Application Examples ASDA Series Application Note
3-52
March, 2015
d. Set master axis lead
It is estimated that master axis will travel 33 cm (10% more). Therefore, if P5-83 is set to 1, then
P5-84 = 10.185916(pulse/mm)*330(mm) = 3361.
Figure 3.3.18 Pulse number setting of master axis
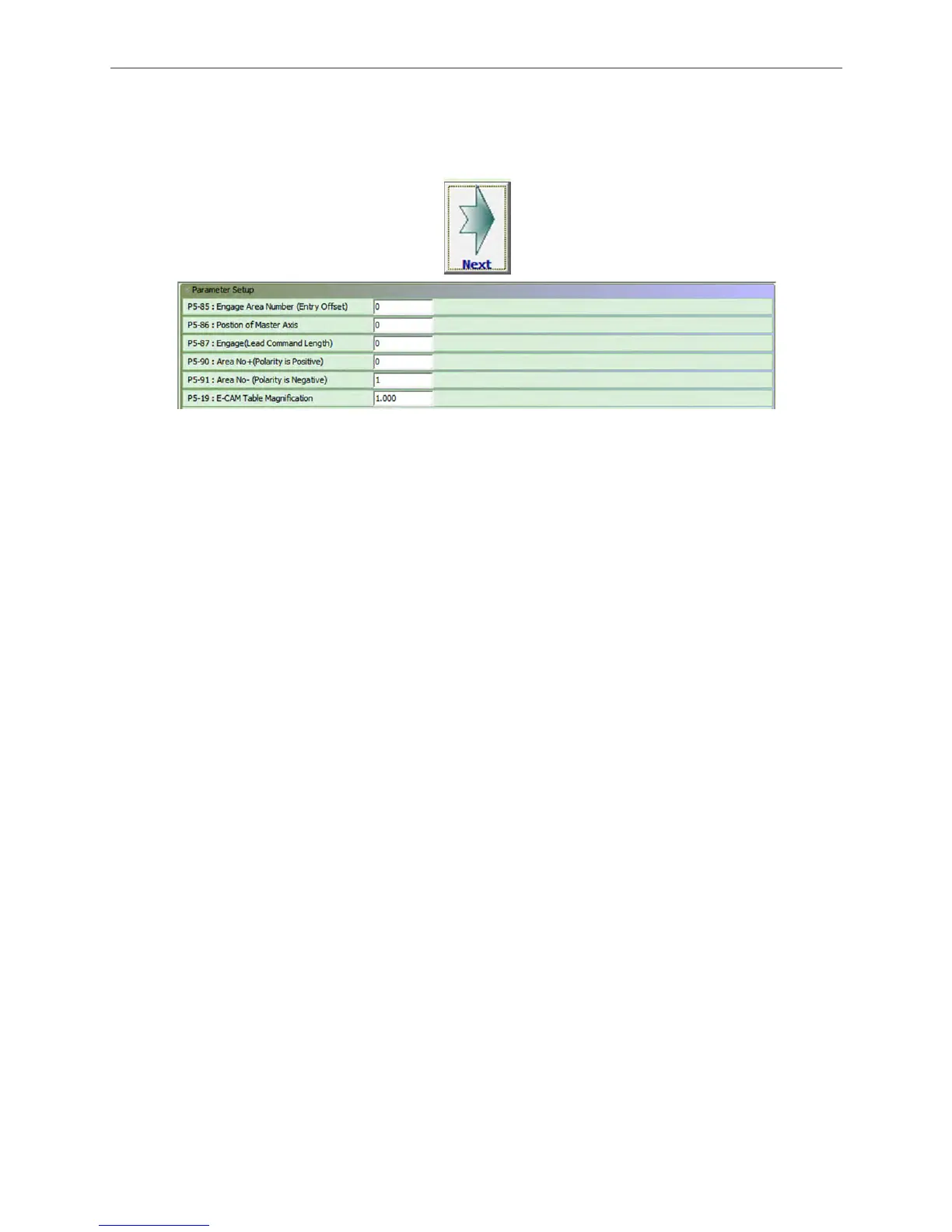
e. Create an E-cam curve
Refer to mark 1 in Figure 3.3.19, setup Waiting Area, Acceleration Area, Constant Speed
Area, Deceleration Area and Stop Area. Among the setting, motor inertia ought to be
considered in Acceleration / Deceleration Area. If the motor inertia is larger, the acceleration /
deceleration curve will be steeper which might result in command delay, motor overload or
regeneration error. Thus, if acceleration / deceleration cannot be calculated precisely, do field
test first. In addition, when creating curve, a longer Constant Speed Area is more ideal, since it
is applied in real working area. Meanwhile, it is better to leave some time for Stop Area;
otherwise, it might be unable to complete homing. See mark 2 in Figure 3.3.19, the setting of S
Curve No. is for smooth E-cam curve so that the command will not be changed dramatically. The
ideal setting value is equal to the value of Stop Area, such as 10. Then, press Create Table
which is marked 3, the system will create the table and the curve.
Mark 4 shows the speed of master axis is 9.817477387, which is the target speed the camshaft
needs to follow (This value varies with Master Simulation Speed, but it will not influence the
curve creating.). Move the cursor to Constant Speed Area, see mark 5. In speed field, the value
is 9.867 (>9.8174477387, Master Simulation Speed). Thus, the speed of camshaft axis is slightly
faster than master axis. Users can adjust Acceleration / Deceleration Area or master / slave
axis lead to make the two values the same.

 Loading...
Loading...











