52
6 Congestion management
configuration
NOTE:
Support of the H3C WX series access controllers for features may vary by AC model. For more
information, see Compatibility Matrices.
Causes, impacts, and countermeasures of congestion
Congestion occurs on a link or node when traffic size exceeds the processing capability
of the link or node. It is typical of a statistical multiplexing network and can be caused by
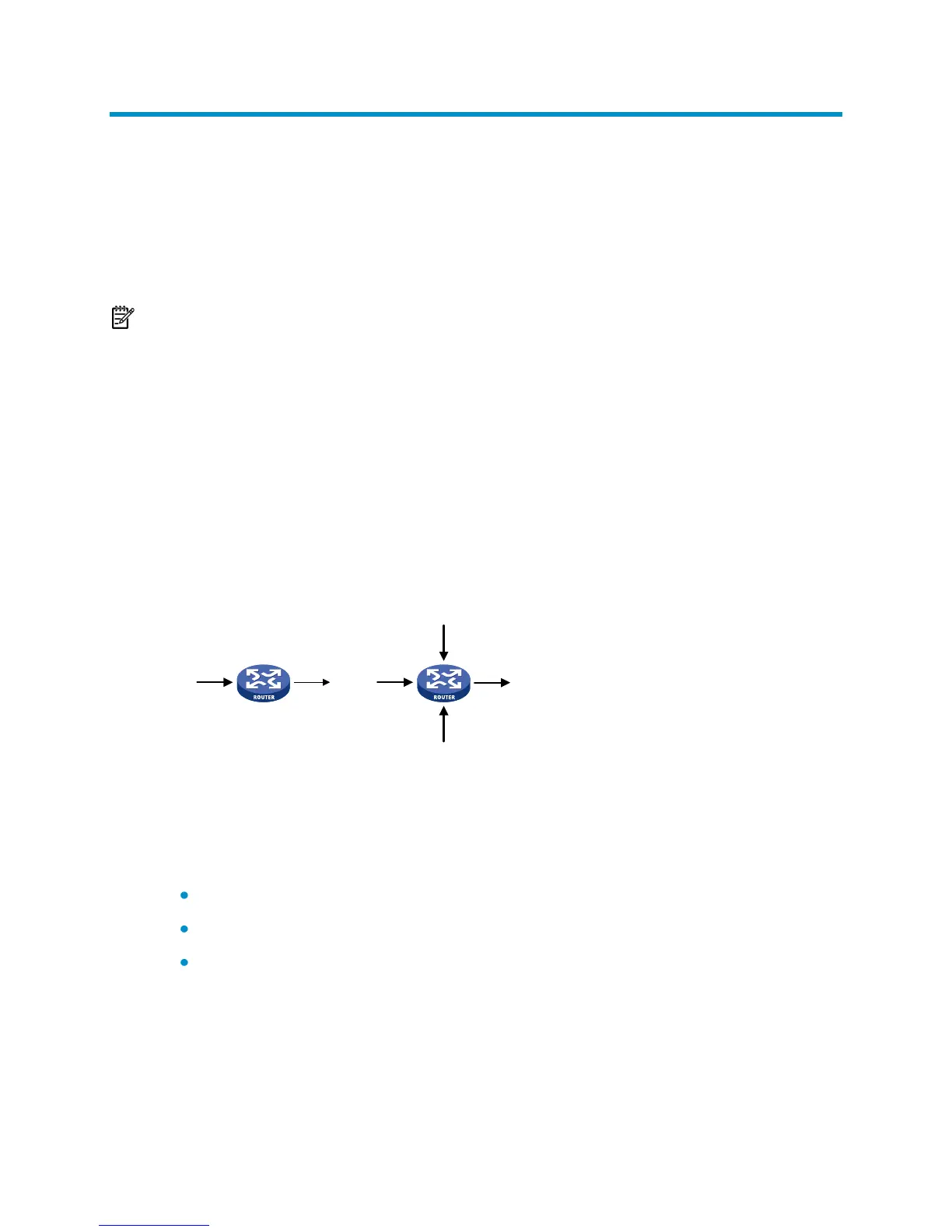
link failures, insufficient resources, and various other causes. Figure 10 shows two
common congestion scenarios:
Figure 10 Traffic congestion causes
100M>10M
(100M+10M+50M(>100M
100M
100M
100M
50M
10M
10M
(1( (2(
Congestion may bring these negative results:
Increased delay and jitter during packet transmission
Decreased network throughput and resource use efficiency
Network resource (memory in particular) exhaustion and even system breakdown
Congestion is unavoidable in switched networks or multi-user application environments.
To improve the service performance of your network, you must take measures to
manage and control it.
One major issue that congestion management deals with is how to define a resource
dispatching policy to prioritize packets for forwarding when congestion occurs.

 Loading...
Loading...