SCS100/200/400 User Guide 6: Application Setup
2. The SCS checks to see if this user’s identity key is listed in the AUTHORIZED_KEYS
(or AUTHORIZED_KEYS2) file on the SCS.
If the user’s identity key is not listed in the AUTHORIZED_KEYS file on the SCS,
then the authentication attempt fails. If the identity key is listed, then the process
continues.
3. The SSH client then sends the private half of the user’s identity key to the SCS.
4. The SCS compares the private half of the user’s identity key to the key stored in the
host_rsa_key (or host_dsa_key) file on the SCS.
5. If the private keys match, then the user’s identity is confirmed and an SSH
connection forms.
If RSA or DSA user authentication fails, the SCS prompts for a username and password
(or just a password, if the SSH client forwarded the username). The user’s name and
password are then checked against the Radius, SecurID, or local user databases, in
order of their precedence settings. (See the SCS Reference Manual for information on
authentication precedence.)
Setting up RSA Shared Key Authentication (for SSHv1)
This procedure assumes you have generated the RSA authentication keys and copied
the public half of the key pair to a file called AUTHORIZED_KEYS on your local
computer.
1. FTP to the IP address of the SCS.
2. Log in with the username of root and enter the privileged password (system by
default).
3. Change directories to /flash/ssh/.
4. “Put” the AUTHORIZED_KEYS file into that directory.
5. Reboot the SCS.
RSA Method from Unix (OpenSSH) - No Passphrase
sshuser@UNIXHOST /# SSH –1 SSHUSER 172.19.21.51
Lantronix SCS Version B1.0/405(011102)
Type HELP at the ‘Local_33>’ prompt for assistance.
Username>
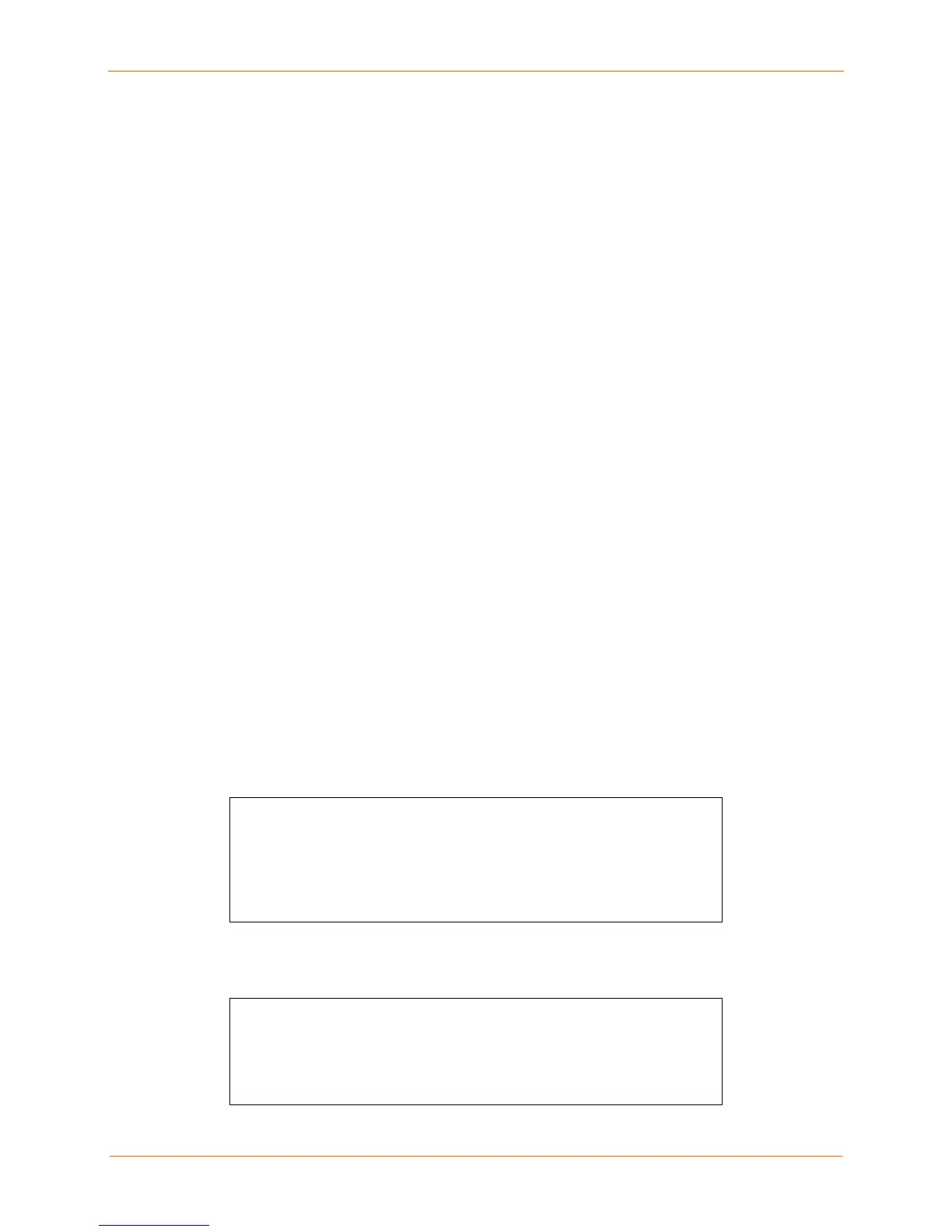
RSA Method from Unix (OpenSSH) - with Passphrase
sysadmin@UNIXHOST/# -1sysadmin
172.19.21.51
sysadmin@172.19.21.51’s password:
Lantronix SCS200 Version B1.0/405(011102)
Type HELP at the ‘Local_34>’ ‘prompt for assistance
6-17

 Loading...
Loading...