UMG 103-CBM www.janitza.com
42
10.3 Direction of rotary field
In the GridVis software, check the direction of
the voltage rotating field.
· Usually it is a “right” rotating field.
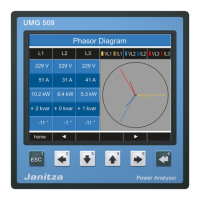
10.3.1 Fundamentals on the phasor diagram
The phasor diagram graphically describes the
phase shift or phase angle between the voltage
and the current. The phasors rotate at a constant
angular speed – proportional to the frequency of
the voltage and current – around an origin. The
phasor diagram thus shows the momentary state
of the variables in an AC circuit.
Representation of ohmic resistance:
· Voltage and current are in phase.
u
i
Representation of inductance:
· The voltage is ahead of the current.
· The phase shift for an “ideal coil” is 90°.
u
i
Representation of capacitance:
· The current is ahead of the voltage.
· The phase shift of an “ideal capacitor” is 90°.
u
i
With a combination of the states, the phase angle
“current to voltage” can assume values between
-90° and +90°.
U
I
Current: Displayed with
short phasors
Voltage: Displayed with
long phasors
Example phasor diagram (3-phase)
UL1
IL1
IL2
UL2
UL2
IL3
Current and voltage are shifted against each other.
The current is ahead the voltage, i.e. the network
is capacitively loaded.

 Loading...
Loading...