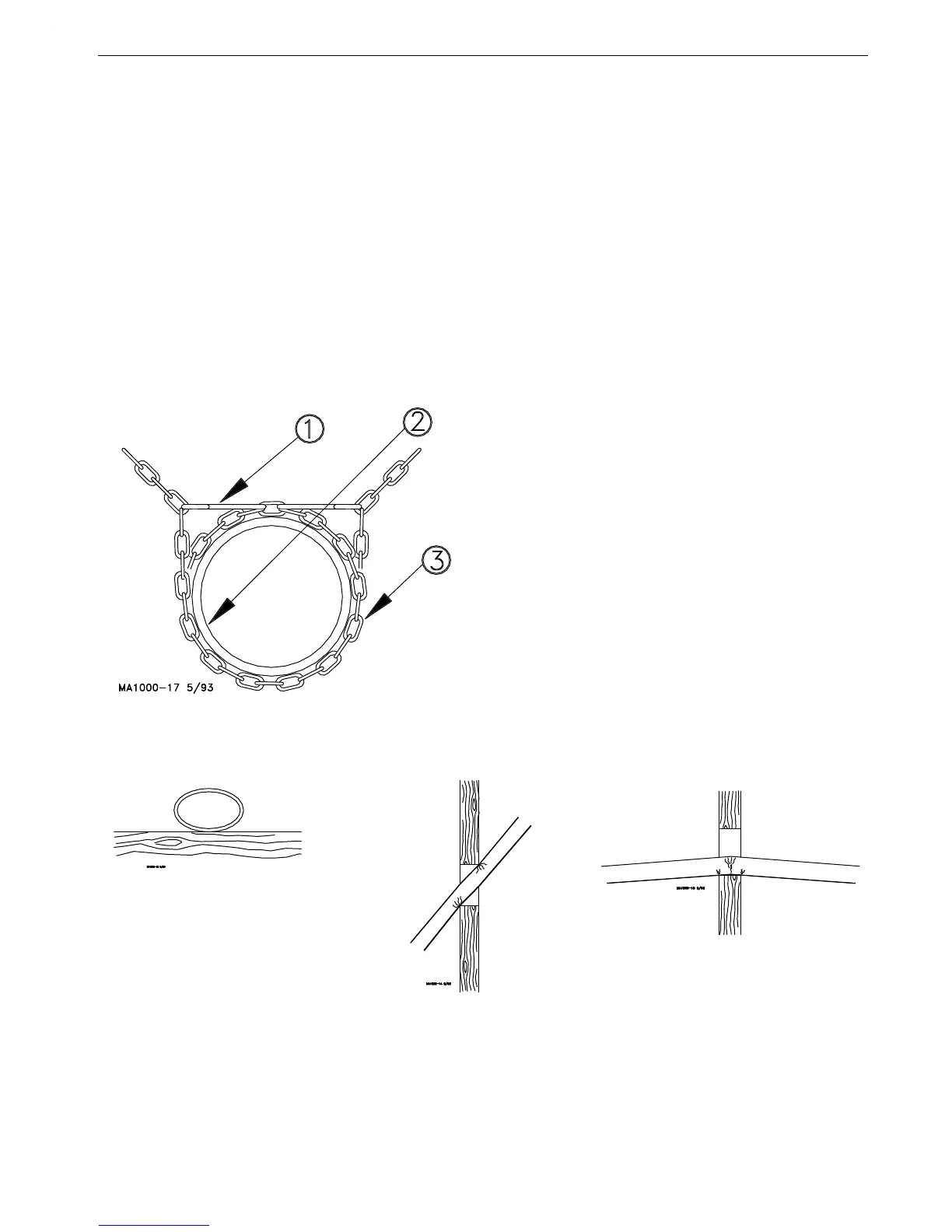
Key Description
1 “S” Hook
2 Auger Tube
3 Chain
Figure 7.Proper Auger Tube Connection
Auger tube flattened
because the supports are
not high enough to keep
the weight of the auger
tube off the wall.
Auger tube pinched because
the Auger Tube is not in line
with the hole in the Wall.
Auger tube flattened because the
supports are not high enough to
keep the weight of the auger tube
off the wall.
Figure 8.Faulty Tube Installations
 Loading...
Loading...