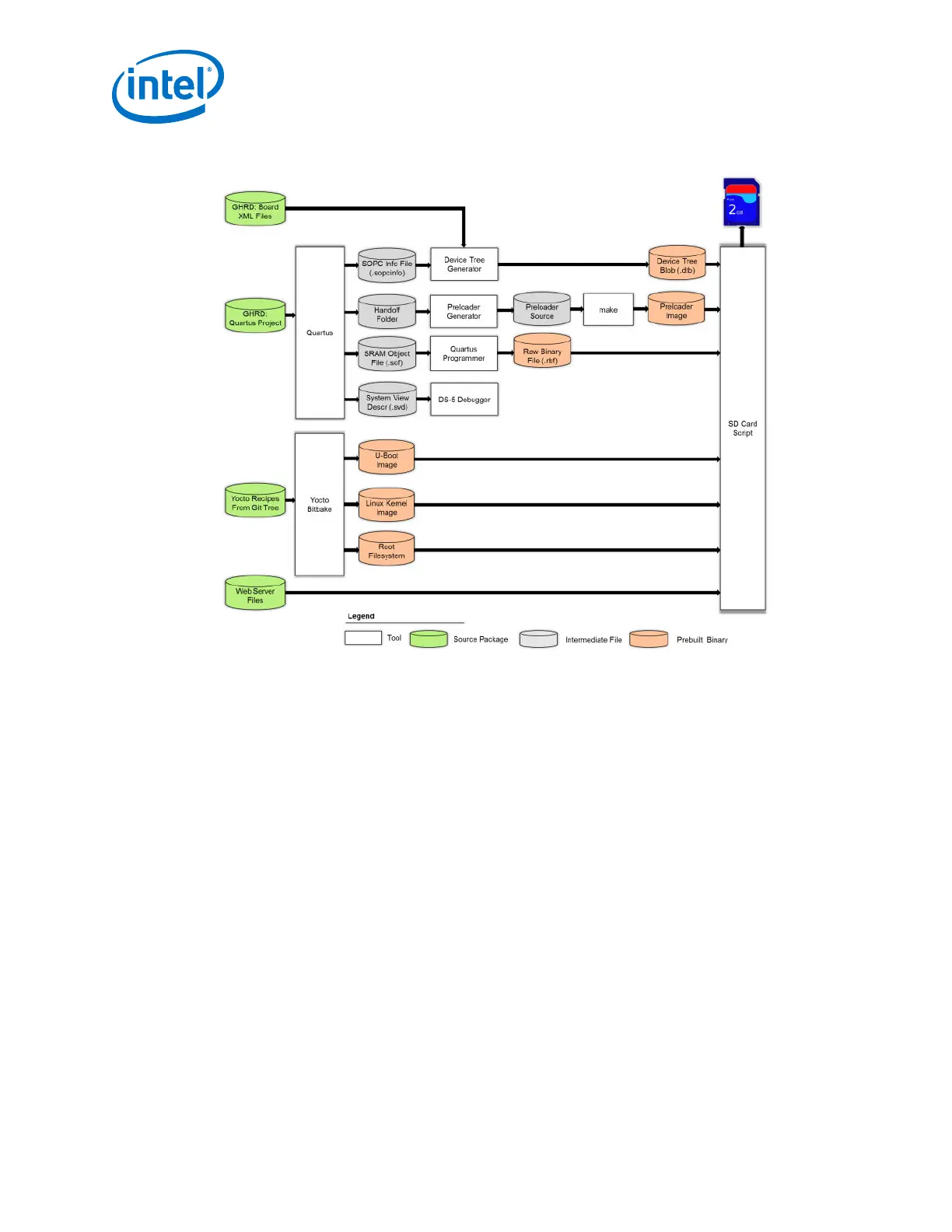
Figure 10. GSRD for Linux - Build Flow
The above build flow is the one used for the GSRD for Linux but it can be tweaked to
match the individual needs of each project. For example:
• Linux kernel could be built separately without using Yocto Bitbake.
• Linux filesystem could be built separately without using Yocto Project.
• Linux Device Tree could be managed without using the Device Tree Generator. For
example, it can be manually edited.
Related Information
GSRD User Manuals
5.1.3.4. Linux Device Tree Design Considerations
The Linux Device Tree is a data structure that describes the underlying hardware to
the Linux operating system kernel. By passing this data structure the OS kernel, a
single OS binary may be able to support many variations of hardware. This flexibility is
particularly important when the hardware includes an FPGA.
The recommended procedure for managing the Linux Device Tree is:
5. Embedded Software Design Guidelines for SoC FPGAs
AN-796 | 2018.06.18
AN 796: Cyclone V and Arria V SoC Device Design Guidelines
56
 Loading...
Loading...