17-13
Catalyst 3750 Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-16180-02
Chapter 17 Configuring STP
Configuring Spanning-Tree Features
• Configuring a Secondary Root Switch, page 17-17 (optional)
• Configuring Port Priority, page 17-18 (optional)
• Configuring Path Cost, page 17-20 (optional)
• Configuring the Switch Priority of a VLAN, page 17-21 (optional)
• Configuring Spanning-Tree Timers, page 17-22 (optional)
Default Spanning-Tree Configuration
Table 17-3 shows the default spanning-tree configuration.
Spanning-Tree Configuration Guidelines
Each stack member runs its own spanning tree, and the entire stack appears as a single switch to the rest
of the network.
If more VLANs are defined in the VTP than there are spanning-tree instances, you can enable PVST+
or rapid PVST+ on only 128 VLANs on each switch stack. The remaining VLANs operate with spanning
tree disabled. However, you can map multiple VLANs to the same spanning-tree instances by using
MSTP. For more information, see Chapter 18, “Configuring MSTP.”
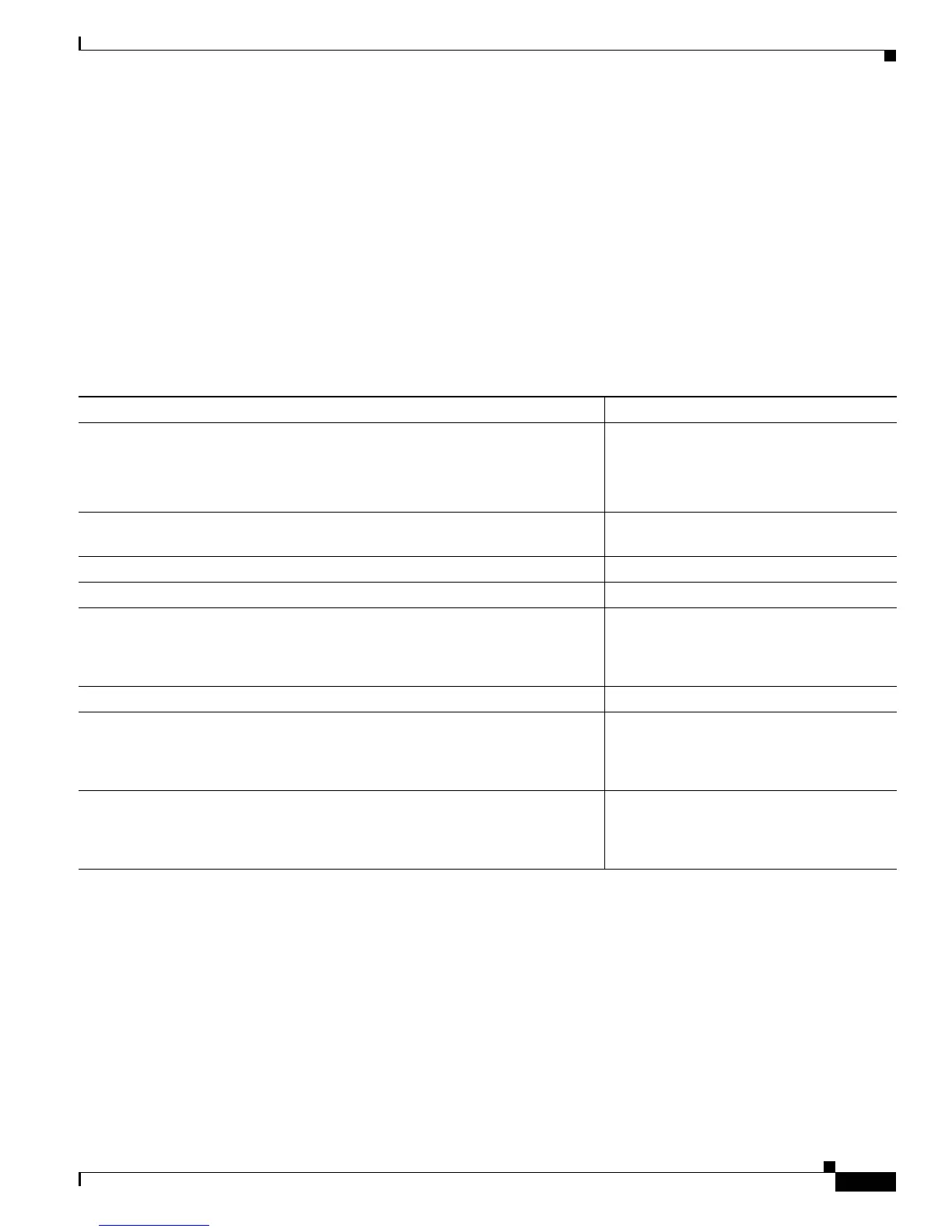
Table 17-3 Default Spanning-Tree Configuration
Feature Default Setting
Enable state Enabled on VLAN 1.
For more information, see the “Supported
Spanning-Tree Instances” section on
page 17-10.
Spanning-tree mode PVST+. (Rapid PVST+ and MSTP are
disabled.)
Switch priority 32768.
Spanning-tree port priority (configurable on a per-interface basis) 128.
Spanning-tree port cost (configurable on a per-interface basis) 1000 Mbps: 4.
100 Mbps: 19.
10 Mbps: 100.
Spanning-tree VLAN port priority (configurable on a per-VLAN basis) 128.
Spanning-tree VLAN port cost (configurable on a per-VLAN basis) 1000 Mbps: 4.
100 Mbps: 19.
10 Mbps: 100.
Spanning-tree timers Hello time: 2 seconds.
Forward-delay time: 15 seconds.
Maximum-aging time: 20 seconds.

 Loading...
Loading...











