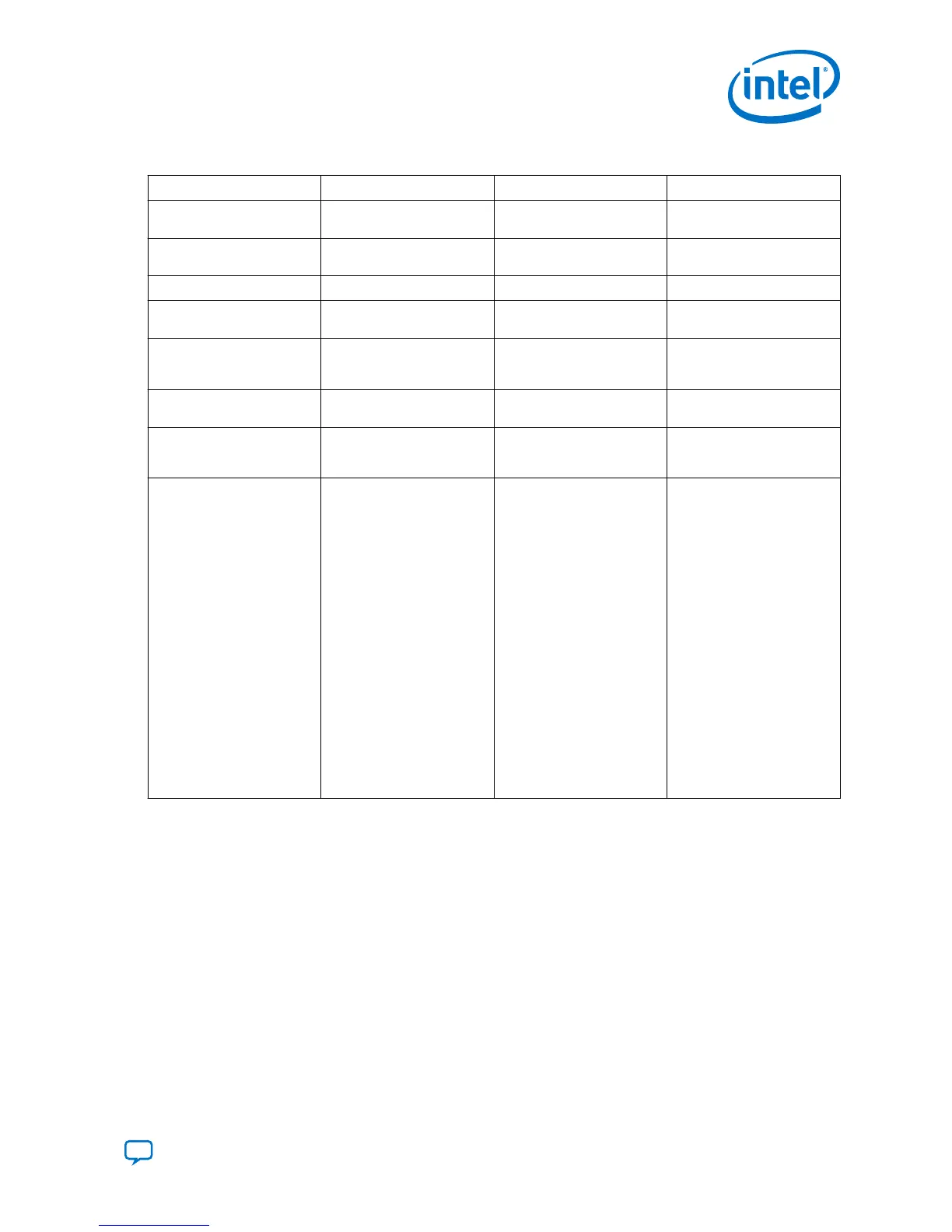
Table 18. Differences between Flushed, Extended, and Bfloat Formats
Features Flushed Extended Bfloat16/Bfloat 16+
Input format
(sign.exponent.mantissa)
1.5.10 1.5.10 1.8.7 or 1.8.10 (Bfloat16+)
FP16 operation format
(sign.exponent.mantissa)
1.5.10 1.8.10 1.8.10
Input width 16 bit 16 bit 16 or 19 bit (Bfloat16+)
Minimum representable
exponent
5'h01 - 5'h0f = -14 8'h01 - 8'h7f = -126 8'h01 - 8'h7f = -126
FP16 Subnormal No support for subnormal.
Subnormal result is flushed
to zero.
Subnormal results can be
represented as normal
numbers
No support for subnormal.
Subnormal result is flushed
to zero.
Exception flags Overflow, underflow,
inexact, and invalid
Infinite, zero, inexact, and
invalid
Overflow, underflow,
inexact, and invalid
Invalid flag behavior Asserted when there is an
ill-defined operation
Asserted when there is an
ill-defined operation or a
qNaN input
Asserted when there is an
ill-defined operation
Rounding Round to nearest even
(RNE)
RNE:
• if both FP16 operands
are normal numbers
• if one of the FP16
operands is a subnormal
number and mantissa
product is ≥ 1
• if one of the FP16
operands is a subnormal
number and mantissa
product =
“0.1111111111|
1xxxxxxxxx”
• when using adder/
subtractor operations
Round to zero(RZ)
• if both FP16 operands
are subnormal numbers
• if one of the FP16
operands is a subnormal
number and mantissa
product is ≤ 1
RZ
3.2.2.2. Sum of Two FP16 Multiplication Mode
This mode performs a summation of two half-precision multiplication and provide a
single-precision result:
fp32_result = (fp16_mult_top_a*fp16_mult_top_b) +
(fp16_mult_bot_a*fp16_mult_bot_b)
The following are exception flags supported in flushed and bfloat16 formats:
•
fp16_mult_top_invalid
•
fp16_mult_top_inexact
•
fp16_mult_top_overflow
•
fp16_mult_top_underflow
3. Intel Agilex Variable Precision DSP Blocks Operational Modes
UG-20213 | 2019.04.02
Send Feedback
Intel
®
Agilex
™
Variable Precision DSP Blocks User Guide
45
 Loading...
Loading...