Quantum Series Videowall Processing Systems • Reference Information 8181
Network Setup
What is an IP Address?
An IP address is a 32-bit binary number that is used to identify each device on an
Ethernet network. This number is usually four decimal numbers (called “octets”), each
in the range of 0 to 255 and separated by dots, such as 198.123.34.240. This is called
“dotted decimal notation.”
An IP address is divided into two parts: a network identifier and a host identifier.
Each address on a given network must have the same network identifier value but a
unique host identifier. As a result, there are different classes that define the range of valid
addresses and which parts of the address are used for the network and host identifiers.
The most common IP address classes are:
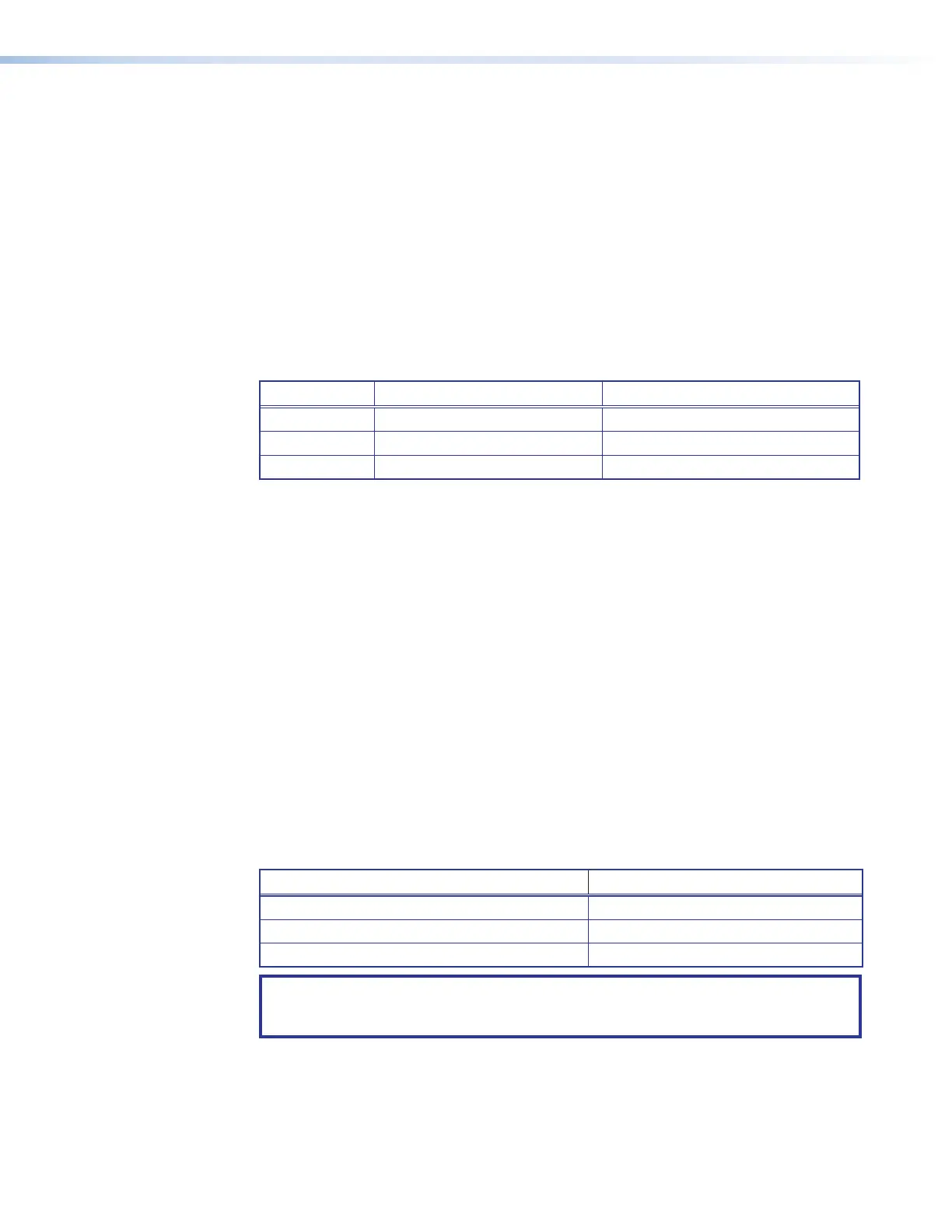
Class Name Valid Address Range Identifier Arrangement
Class A 0.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254
NNN.HHH.HHH.HHH
Class B 128.0.0.1 to 191.255.255.254
NNN.NNN.HHH.HHH
Class C 192.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254
NNN.NNN.NNN.HHH
NNN refers to the network identifier and HHH refers to the host identifier.
Choosing IP Addresses
If the computer and Quantum processor are directly connected or connected via their
own independent network, follow the guidelines below for choosing the IP addresses.
However, if you intend to connect your computer and Quantum processors to an existing
network, notify the network administrator and ask him or her to allocate suitable IP
addresses.
On an independent network, it is generally recommended that you use the Class C format
(from 192.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254).
There are two rules for choosing IP addresses:
• The network identifier must be the same for each IP address.
• The host identifier must be unique for each address.
Applying these rules to Class C addresses, the first three decimal values of your IP
address must all be the same, while the last value is used to uniquely identify each device.
The following is an example of a valid Class C addressing scheme:
Device IP Address
Computer running Quantum Control Software 192.168.180.41
Quantum processor 1 192.168.180.42
Quantum processor 2 192.168.180.43
NOTE: The host identifiers (41, 42, and 43 in the above example) do not need to be
sequential or in any particular order. However, it is recommended that you group the
numbers for simplicity.

 Loading...
Loading...