50 Storage overview
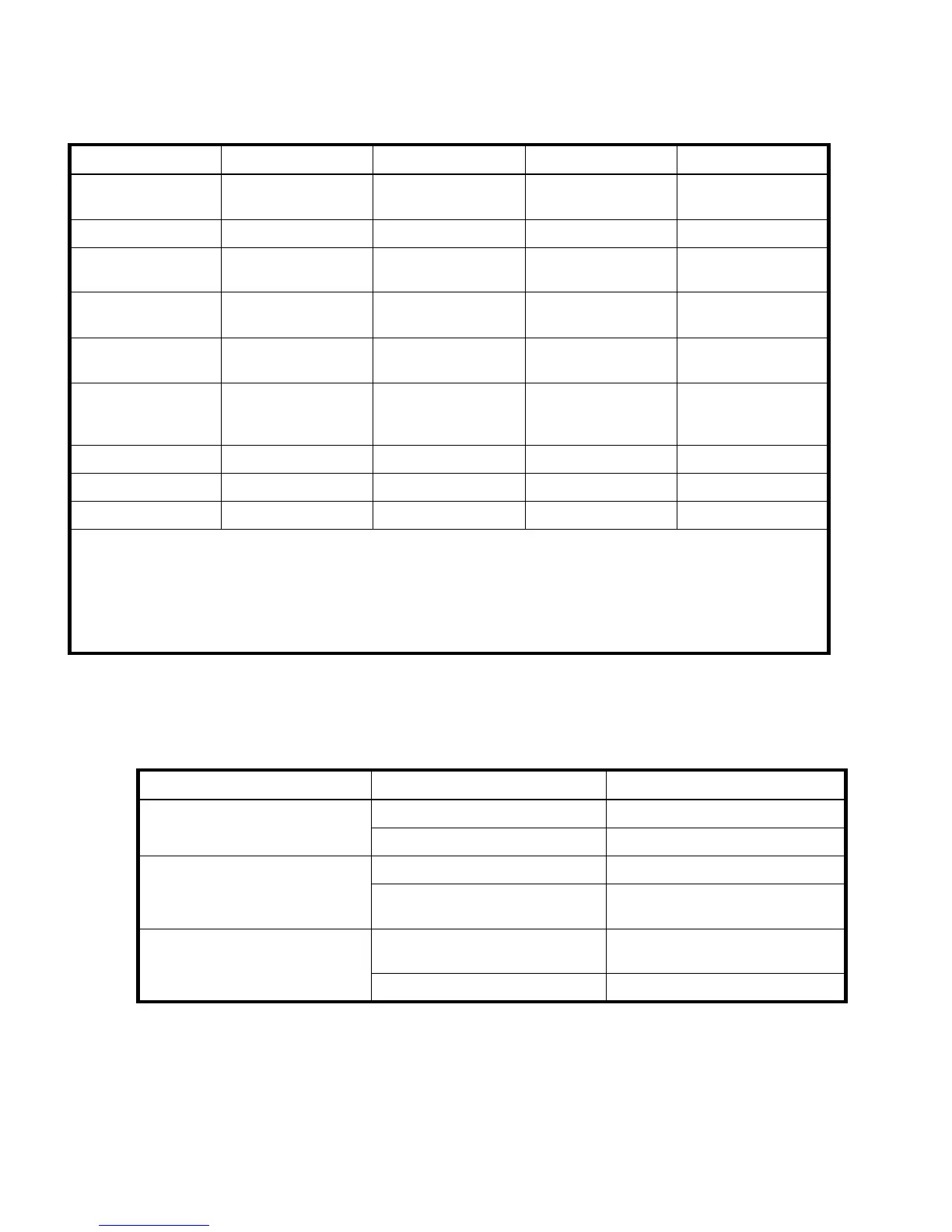
Comparison of RAID methods
Table 7 summarizes important features of the different RAID levels.
Choosing a RAID level
Use Table 8 to help you determine the best RAID level for your environment.
Table 7 Summary of RAID methods
RAID 0 RAID 1+0 RAID 5 RAID 6
Alternative name Striping Mirroring Distributed Data
Guarding (DDG)
Advanced Data
Guarding (ADG)
Usable drive space* 100% 50% 67% to 93% 50% to 96%
Usable drive space
formula
n n/2 (n-1)/n (n-2)/n
Minimum number of
physical drives
1234
Tolerates physical drive
failure?
No Yes Yes Yes
Tolerates simultaneous
failure of more than
one physical drive?
No Only if no two failed
drives are in a mirrored
pair
No Yes
Read performance High High High High
Write performance High Medium Low Low
Relative cost Low High Medium Medium
*Values for usable drive space are calculated with these assumptions:
• All physical drives in the array have the same capacity.
• Online spares are not used.
• No more than 14 physical drives are used per array for RAID 5.
• No more than 56 drives are used with RAID 6.
Table 8 Choosing a RAID level
Most important characteristic Also important Suggested RAID level
Fault tolerance Cost effectiveness RAID 6
I/O performance RAID 1+0
Cost effectiveness Fault tolerance RAID 6*
I/O performance RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is
not required)
I/O performance Cost effectiveness RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is
not required)
Fault tolerance RAID 1+0

 Loading...
Loading...