IONPURE
®
MX CEDI Modules
Page 14 of 32 IP-MAN-MX-Rev E
4. PREPARATION FOR STARTUP
4.1. Verify Quality Meets MX Feed Water Requirements
Test the MX feed water quality by running the RO system to drain and testing to make
sure the feed water quality meets all the feed water requirements given in Table 2.2.
Below are some of the test kits or devices that may be useful:
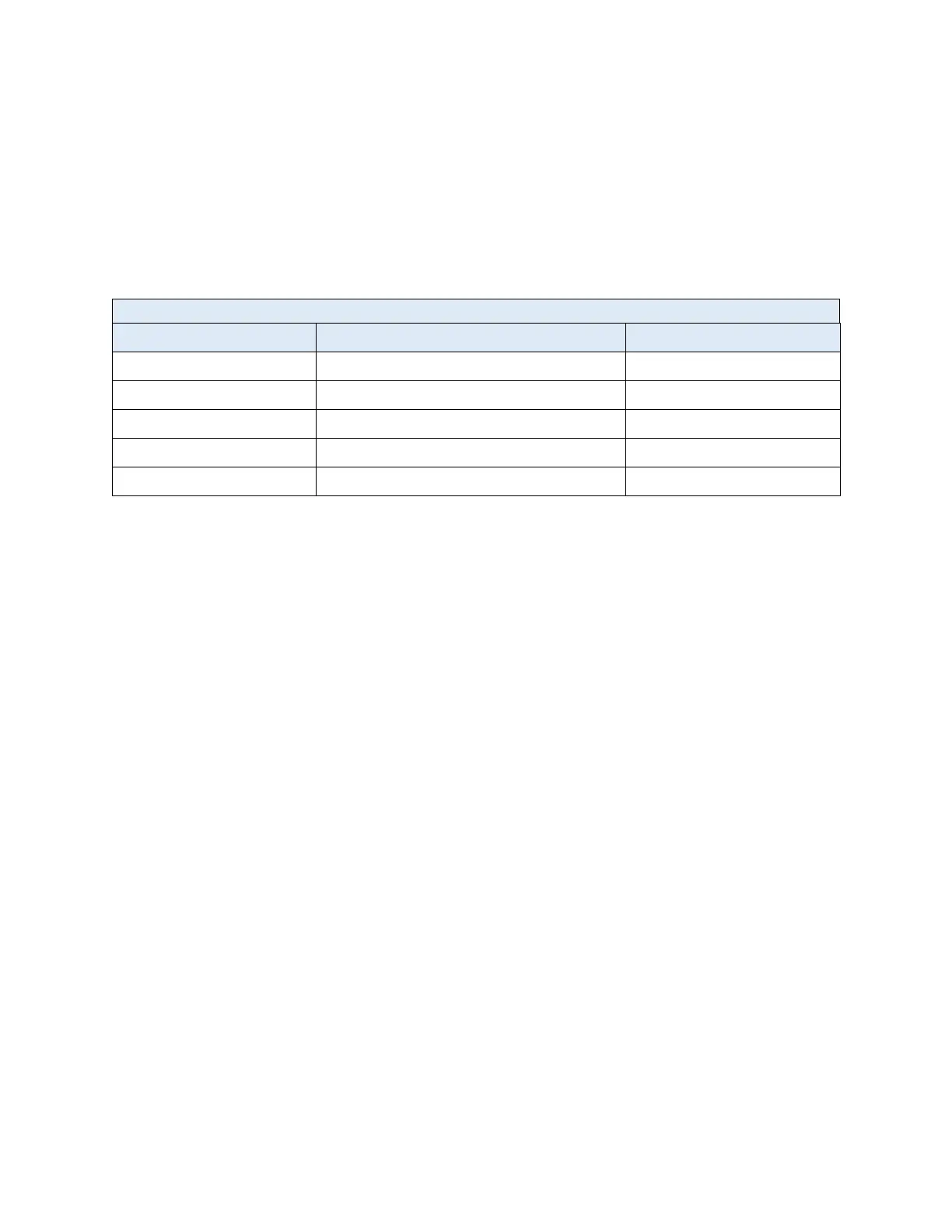
Table 4-1 Useful Equipment for Feed Water Testing
Analyte Model Minimum Increment
Conductivity Myron L Ultrameter II 4P 0.1 µS/cm
CO
2
Hach CA-23 (#143601) 1.25 mg/l
Cl
2
Hach CN-70 (#1454200) 0.02 mg/l
Hardness Hach HA-71A (#145201) 1.0 mg/l
Silica Hach SI-7 (#2255000) 0.02 ppm
4.2. Estimate DC Current Required
An important part of the startup process for the MX Module is setting the operating current
correctly for each site.
The amount of DC current required depends on the following site-specific conditions:
• Flow rate per module
• CEDI feed water conductivity equivalent (FCE)
• Measured feed water conductivity (may require a portable conductivity meter)
• Feed water carbon dioxide concentration (requires test kit listed above)
• Feed water silica concentration (usually low enough to be neglected)
• Product water quality required
The best way to determine the amount of DC current required is to use the Ionpure
projection tool, IP-PRO. Alternatively it can be estimated using the MX-specific equation
below (based on Faraday’s Law). Note: this is for nominal product water flow and 10%
current efficiency.
DC amps = (0.034)(FCE, µS/cm)
Where FCE = measured µS/cm + (ppm CO
2
)(2.79) + (ppm SiO
2
)(2.04)

 Loading...
Loading...











