Measurement principle of transmitter
CO, NO, NO
2
and NH
3
transmitter
The VarioGard CO, NO, NO
2
and NH
3
transmitters are electrochemical
measuring transducers for measuring the partial pressure of the respective
gas under atmospheric conditions.
The ambient air being monitored diffuses through a membrane into the liquid
electrolyte in the sensor. The electrolyte contains a sensing electrode, a
counter electrode and a reference electrode. An electronic potentiostat-
circuit ensures a constant electrical voltage between sensing electrode and
reference electrode. Voltage, electrolyte and electrode material are selected
to suit the gas being monitored so that it is transformed electrochemically on
the sensing electrode. The flow of electrons generated by the reaction is a
measure of the gas concentration.
At the same time, oxygen from the ambient air reacts electrochemically at the
counter electrode.
O
2
transmitter
The VarioGard O
2
transmitter is an electrochemical measuring transducer for
measuring the O
2
concentration in ambient air.
The ambient air to be measured diffuses through a capillary to the measuring
electrode. At the electrode, the oxygen is converted by electrochemical
reaction. An external potentiometer-type regulator maintains a constant
voltage for this reaction between the measuring electrode and an additional
reference electrode. The flow of electrons generated by the reaction is a
measure of the oxygen concentration.
The reverse reaction takes place at the counter electrode.
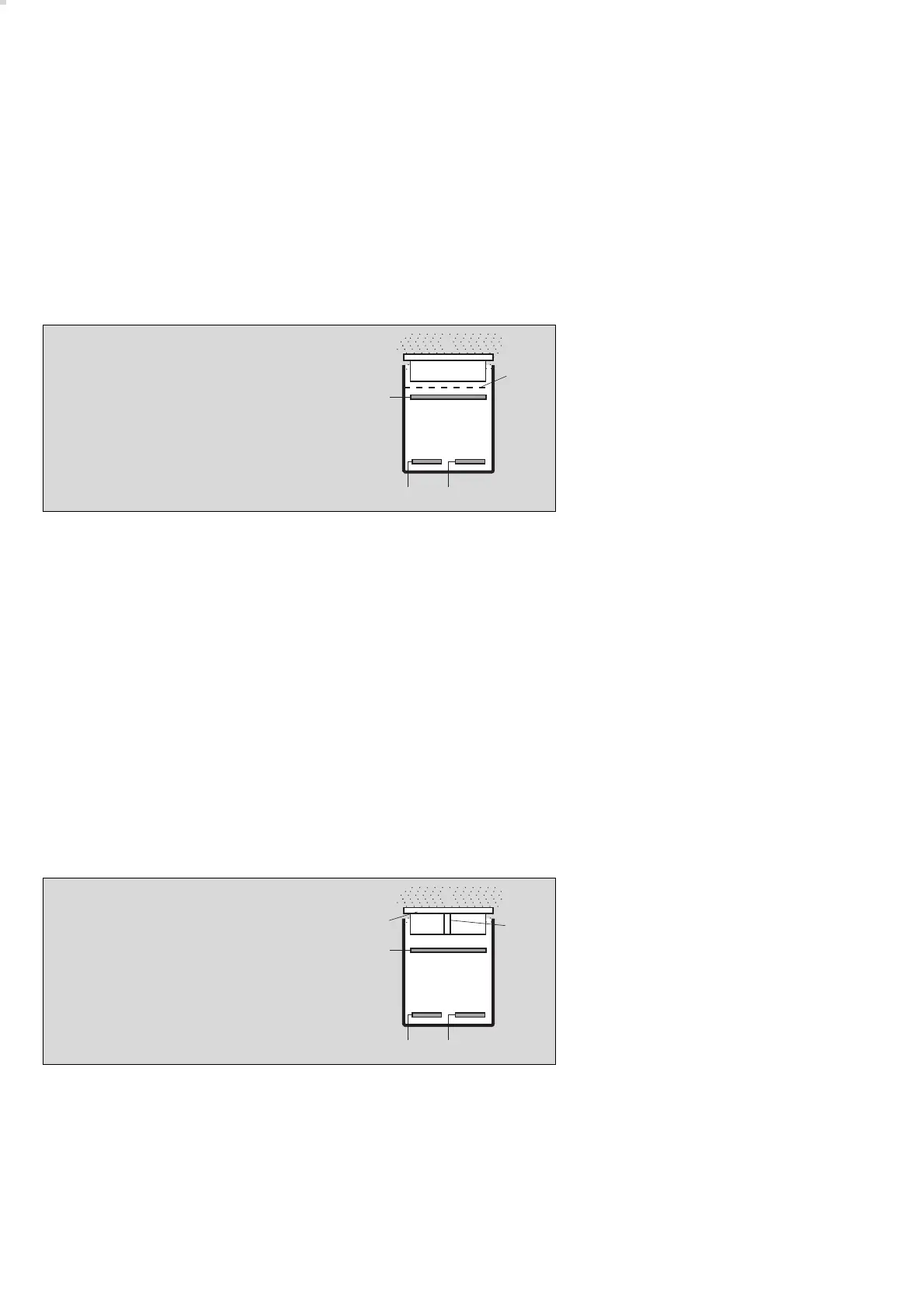
Measurement principle of transmitter
80
02723572en 02623572en
1
5
67
3
4
1 measured gas
2 dustfilter
3 capillary
4 sensing electrode
5 electrolyte
6 reference electrode
7 counter electrode
2
1
5
67
3
4
1 measured gas
2 dustfilter or selective filter
3 membrane
4 sensing electrode
5 electrolyte
6 reference electrode
7 counter electrode
2
 Loading...
Loading...