Working with VSCs
Key concepts
4-4
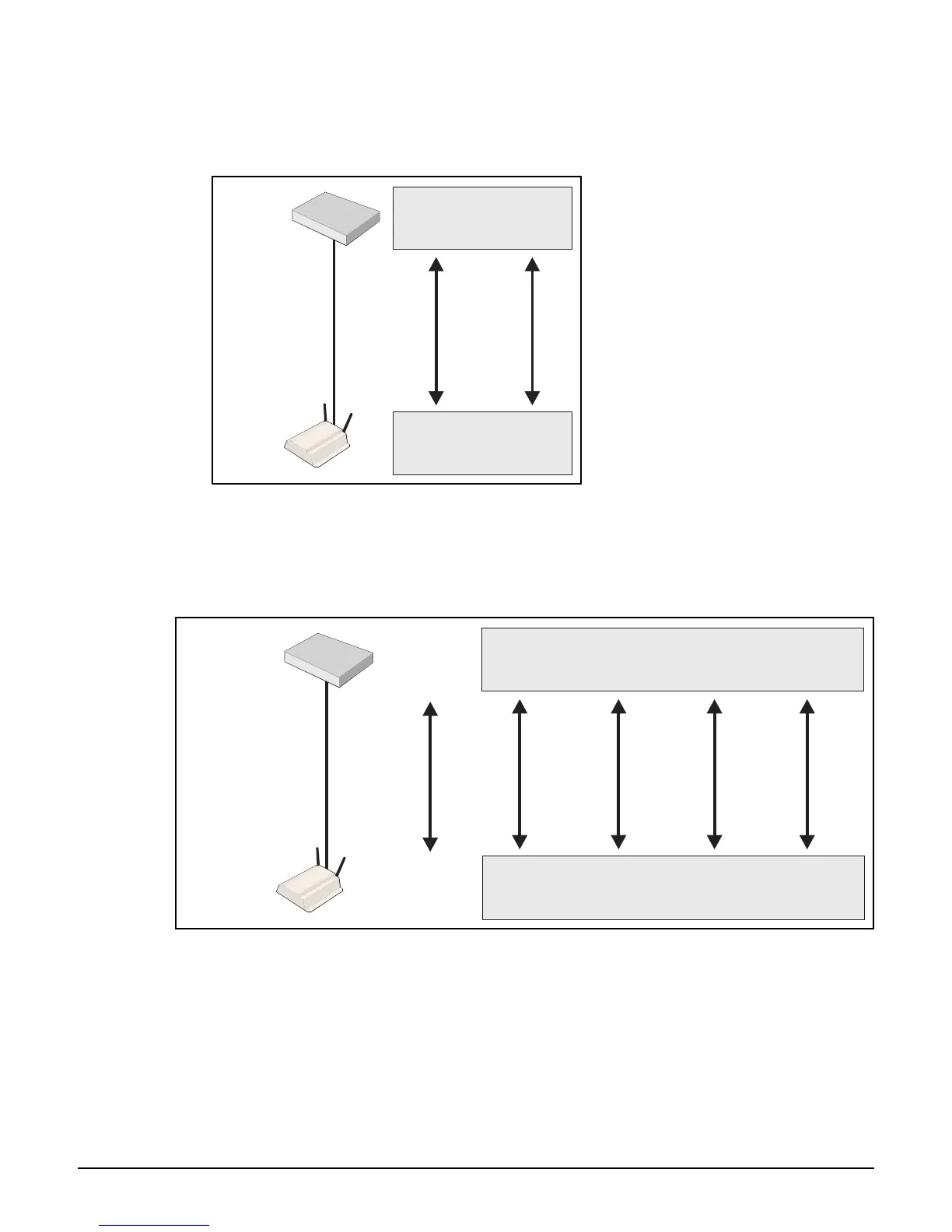
In this type of installation, VSC definitions on both the AP and controller must match so that
traffic from wireless users connected to the AP can be sent to the controller for handling. For
example, if two VSCs are being used, they could be configured as follows:
Management with VLANs
When operating in a VLAN environment, management traffic can be carried on its own VLAN.
Configure the VSC on both the autonomous AP and the controller as illustrated.
In this example, the traffic for each wireless network is carried on its own VLAN. This leaves
only management traffic from the autonomous AP on VLAN 10. A static IP is assigned on both
ends to permit the two devices to communicate.
SSID = Employee
SSID = Employee
SSID = Guest
VLAN ID = 20
SSID = Guest
VLAN ID = 20
VSC Profiles
VSC Profiles
Autonomous AP
Controller
SSID = VSC3
VLAN ID = 40
VSC Profiles
VSC Profiles
Default
VLAN ID = 10
IP address =
192.168.2.2
VLAN ID = 10
IP address =
192.168.2.1
SSID = VSC2
VLAN ID = 30
SSID = VSC1
VLAN ID = 20
SSID = VSC3
VLAN ID = 40
SSID = VSC2
VLAN ID = 30
SSID = VSC1
VLAN ID = 20
VLAN 10 = 192.168.2.1
LAN port = 192.168.1.1
VLAN 10 = 192.168.2.2
LAN port = 192.168.1.2
(IP = 192.168.1.1)
SSID = VSC4
VLAN ID = 50
Autonomous AP
Controller
SSID = VSC4
VLAN ID = 50

 Loading...
Loading...