MI 3000 EasiPLUS Measurements
39
5.4 Fault loop impedance and prospective fault current
The loop impedance function has two sub-functions available:
Zs sub-function performs a fast fault loop impedance measurement on supply systems
which do not contain RCD protection.
Zs(rcd) trip-lock sub-function performs fault loop impedance measurement on supply
systems which are protected by RCDs..
5.4.1 Fault loop impedance
The fault loop impedance measures the impedance of the fault loop in the event that a
short-circuit to an exposed conductive parts occurs (i.e. a conductive connection occurs
between the phase conductor and protective earth conductor). In order to measure loop
impedance the instrument uses a high test current.
Prospective fault current (IPFC) is calculated on the basis of the measured resistance
as follows:
PEL
N
PFC
Z
U
I
Where:
Nominal input voltage U
N
Voltage range
115 V
(100 V U
L-PE
160 V)
230 V
(160 V U
L-PE
264 V)
For additional information concerning fault loop impedance measurement refer to
Metrel’s handbook Measurements on electric installations in theory and practice.
5.4.1.1 How to perform fault loop impedance measurement
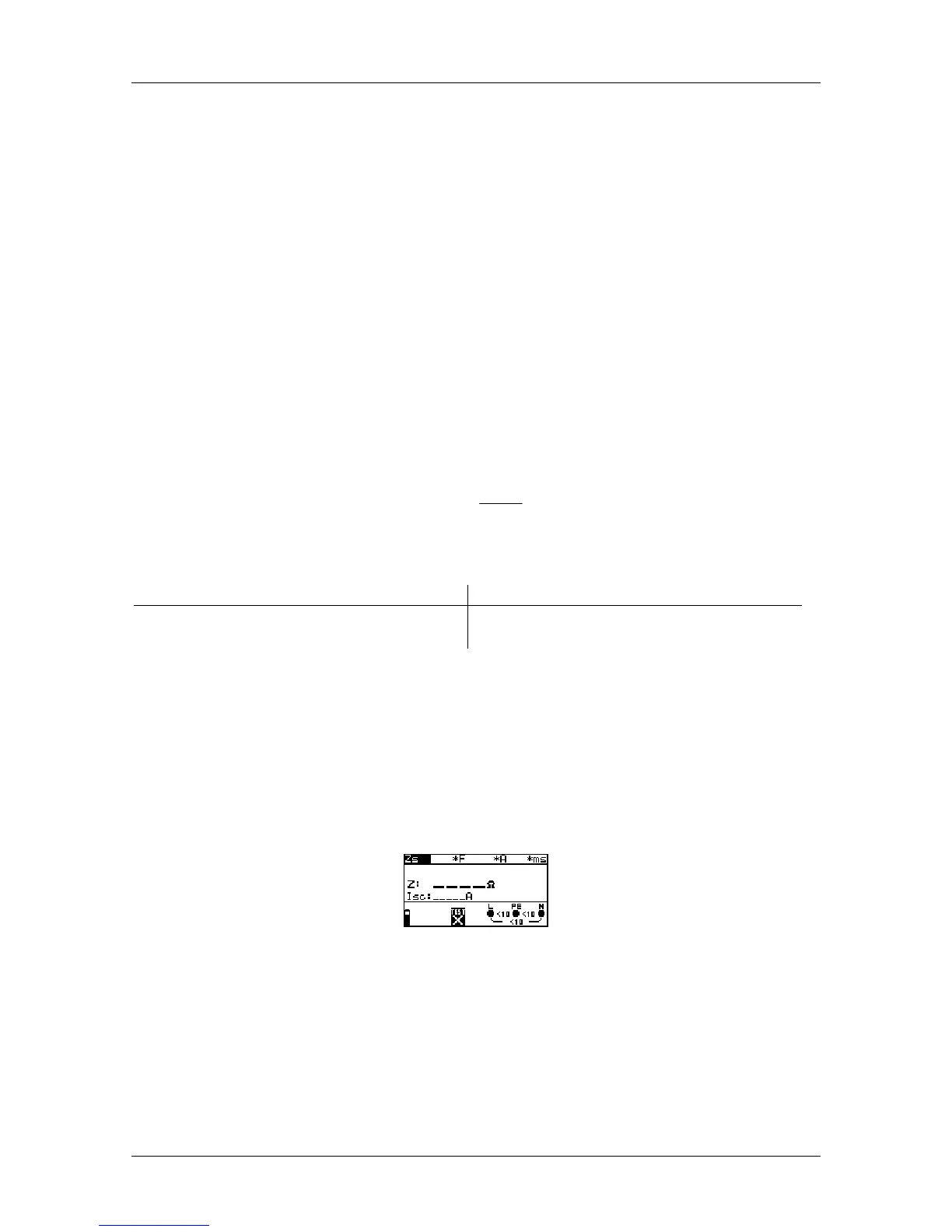
Step 1 Select the LOOP function with the function selector switch and use the /
keys to select the Zs sub-function. The following menu is displayed:
Figure 5.28: Loop impedance measurement menu
Step 2 Set the following measuring parameters:
Fuse type,
Fuse current rating,
Fuse trip-out time,
Impedance scaling factor (see chapter 4.5.2 Impedance scaling factor
adjustment
).

 Loading...
Loading...