MI 3000 EasiPLUS Measurements
43
5.5 Line impedance and prospective short-circuit current
The line impedance is a measurement of the impedance of the current loop when a
short-circuit to the neutral conductor occurs (conductive connection between phase
conductor and neutral conductor in single-phase system or between two phase
conductors in three-phase system). A high test current is used to perform the line
impedance measurement.
Prospective short circuit current is calculated as follows:
)(LNL
N
PSC
Z
U
I
Where:
Nominal input voltage U
N
Voltage range
115 V
(100 V U
L-PE
160 V)
230 V
(160 V
U
L-PE
264 V)
400 V
(264 V U
L-PE
440 V)
For additional information concerning line impedance refer to Metrel’s handbook
Measurements on electric installations in theory and practice.
How to perform line impedance measurement
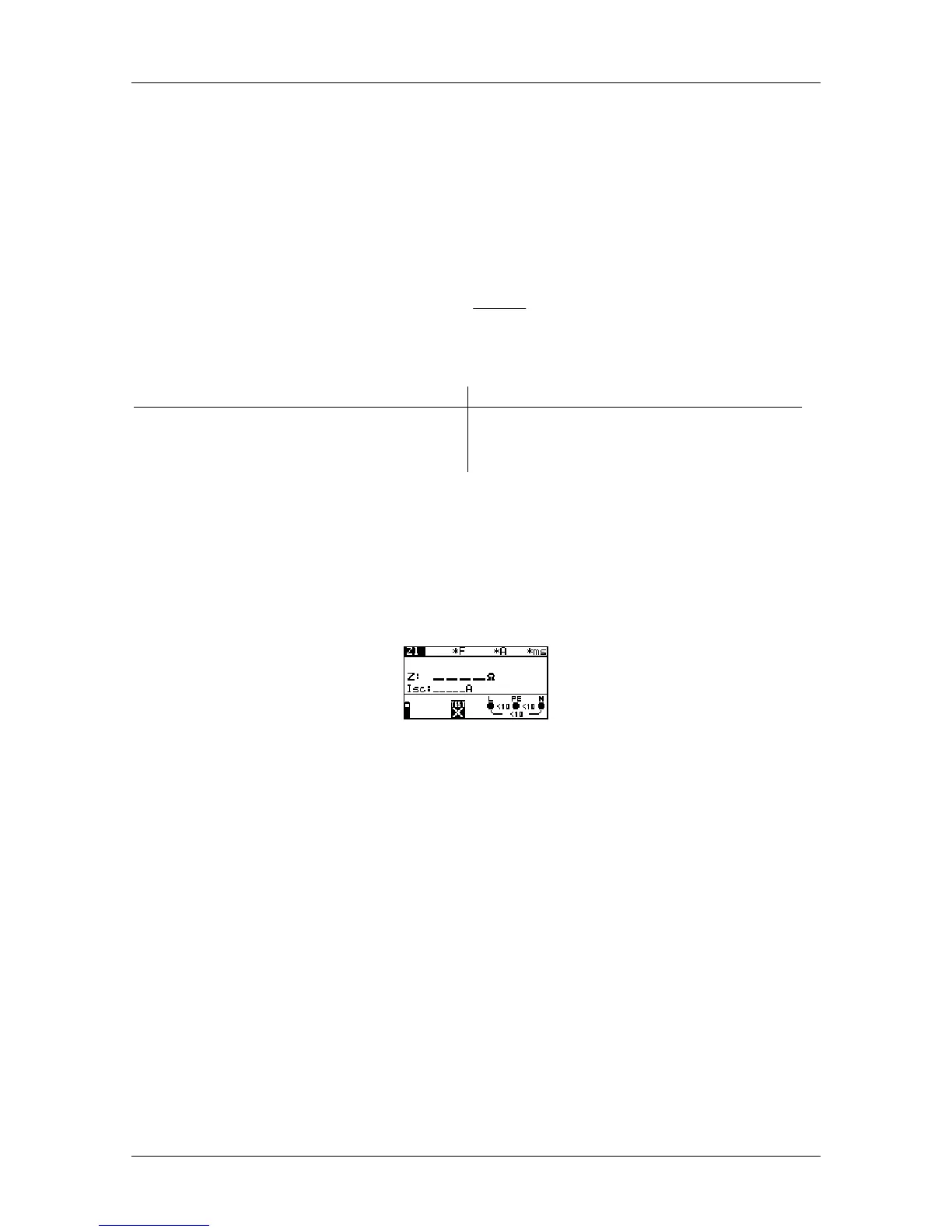
Step 1 Select the LINE function with function selector switch. The following menu is
displayed:
Figure 5.33: Line impedance measurement menu
Step 2 Set the following measuring parameters:
Fuse type,
Fuse current rating,
Fuse trip-out time,
Impedance scaling factor (see chapter 4.5.2 Impedance scaling factor
adjustment
).
The complete list of available fuse types can be found in Appendix A.
Step 3 Connect the appropriate test leads to the instrument and follow the
connection diagram shown in figure 5.34 to perform phase-neutral or phase-
phase line impedance measurement. Use the Help function if necessary.

 Loading...
Loading...